Digital payments are expected to reach US$9.5 trillion in 2023. Businesses of all sizes must understand the complex fundamentals behind payment processing in order to stay competitive and offer their customers simple, secure and convenient ways to pay.
For businesses that accept customer payments, payment processing plays a significant role in managing cash flow, enhancing customer satisfaction and mitigating fraud risks. As the payment industry evolves alongside rapid technological advancements and changing customer behaviour, businesses must stay up to date with industry trends, regulations and security standards to ensure that they can adapt.
Below, we'll examine different aspects of payment processing, including the components, how payment processing works, best practices for businesses, and the importance of choosing the right provider to help you build and maintain an effective payment-processing system. By understanding these concepts, businesses can make informed decisions about their payment-processing strategies and solutions, while providing a payment experience that drives growth.
What's in this article?
- What is payment processing?
- Why payment processing is important for businesses
- Components of payment processing
- How does payment processing work?
- Payment processing best practices for businesses
What is payment processing?
Payment processing is the sequence of actions that transfers funds securely between a payer and a payee. Typically, it involves the authorisation, verification and settlement of transactions through electronic payment systems.
Payment processing systems cater to various types of transactions, including credit and debit cards, electronic funds transfers (EFTs), automated clearing house (ACH) transfers, mobile payments, digital wallets and cryptocurrencies. A diverse set of stakeholders – including banks, financial institutions, payment processors, technology providers, businesses and regulatory bodies – develop and manage these systems.
Why payment processing is important for businesses
A wide range of technologies, services and financial instruments (any physical or digital instrument used to make cashless transactions, such as a credit or debit card) work together to ensure that funds are transferred between parties quickly and securely. Payment-processing systems facilitate trade, support e-commerce and promote economic growth. The payment-processing solutions adopted by a business dictate how well that business is able to interact with customers – and the broader world of commerce.
Additionally, businesses of all sizes depend on efficient and reliable payment processing to help manage cash flow, customer satisfaction and overall business operations. By offering a variety of payment options, businesses can cater to the diverse preferences of their customers, increasing convenience and fostering trust. In addition, a well-functioning payment-processing system also helps to reduce the risk of fraud, ensure data security and maintain compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
In recent years, the payment-processing landscape has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in technology, changing customer behaviour and the rise of new market players. These changes have resulted in the emergence of innovative payment solutions, greater accessibility to financial services and increased competition in the industry. As a result, businesses and customers can now benefit from payment-processing options that are faster, more secure and more convenient.
Components of payment processing
Payment processing involves multiple components that work together to enable secure, efficient transactions between the customer and the business. These components include:
- The customer: the individual or entity that initiates the payment for goods or services.
- The merchant: the business or service provider that accepts the payment from the customer.
- The payment method: the method that the customer uses to make the payment, such as credit cards, debit cards, electronic wallets or cryptocurrencies.
- The point-of-sale (POS) system: the physical or digital platform where the transaction takes place, such as a retail terminal, e-commerce website or mobile app.
- The payment gateway: a service that securely captures and transmits payment information from the POS system to the payment processor or acquiring bank, ensuring the encryption and security of sensitive data during the transaction process.
- The payment processor: a third-party company that handles the technical aspects of the transaction, including validating payment information, obtaining authorisation and managing communication between the acquiring and issuing banks.
- The acquiring bank, or acquirer: the financial institution that holds the merchant's account, receives the payment on its behalf, processes the transaction and settles the funds in the merchant's account.
- The card network: organisations (e.g. Visa, Mastercard and American Express) that establish the rules, standards and infrastructure for processing transactions, using their branded payment instruments.
- The issuing bank, or issuer: the financial institution that has issued the payment instrument to the customer and is responsible for authorising or declining the transaction, based on the customer's account status, available funds and other factors.
- Payment security: technologies and standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), tokenisation or encryption, that ensure the safety and integrity of payment information and protect against fraud and data breaches.
- Settlement and reconciliation: the process of transferring funds between the issuing bank and the acquiring bank, followed by updating the merchant's account and generating transaction records for both the customer and the merchant.
Each component plays an important role in the process, ensuring that transactions are completed securely, efficiently and in compliance with applicable regulations and industry standards.
How does payment processing work?
The process involves several steps and multiple parties. Here’s an explanation of how payment processing works:
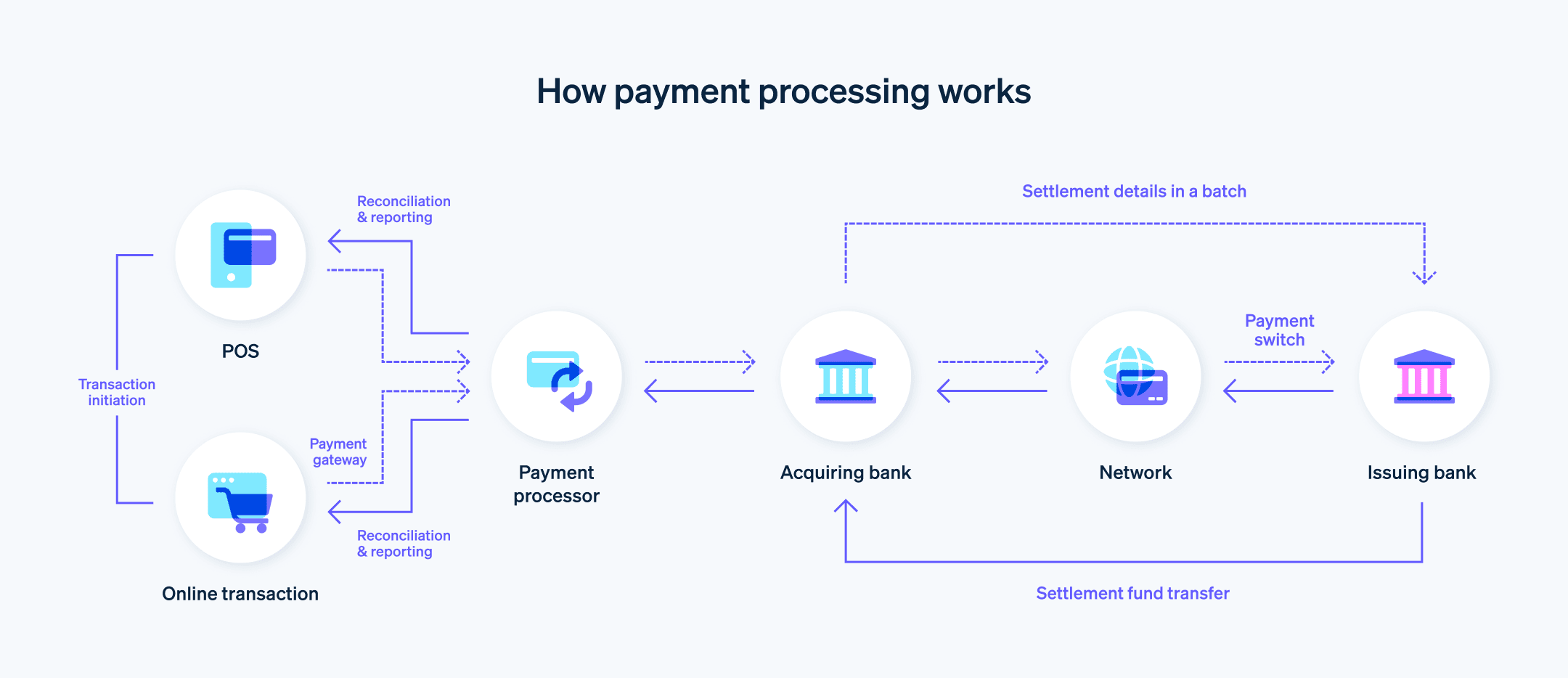
1. Transaction initiation
The customer initiates the payment by providing their payment information (e.g. a credit card, debit card, or another payment method) at the point of sale in a physical store, or through an online platform such as an e-commerce website or mobile app.
2. Payment gateway
Once the customer submits their payment information, it’s securely transmitted to the payment gateway, which acts as a bridge between the customer, the business, and the payment processor. The payment gateway is responsible for encrypting the transaction data and ensuring the data is transmitted securely to the payment processor or the acquiring bank.
3. Transaction authorisation
The payment processor receives the transaction data from the payment gateway and validates the information. It then forwards the transaction details to the acquiring bank, which sends the information to the card network for validation and authorisation.
4. Issuing-bank verification
The card network forwards the transaction details to the issuing bank. The issuing bank verifies the customer’s account status, checks the available balance or credit limit, and assesses any potential risks. Based on these factors, the issuing bank either approves or declines the transaction.
5. Authorisation response
The issuing bank sends back the authorisation response – approval or decline – through the card network to the acquiring bank, which then forwards the response to the payment processor. The payment processor then sends the response to the payment gateway, which communicates the result to the business’s POS system or online platform.
6. Transaction completion
If the transaction is approved, the business completes the sale by providing the customer with the goods or services. If the transaction is declined, the business may request an alternative payment method from the customer.
7. Transaction settlement
At the end of each day, the business sends a batch of approved transactions to the payment processor or the acquiring bank for settlement. The acquiring bank requests the funds from the issuing bank through the card network. The issuing bank transfers the funds to the acquiring bank, which then deposits the money into the business’s account, usually within a few business days.
8. Reconciliation and reporting
The business reconciles the settled transactions with its sales records and any transaction fees charged by the payment processor, acquiring bank, or other parties involved. Both the business and the customer receive transaction records, such as invoices, receipts, or account statements.
Payment processing best practices for businesses
Implementing payment-processing best practices can enhance the customer experience, minimise the risk of fraud and maintain compliance with industry regulations and standards. Additionally, upholding these best practices is a good way to cultivate a well-structured set of internal processes for payments, which will use resources efficiently and minimise errors.
Here are some key payment-processing best practices for businesses:
Build a secure payment environment
Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, tokenisation and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates, to protect sensitive payment data during transmission and storage. Comply with PCI DSS and other relevant security standards to guarantee a secure payment environment.Offer diverse payment options
Cater to the diverse preferences of your customers and enhance their shopping experience by offering multiple payment options, such as credit and debit cards, digital wallets and alternative payment methods.Use a reputable payment processor
Choose a reliable and reputable payment processor that offers comprehensive payment-processing solutions, advanced fraud-prevention tools, competitive fees and excellent customer support.Update hardware and software on a regular basis
Ensure that your payment-processing software, hardware and integrations are up to date with the latest security patches and advancements in technology. This reduces vulnerabilities and maintains the efficiency and security of your payment-processing system.Train employees
Educate your employees about payment-processing best practices, security protocols and fraud-prevention measures. Ensure that they are aware of your company's payment-processing policies and procedures, and can recognise and respond to potential security threats.Implement fraud-prevention tools
Employ advanced fraud-prevention tools, such as address verification service (AVS) and card verification value (CVV) checks, as well as 3D Secure authentication, to minimise the risk of fraudulent transactions and chargebacks.Monitor transactions
Monitor and review your payment-processing activities on a regular basis for any unusual patterns or signs of fraud. Set up notifications to stay informed about any suspicious activity in real time.Maintain clear refund and chargeback policies
Develop and communicate clear refund and chargeback policies to your customers in order to reduce disputes and misunderstandings. Provide comprehensive customer service to resolve issues promptly, minimising the risk of chargebacks.Streamline reconciliation and reporting
Implement efficient reconciliation and reporting processes to ensure accurate accounting, the timely settlement of funds and effective monitoring of your payment-processing activities.Stay informed about industry trends and regulations
Payment processing is constantly evolving. Stay up to date with the latest developments in payment processing technologies, industry best practices and regulatory changes to ensure that your business remains compliant and competitive.
A payment-processing provider, such as Stripe, can maintain these best practices, giving businesses access to an efficient and functional payment-processing system without putting strain on their resources. For more information about how Stripe caters to the complex payment-processing needs of modern businesses, start here.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.