O PayPal tem grande presença no setor de pagamentos e se adaptou a uma variedade de mercados com seus recursos focados no usuário e compatibilidade com plataformas de e-commerce. Como forma de pagamento, o PayPal transformou a forma como pessoas físicas e jurídicas realizam transações internacionais, permitindo que os clientes paguem em suas moedas locais e que as empresas aceitem pagamentos de uma base diversificada de clientes.
Apesar das complexidades de operar em várias regiões, a PayPal continua priorizando a experiência do cliente. Seu foco em interfaces do cliente, segurança e confiança contribuiu para sua adoção generalizada. A empresa demonstra seu compromisso com esses princípios no atendimento ao cliente e na proteção contra fraudes, que se tornaram referências para o setor.
O PayPal tem uma influência considerável em todo o mundo, proporcionando a pequenas empresas e empreendedores acesso a mercados internacionais e afetando o comércio e o fluxo de dinheiro em todo o mundo. Neste artigo, explicamos como o PayPal funciona e como sua empresa pode usar o PayPal para aceitar pagamentos.
Neste artigo:
- O que é PayPal?
- Como aceitar pagamentos no PayPal
- Requisitos para as empresas começarem a aceitar o PayPal
- Custos e tarifas do PayPal
- Vantagens para a empresa em aceitar o PayPal
- Medidas de segurança do PayPal
- Como funciona o PayPal
- Onde o PayPal é usado?
- Quem usa o PayPal?
- Alternativas ao PayPal
O que é PayPal?
PayPal é uma plataforma de pagamentos digitais que permite aos usuários enviar e receber dinheiro on-line. Ele oferece transações para compras online, transferências pessoais ou ponto a ponto e pagamentos comerciais.
Para os clientes, o PayPal funciona como uma carteira digital, permitindo que façam compras online sem compartilhar dados do cartão de crédito com diferentes empresas. Os clientes podem vincular contas bancárias e cartões de crédito e débito à conta PayPal para enviar e receber dinheiro ou pagar por bens e serviços com facilidade.
Como aceitar pagamentos no PayPal
Quando alguém envia dinheiro para um endereço de e-mail ou número de celular vinculado ao PayPal, o proprietário da conta recebe uma notificação informando que os fundos estão disponíveis. Para acessar o dinheiro, ele precisa ter uma conta do PayPal e confirmar seu endereço de e-mail.
Você pode integrar botões e links de pagamento do PayPal no site da sua empresa ou compartilhá-los diretamente com os clientes. Assim que sua empresa receber um pagamento, os fundos aparecerão na página inicial da conta PayPal. De lá, você pode transferir os fundos para uma conta bancária ou mantê-los como saldo no PayPal para fazer compras ou enviar dinheiro.
A maioria dos pagamentos via PayPal é instantânea, e os usuários recebem o dinheiro na sua conta logo após o remetente concluir a transação. Pagamentos internacionais geralmente aparecem nas contas PayPal dos usuários em minutos, embora, em alguns casos, possa levar algumas horas, dependendo da forma de pagamento e da moeda.
Requisitos para as empresas começarem a aceitar o PayPal
1. Configurar uma conta empresarial do PayPal
Para começar a usar o PayPal, as empresas precisam criar uma conta comercial na plataforma. É preciso fornecer dados legais como o nome da empresa e o endereço comercial, e dados pessoais do proprietário da empresa. O PayPal verifica esses dados para cumprir regulamentos de combate à lavagem de dinheiro (AML) e assegurar que somente empresas verificadas estejam usando seus serviços em transações autênticas.
2. Vincular uma conta bancária
Em seguida, as empresas devem vincular uma conta bancária à conta comercial no PayPal para permitir transferências de fundos. O PayPal confirma a conta vinculada depositando pequenas quantias e solicitando que a empresa verifique esses valores para confirmar a conexão.
3. Aceitar o contrato do usuário
Para usar o PayPal, cada empresa precisa concordar com o Contrato do Usuário e a Política de Uso Aceitável do PayPal. Esses documentos descrevem os casos de uso permitidos dos serviços do PayPal, bem como as atividades proibidas.
4. Enviar informações fiscais
A conformidade fiscal é inegociável para as empresas que usam o PayPal. As empresas precisam enviar seus números de identificação fiscal (como um Número de Identificação do Empregador, ou EIN, nos EUA) ao PayPal e se alinhar aos regulamentos fiscais locais.
5. Verificar seu endereço de e-mail
É necessário fornecer um endereço de e-mail funcional para gerenciar uma conta PayPal e para o PayPal se comunicar com a empresa. Esse e-mail deve ser verificado antes de ser usado, uma etapa de segurança padrão para pagamentos digitais.
6. Selecionar as moedas da transação
As empresas precisam determinar as moedas nas quais realizarão transações e informá-las ao PayPal antes de processar pagamentos na plataforma.
7. Integrar o pagamento móvel
As empresas que optam por realizar transações por dispositivos móveis também devem integrar as soluções de pagamento móvel do PayPal, garantindo a compatibilidade do sistema e uma experiência de fácil uso para os clientes.
Custos e tarifas do PayPal
Para empresas
Tarifas de transação: As empresas que usam o PayPal incorrem em várias tarifas de transação. Estas podem incluir uma tarifa fixa por transação processada, mais uma tarifa definida como porcentagem do valor da transação.
Tarifas de estorno e contestação: Quando os clientes registram uma contestação ou estorno, as empresas enfrentam tarifas adicionais. O PayPal cobra uma tarifa da empresa para cobrir o custo do processamento do estorno, e esse valor varia conforme o país.
Taxas internacionais e de conversão de moeda: Para transações comerciais internacionais, o PayPal cobra uma porcentagem do valor da transação para compensar o processo de conversão de moeda. Também há uma tarifa fixa que varia de acordo com as moedas envolvidas e o país onde a conta PayPal está localizada.
Tarifas de recebimento e retirada: O recebimento de dinheiro em uma conta PayPal geralmente é gratuito para transações pessoais domésticas, mas incorre em uma tarifa em casos de transações comerciais e transferências internacionais. Há também uma tarifa de saque se a empresa optar por transferir fundos instantaneamente da conta PayPal para uma conta bancária em vez de usar a função de transferência padrão.
Para clientes e pessoas físicas
Tarifas internacionais: Para pessoas físicas, enviar dinheiro para amigos e familiares dentro do mesmo país geralmente é gratuito quando financiado pelo saldo PayPal ou uma conta bancária vinculada à conta PayPal. O envio internacional de dinheiro do saldo PayPal ou da conta bancária tem uma tarifa.
Tarifas de conversão de moedas: Quando uma transação envolve uma conversão de moeda, o PayPal aumenta a taxa de câmbio, resultando em um custo adicional para o cliente. Essa tarifa é uma porcentagem do valor da transação e varia de acordo com o tipo de transação.
Tarifas de cartão de débito e crédito: O recebimento de pagamentos por cartão de crédito ou débito incorre em tarifas que a PayPal cobre para bancar os custos impostos pelas bandeiras de cartão.
Tarifas de retirada de caixa eletrônico: Para clientes que usam o cartão de débito PayPal, retirar dinheiro em um caixa eletrônico incorre uma tarifa fixa por transação.
Vantagens para a empresa em aceitar o PayPal
Há muitas vantagens em usar o PayPal para sua empresa:
- Acesso a novos mercados e clientes focados em tecnologia
- Transações simplificadas
- Transação mais rápida e conveniência para os clientes
- Aumento da satisfação dos clientes
- Altos padrões de segurança e conformidade
- Transações internacionais simplificadas
- Mais proteção ao cliente
- Mais confiança para o cliente e mais credibilidade para a marca
- Mais proteção para as empresas
- Suporte ao cliente atualizado para empresas e clientes
Medidas de segurança do PayPal
O PayPal combina novas tecnologias, conformidade regulatória e educação dos usuários para criar um ambiente de transação seguro para seus usuários. Aqui estão algumas das medidas de segurança que o PayPal implementa:
Aplica técnicas de criptografia: O PayPal protege os dados em trânsito dos clientes e das transações usando rígidos protocolos de criptografia, como SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) e TLS (Transport Layer Security).
__ Usa proteção contra fraudes avançada:__ O PayPal monitora as transações em tempo real para detectar atividades suspeitas, alimentado por algoritmos de machine learning que analisam grandes conjuntos de dados para identificar padrões indicativos de fraude.
Mantém autenticação de dois fatores: Para aumentar a segurança das contas, o PayPal implementa a autenticação de dois fatores (2FA), que exige que os clientes forneçam duas formas de identificação antes de conceder o acesso.
Conduz verificação biométrica: O aplicativo móvel PayPal pode verificar a identidade de um cliente por meio de impressão digital e reconhecimento facial, mesmo que sua senha seja comprometida.
Mantém os padrões de segurança de dados: O PayPal cumpre o PCI DSS para proteger os dados dos titulares de cartão, implementando controles rigorosos e realizando auditorias regulares para garantir a conformidade contínua.
Cumpre os regulamentos de segurança: O PayPal está em conformidade com os regulamentos locais que regem a segurança de pagamentos. Na Europa, por exemplo, a plataforma está em conformidade com o Regulamento Geral de Proteção de Dados (GDPR).
Como funciona o PayPal
Diferentes tipos de usuários em todo o mundo usam o PayPal, incluindo clientes individuais, pequenas e grandes empresas e organizações sem fins lucrativos. Veja como funcionam os pagamentos com PayPal:
Configuração da conta e verificação de usuários
Os usuários começam criando uma conta no PayPal e vinculando formas de pagamento, como conta bancária ou cartão de crédito. O PayPal verifica a identidade do usuário antes de processar os pagamentos, um requisito regulatório para maior segurança. Os usuários podem receber dinheiro com uma conta pessoal ou empresarial do PayPal, desde que o endereço de e-mail ou número de celular seja confirmado.Iniciação da transação
Os compradores iniciam os pagamentos selecionando o PayPal como forma de pagamento no checkout, seja no site da empresa ou por transferência ponto a ponto. O comprador insere suas credenciais do PayPal e, em seguida, a plataforma solicita que ele selecione uma fonte de fundos preferida, como uma conta bancária, cartão de crédito ou saldo PayPal.Direcionamento de pagamentos
Após a confirmação da fonte de financiamento, o PayPal solicita os fundos dessa fonte. Se a fonte for um saldo do PayPal, a transação é concluída quase instantaneamente. Para transferências bancárias ou pagamentos com cartão de crédito, o PayPal se comunica com as instituições financeiras relevantes por meio de canais seguros.Segurança e privacidade de dados
Durante todo o processo de transação, o PayPal emprega padrões avançados de criptografia para manter a segurança e a privacidade dos dados. O PayPal não compartilha informações financeiras completas com os vendedores, o que reduz as chances de comprometimento de dados sensíveis.Estrutura de tarifas
O PayPal cobra tarifas dos clientes por determinadas transações, incluindo conversões de moedas e pagamentos internacionais. Também cobra tarifas das empresas, calculadas como uma porcentagem do valor da transação mais um valor fixo.Gestão de riscos e proteção contra fraudes
O PayPal monitora transações em busca de atividades suspeitas usando modelos de risco e algoritmos proprietários. As medidas de prevenção contra fraudes da plataforma incluem autenticação de dois fatores, confirmações de transações por e-mail e análise de fraudes em tempo real.Resolução de contestações e proteção de compradores
O PayPal oferece um serviço de resolução de contestações, o qual permite que compradores e vendedores registrem reclamações se houver um problema com uma transação. A política de Proteção ao Comprador do PayPal oferece reembolsos para compras que não chegaram ou não correspondem à descrição, reforçando a confiança na plataforma de pagamentos.Compensação e liquidação de fundos
Depois que uma transação é autorizada e processada, o PayPal liquida os fundos, deduzindo o dinheiro da conta do comprador e creditando-o no saldo PayPal do vendedor. Os vendedores podem transferir o saldo no PayPal para suas contas bancárias ou manter os fundos no PayPal para transações futuras.Pagamentos móveis
Com as soluções de pagamento por dispositivos móveis como o PayPal One Touch, os clientes podem fazer pagamentos em seus dispositivos móveis sem inserir dados de login para cada transação. Esse serviço depende de autenticação de dispositivo para garantir uma maior segurança.
Onde o PayPal é usado?
A base de clientes do PayPal abrange vários continentes. Em 2024, o PayPal tinha 434 milhões de contas ativas de consumidores e comerciantes, processando $1,68 trilhão em volume total de pagamentos em 26 bilhões de transações. Isso demonstra seu amplo alcance e a confiança que conquistou com clientes e empresas.
América do Norte
Uma parte substancial da receita do PayPal vem de seus clientes nos Estados Unidos, com 57% dos adultos dos EUA usando o PayPal, de acordo com uma pesquisa de 2022. O PayPal está profundamente enraizado no [setor de comércio eletrônico] dos EUA (https://stripe.com/resources/more/ecommerce-checkout-best-practices), fornecendo um método confiável e familiar para transações digitais. A conveniência do pagamento com um clique do PayPal atrai a cultura acelerada de compras, e suas políticas de proteção ao comprador são um forte atrativo para clientes cautelosos com fraudes on-line.Europa
A presença da plataforma na Europa varia conforme a região. Os países da Europa Ocidental têm altos níveis de uso do PayPal, com PayPal usado para pagamentos on-line com mais frequência na Alemanha e Itália do que nos Estados Unidos em 2023. Os países do Leste Europeu também estão adotando cada vez mais o PayPal, coincidindo com o aumento do comércio eletrônico nessa região. A conformidade da empresa com as regulamentações financeiras da União Europeia a torna uma escolha segura para transações transfronteiriças na Europa.Ásia-Pacífico
O uso do PayPal na região Ásia-Pacífico varia muito. Na Austrália e no Japão, o PayPal é preferido para transações domésticas e internacionais. Na Índia, a plataforma é usada principalmente para pagamentos internacionais, capitalizando sobre o significativo mercado de freelancers e empresas com clientes em todo o mundo.América Latina
O PayPal tem se tornado cada vez mais prevalente no crescente marketplace online da América Latina. Em 2023, o uso do PayPal para pagamentos no ponto de venda no México subiu para uma nova alta de 63%. A PayPal também estabeleceu parcerias com instituições financeiras locais para obter um melhor alinhamento com os hábitos de pagamento específicos dos clientes da América Latina.Oriente Médio
No Oriente Médio, o uso de PayPal aumentou em países como os Emirados Árabes Unidos, principalmente para compras online internacionais. Os clientes e as empresas da região consideram a capacidade de usar várias moedas e as medidas de segurança da PayPal conducentes a um comércio internacional seguro e direto.
Quem usa o PayPal?
O PayPal atende a uma ampla variedade de indústrias e clientes em todo o mundo. A versatilidade da forma de pagamento atende às necessidades de pequenas empresas, grandes corporações e indivíduos.
Empresas de e-commerce e varejistas on-line: De [startups] emergentes (https://stripe.com/resources/more/what-are-the-stages-of-a-startup) a mercados estabelecidos, as empresas on-line contam com os pagamentos do PayPal graças à sua reputação e facilidade de uso.
Provedores de serviços e freelancers: Com a ascensão da gig economy, mais de 100 milhões de freelancers e prestadores de serviços tornaram-se usuários frequentes do PayPal. Ele oferece uma interface simples para faturamento e rastreamento de pagamentos, o que é importante para quem gerencia as finanças da sua empresa.
Organizações sem fins lucrativos: Os botões de doação e os descontos para organizações sem fins lucrativos do PayPal fazem dele a solução de pagamento preferencial para instituições de caridade e fundações. A plataforma também oferece recursos para criar campanhas de doação e fornece relatórios simplificados para rastreamento e conformidade.
Criadores de conteúdo digital: Criadores de conteúdo que atuam em plataformas como YouTube, Twitch e Patreon frequentemente usam o PayPal para receber apoio financeiro das suas comunidades. A capacidade da plataforma de lidar com pagamentos pequenos e irregulares a torna ideal para quem depende do patrocínio de um público diversificado.
Empresas baseadas em assinatura:__ Empresas com serviços de assinatura — como streaming de mídia, software ou clubes de caixa do mês — frequentemente integram o PayPal para pagamentos recorrentes. Os clientes podem configurar pagamentos automáticos para facilitar o gerenciamento de suas assinaturas.
Compradores on-line: O PayPal é muito popular entre os consumidores que fazem compras na Internet. Ele permite transações seguras que não compartilham os dados do cartão com empresas, e seu Programa de Proteção ao Comprador oferece uma rede de segurança para compras feitas em muitos sites de e-commerce.
Força de trabalho global: À medida que o trabalho remoto se torna mais comum, empresas no exterior usam cada vez mais o PayPal para pagar seus funcionários remotos. A capacidade da plataforma de gerenciar pagamentos internacionais e converter moedas é particularmente vantajosa para esse grupo demográfico de funcionários.
Pequenas empresas: Pequenas empresas, incluindo vendedores locais e artesãos que vendem produtos por meio de mercados on-line, costumam aceitar pagamentos do PayPal usando o programa Proteção ao Vendedor do PayPal.
Família e amigos:Muitos clientes usam extensivamente os serviços de transferência pessoal do PayPal para enviar dinheiro a familiares e amigos. Seja dividindo uma conta, compartilhando presentes ou ajudando um ente querido financeiramente, a facilidade de uso do PayPal o torna uma das principais opções para transferências pessoais.
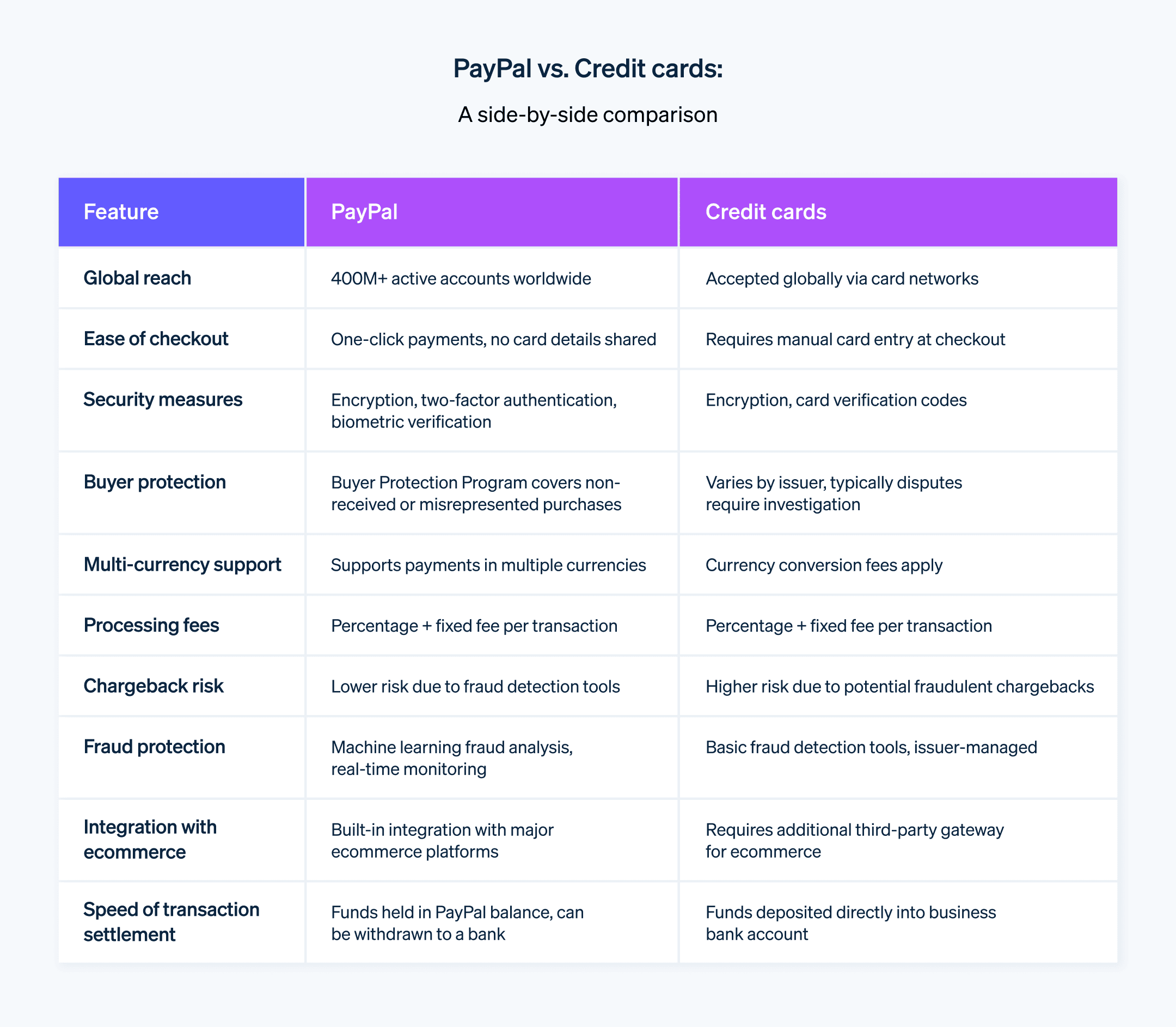
Alternativas ao PayPal
Embora o PayPal seja uma forma de pagamento popular, vários concorrentes oferecem serviços comparáveis. As empresas que escolherem quais formas de pagamento aceitar devem considerar conveniência, tarifas de transação e recursos internacionais.
Venmo: de propriedade do PayPal, o Venmo ganhou popularidade por ser carteira digital com recursos de pagamento pessoa para pessoa. Cada vez mais, o Venmo também está sendo adotado por empresas para transações de clientes, especialmente pelo público millennial.
Google Pay: o Google Pay combina pagamentos na web e no aplicativo para usuários de Android. O Google Pay se integra a outros serviços do Google, criando uma experiência de pagamento fluida dentro do ambiente Google.
Apple Pay: projetado para usuários da Apple, o Apple Pay permite realizar transações via iPhone, iPad, Mac e Apple Watch. A plataforma prioriza a segurança e privacidade, usando autenticação biométrica para aprovar transações.
Amazon Pay: capitalizando sobre a vasta base de clientes da Amazon, o Amazon Pay permite que os clientes usem seus dados da conta Amazon para fazer compras em sites de terceiros. Isso simplifica o processo de checkout e pode aumentar as taxas de conversão.
Wise: Com foco em pagamentos internacionais, a Wise (antiga TransferWise) oferece contas de pagamento sem fronteiras para enviar dinheiro internacionalmente de maneira fácil e econômica. O Wise é particularmente vantajoso para empresas que lidam com moedas estrangeiras.
Saiba mais sobre como o Stripe Payments pode impulsionar seus pagamentos online e presenciais, ou comece agora.
O conteúdo deste artigo é apenas para fins gerais de informação e educação e não deve ser interpretado como aconselhamento jurídico ou tributário. A Stripe não garante a exatidão, integridade, adequação ou atualidade das informações contidas no artigo. Você deve procurar a ajuda de um advogado competente ou contador licenciado para atuar em sua jurisdição para aconselhamento sobre sua situação particular.