Digitala betalningar förväntas uppgå till 9,5 biljoner USD år 2023. Företag i alla storlekar måste förstå de komplexa grunderna inom betalningsbehandling för fortsätta vara konkurrenskraftiga och erbjuda kunderna enkla, säkra och bekväma sätt att betala.
För företag som tar emot kundbetalningar spelar betalningsbehandling en viktig roll för att hantera kassaflödet, förbättra kundnöjdheten och minska risken för bedrägerier. I takt med att betalningsbranschen utvecklas med snabba tekniska framsteg och förändrade kundbeteenden måste företag hålla koll på branschtrender, förordningar och säkerhetsstandarder för att anpassa sig till marknaden.
Nedan undersöker vi olika aspekter av betalningsbehandling, inklusive komponenterna, hur betalningsbehandling fungerar, bästa praxis för företag och vikten av att välja rätt leverantör som kan bidra till att bygga och underhålla ett effektivt system för betalningsbehandling. Genom att förstå de här begreppen kan företag fatta välgrundade beslut om sina strategier och lösningar för betalningsbehandling – och erbjuda en betalningsupplevelse som driver tillväxt.
Vad innehåller den här artikeln?
- Vad är betalningsbehandling?
- Varför betalningsbehandling är viktigt för företag
- Betalningsbehandlingens komponenter
- Hur fungerar betalningsbehandling?
- Bästa praxis för betalningsbehandling för företag
Vad är betalningsbehandling?
Betalningsbehandling är den sekvens av åtgärder som på ett säkert sätt överför medel mellan en betalare och en betalningsmottagare. Vanligtvis involverar det auktorisering, verifiering och avräkning av transaktioner genom elektroniska betalningssystem.
System för betalningsbehandling tillgodoser olika typer av transaktioner, inklusive kredit- och bankkort, elektroniska överföringar av pengar (EFT), överföringar via Automated Clearing House (ACH), mobilbetalningar, digitala plånböcker och kryptovalutor. En rad olika intressenter – däribland banker, finansinstitut, betalleverantörer, teknikleverantörer, företag och tillsynsmyndigheter – utvecklar och hanterar dessa system.
Varför betalningsbehandling är viktigt för företag
Ett brett utbud av tekniker, tjänster och finansiella instrument (alla fysiska eller digitala instrument som används för att utföra kontantfria transaktioner, t.ex. ett kredit- eller bankkort) samverkar för att säkerställa snabb och säker överföring av pengar mellan parter. System för betalningsbehandling underlättar handel, stöder e-handel och främjar ekonomisk tillväxt. De betalningslösningar som ett företag använder avgör hur väl företaget kan interagera med kunderna och handeln i stort.
Dessutom är företag av alla storlekar beroende av effektiv och pålitlig betalningsbehandling för att hantera kassaflöde, kundnöjdhet och den övergripande affärsverksamheten. Genom att erbjuda en mängd olika betalningsalternativ kan företag tillgodose sina kunders olika preferenser, göra det bekvämare för dem och främja förtroende. Ett välfungerande system för betalningsbehandling bidrar också till att minska risken för bedrägerier, upprätthålla datasäkerheten och säkerställa efterlevnad av relevanta förordningar och branschstandarder.
Under de senaste åren har landskapet för betalningsbehandling utvecklats avsevärt genom tekniska framsteg, förändrade kundbeteenden och uppkomsten av nya marknadsaktörer. Dessa förändringar har lett till innovativa betalningslösningar, större tillgänglighet till finansiella tjänster och ökad konkurrens inom branschen. Därmed kan företag och kunder nu dra nytta av alternativ för betalningsbehandling som är snabbare, säkrare och bekvämare.
Betalningsbehandlingens komponenter
Betalningsbehandling omfattar flera komponenter som samverkar för att möjliggöra säkra och effektiva transaktioner mellan kunder och företag. Dessa komponenter inkluderar:
- Kunden: Den fysiska eller juridiska personen som initierar betalningen för varor eller tjänster.
- Handlaren: Företaget eller tjänsteleverantören som tar emot betalningen från kunden.
- Betalningsmetoden: Den metod som kunden använder för att genomföra betalningen, t.ex. kreditkort, bankkort, elektroniska plånböcker eller kryptovalutor.
- POS-systemet (Point-of-Sale): Den fysiska eller digitala plattformen där transaktionen utförs, t.ex. en kortterminal i en butik, en e-handelswebbplats eller mobilapp.
- Betalningsgatewayen: En tjänst som på ett säkert sätt samlar in och överför betalningsinformation från POS-systemet till betalleverantören eller den inlösande banken, vilket säkerställer kryptering och säkerhet för känsliga uppgifter under transaktionsprocessen.
- Betalleverantören: Ett tredjepartsföretag som hanterar de tekniska aspekterna av transaktionen, inklusive validering av betalningsinformation, inhämtande av auktorisering och hantering av kommunikationen mellan den inlösande och utfärdande banken.
- Den inlösande banken, eller inlösaren: Det finansinstitut som innehar handlarens konto, tar emot betalningen för dess räkning, behandlar transaktionen och sätter in pengarna på handlarens konto.
- Kortbetalningsnätverket: Organisationer (t.ex. Visa, Mastercard och American Express) som fastställer regler, standarder och infrastruktur för behandling av transaktioner med hjälp av deras varumärkta betalningsinstrument.
- Den utfärdande banken eller utfärdaren: Det finansinstitut som har utfärdat betalningsinstrumentet till kunden och som ansvarar för att godkänna eller avvisa transaktionen baserat på kundens kontostatus, tillgängliga medel och andra faktorer.
- Betalningssäkerhet: Tekniker och standarder – till exempel Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), tokenisering eller kryptering som garanterar betalningsinformationens säkerhet och integritet och skyddar mot bedrägerier och dataintrång.
- Avräkning och avstämning: Processen att överföra medel mellan den utfärdande banken och den inlösande banken, följt av att uppdatera handlarens konto och generera av transaktionsposter för både kunden och handlaren.
Varje komponent spelar en viktig roll i processen och säkerställer att transaktionerna genomförs på ett säkert, effektivt sätt och i enlighet med tillämpliga förordningar och branschstandarder.
Hur fungerar betalningsbehandling?
Processen omfattar flera steg och flera parter. Vi beskriver här hur betalningsbehandling fungerar:
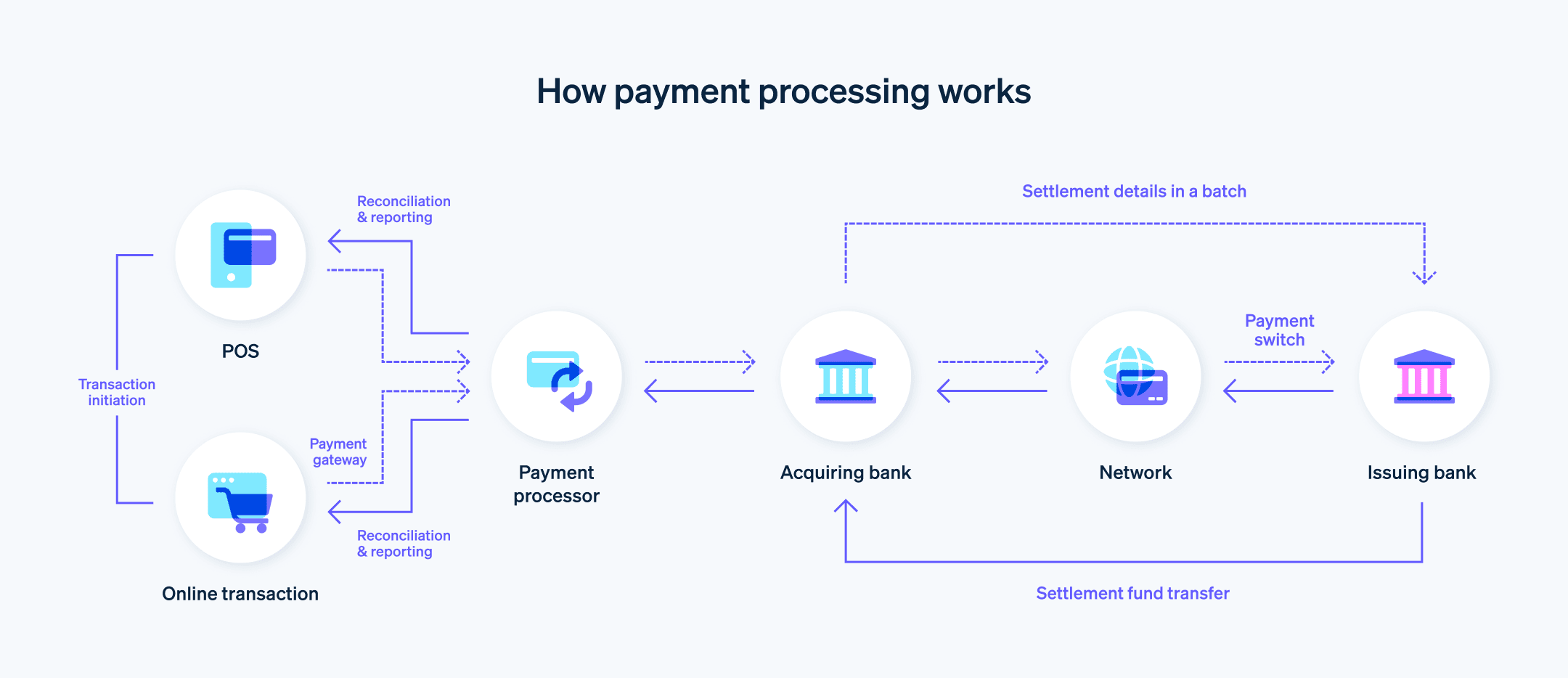
1. Transaktionsinitiering
Kunden initierar betalningen genom att tillhandahålla sina betalningsuppgifter (t.ex. kreditkort, bankkort eller annan betalningsmetod) vid POS-systemet i en fysisk butik eller via en onlineplattform som en e-handelswebbplats eller mobilapp.
2. Betalningsgateway
När kunden skickar in sin betalningsinformation överförs den på ett säkert sätt till betalningsgatewayen som fungerar som en bro mellan kunden, företaget och betalleverantören. Betalningsgatewayen ansvarar för att kryptera transaktionsdata och se till att data överförs på ett säkert sätt till betalleverantören eller den inlösande banken.
3. Transaktionsauktorisering
Betalleverantören tar emot transaktionsdata från betalningsgatewayen och validerar informationen. Den vidarebefordrar sedan transaktionsuppgifterna till den inlösande banken, som i sin tur skickar informationen till kortnätverket för validering och auktorisering.
4. Verifiering från utfärdande bank
Kortnätverket vidarebefordrar transaktionsuppgifterna till den utfärdande banken. Den utfärdande banken verifierar kundens kontostatus, kontrollerar tillgängligt saldo eller kreditgräns och bedömer eventuella risker. Baserat på dessa faktorer godkänner eller avvisar den utfärdande banken transaktionen.
5. Auktoriseringssvar
Den utfärdande banken skickar tillbaka auktoriseringssvaret – godkänt eller avvisat – via kortbetalningsnätverket till den inlösande banken, som sedan vidarebefordrar svaret till betalleverantören. Betalleverantören skickar sedan svaret till betalningsgatewayen, som förmedlar resultatet till företagets POS-system eller onlineplattform.
6. Slutförande av transaktionen
Om transaktionen godkänns slutför företaget försäljningen genom att förse kunden med varorna eller tjänsterna. Om transaktionen avvisas kan företaget begära en alternativ betalningsmetod från kunden.
7. Transaktionsavräkning
I slutet av varje dag skickar företaget en batch med godkända transaktioner till betalleverantören eller den inlösande banken för avräkning. Den inlösande banken begär medlen från den utfärdande banken via kortnätverket. Den utfärdande banken överför pengarna till den inlösande banken, som sedan sätter in pengarna på företagets konto. Detta sker vanligtvis inom några arbetsdagar.
8. Avstämning och rapportering
Företaget stämmer av de avräknade transaktionerna mot sin försäljningshistorik och eventuella transaktionsavgifter som debiterats av betalleverantören, den inlösande banken eller andra inblandade parter. Både företaget och kunden får transaktionsunderlag, till exempel fakturor, kvitton eller kontoutdrag.
Bästa praxis för betalningsbehandling för företag
Genom att implementera bästa praxis för betalningsbehandling kan man förbättra kundupplevelsen, minimera risken för bedrägeri och upprätthålla efterlevnaden av branschförordningar och standarder. När bästa praxis följs bygger man dessutom upp välstrukturerade interna processer för betalningar som använder resurser på ett effektivt sätt och minimerar fel.
Här är några av de viktigaste metoderna för betalningsbehandling för företag:
Skapa en säker betalningsmiljö
Implementera robusta säkerhetsåtgärder, som kryptering, tokenisering och SSL-certifikat (Secure Sockets Layer) för att skydda känsliga betalningsdata under överföring och lagring. Följ PCI DSS och andra relevanta säkerhetsstandarder för att upprätthålla en säker betalningsmiljö.Erbjud olika betalningsalternativ
Tillgodose kundernas olika preferenser och förbättra deras shoppingupplevelse genom att erbjuda flera betalningsalternativ som kredit- och bankkort, digitala plånböcker och alternativa betalningsmetoder.Använd en betalleverantör med gott anseende
Välj en pålitlig och välrenommerad betalleverantör som erbjuder omfattande betalningslösningar, avancerade verktyg för bedrägeribekämpning, konkurrenskraftiga avgifter och utmärkt kundsupport.Uppdatera mjukvara och hårdvara regelbundet
Se till att mjukvara, hårdvara och integrationer för betalningsbehandling har de senaste säkerhetsuppdateringarna och tekniska funktionerna. Detta minskar sårbarheter och bibehåller effektiviteten och säkerheten i systemet för betalningsbehandling.Utbilda anställda
Utbilda anställda om bästa praxis för betalningsbehandling, säkerhetsprotokoll och åtgärder för bedrägeribekämpning. Se till att de är medvetna om företagets policyer och rutiner för betalningsbehandling och att de kan känna igen och reagera på potentiella säkerhetshot.Implementera verktyg för bedrägeribekämpning
Använd avancerade verktyg för att bedrägeribekämpning, t.ex. adressverifieringstjänster (AVS, address verification service), säkerhetskoder (CVV-koder) och 3D Secure-autentisering för att minimera risken för bedrägliga transaktioner och återkrediteringar (chargebacks).Övervaka transaktioner
Övervaka och granska regelbundet betalningsbehandlingen för att se om det finns några ovanliga mönster eller tecken på bedrägeri. Ställ in aviseringar för att få information om misstänkt aktivitet i realtid.Ha tydliga policyer för återbetalningar och återkrediteringar (chargebacks)
Skapa och förmedla tydliga policyer för återbetalning och återkreditering till kunderna för att minska antalet tvister och missförstånd. Tillhandahåll omfattande kundservice för att snabbt lösa problem. Detta minimerar risken för återkrediteringar.Effektivisera avräkning och rapportering
Implementera effektiva avräknings- och rapporteringsprocesser för att upprätthålla korrekt bokföring, snabb utbetalning av medel och effektiv övervakning av betalningsbehandlingen.Håll dig informerad om branschtrender och förordningar
Betalningsbehandling utvecklas hela tiden. Håll dig uppdaterad om den senaste utvecklingen inom teknik för betalningsbehandling, bästa praxis för branschen och regeländringar för att säkerställa att företaget följer rådande förordningar och är konkurrenskraftigt.
En leverantör av betalningsbehandling, som Stripe, kan upprätthålla bästa praxis och ge företag tillgång till ett effektivt, välfungerande system för betalningsbehandling utan att belasta budgeten. För mer information om hur Stripe tillgodoser moderna företags komplexa behov av betalningsbehandling, klicka här.
Innehållet i den här artikeln är endast avsett för allmän information och utbildningsändamål och ska inte tolkas som juridisk eller skatterelaterad rådgivning. Stripe garanterar inte att informationen i artikeln är korrekt, fullständig, adekvat eller aktuell. Du bör söka råd från en kompetent advokat eller revisor som är licensierad att praktisera i din jurisdiktion för råd om din specifika situation.