คาดการณ์กันว่าการชำระเงินแบบดิจิทัลจะมีมูลค่าถึง 9.5 ล้านล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐภายในปี 2023 ธุรกิจทุกขนาดจะต้องเข้าใจพื้นฐานที่ซับซ้อนของการประมวลผลการชําระเงินเพื่อให้แข่งขันกับคู่แข่งได้ และนำเสนอวิธีการชําระเงินที่ง่าย ปลอดภัย และสะดวกสบายให้แก่ลูกค้า
สำหรับธุรกิจที่รับชำระเงินจากลูกค้า การประมวลผลการชำระเงินมีบทบาทสําคัญในการจัดการกระแสเงินสด เพิ่มความพึงพอใจของลูกค้า และบรรเทาความเสี่ยงด้านการฉ้อโกง ขณะที่อุตสาหกรรมการชําระเงินพัฒนาไปพร้อมกับความก้าวหน้าทางเทคโนโลยีอย่างรวดเร็วและพฤติกรรมลูกค้าที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป ธุรกิจต่างๆ จึงต้องเท่าทันข่าวสารเกี่ยวกับแนวโน้มอุตสาหกรรม ระเบียบข้อบังคับ และมาตรฐานการรักษาความปลอดภัยเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าจะปรับตัวได้
ด้านล่างนี้ เราจะสำรวจการประมวลผลการชําระเงินในด้านต่างๆ รวมถึงองค์ประกอบ การทำงานของการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดสําหรับธุรกิจ และความสําคัญของการเลือกผู้ให้บริการที่เหมาะสมเพื่อช่วยให้คุณสร้างและดูแลระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ การเข้าใจแนวคิดเหล่านี้จะช่วยให้ธุรกิจสามารถตัดสินใจเกี่ยวกับกลยุทธ์และโซลูชันการประมวลผลการชําระเงินของตนได้อย่างมีข้อมูล และส่งมอบประสบการณ์การชําระเงินที่กระตุ้นการเติบโตได้
บทความนี้ให้ข้อมูลอะไรบ้าง
- การประมวลผลการชําระเงินคืออะไร
- เหตุใดการประมวลผลการชําระเงินจึงสําคัญต่อธุรกิจ
- องค์ประกอบของการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน
- การประมวลผลการชําระเงินมีหลักการทํางานอย่างไร
- แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินสําหรับธุรกิจ
การประมวลผลการชําระเงินคืออะไร
การประมวลผลการชําระเงินคือลําดับของการดําเนินการที่โอนเงินทุนระหว่างผู้ชําระเงินกับผู้รับเงินอย่างปลอดภัย โดยปกติแล้วจะประกอบด้วยการอนุมัติ การยืนยัน และการชําระเงินของรายการธุรกรรมผ่านระบบการชําระเงินอิเล็กทรอนิกส์
ระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินรองรับธุรกรรมหลายประเภท เช่น บัตรเครดิตและบัตรเดบิต การโอนเงินทางอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ (EFT) การโอนผ่านสํานักหักบัญชีอัตโนมัติ (ACH) การชําระเงินผ่านอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่ กระเป๋าเงินดิจิทัล และคริปโตเคอร์เรนซี โดยผู้มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องหลากหลายกลุ่ม เช่น ธนาคาร สถาบันการเงิน ผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน ผู้ให้บริการเทคโนโลยี ธุรกิจ และหน่วยงานกํากับดูแล เป็นผู้พัฒนาและจัดการระบบเหล่านี้
เหตุใดการประมวลผลการชําระเงินจึงสําคัญต่อธุรกิจ
เทคโนโลยี บริการ และเครื่องมือทางการเงินที่หลากหลาย (เครื่องมือทางการเงินหรือเครื่องมือดิจิทัลใดๆ ที่ใช้ทําธุรกรรมแบบไม่ใช้เงินสด เช่น บัตรเครดิตหรือบัตรเดบิต) ทํางานร่วมกันเพื่อให้การโอนเงินระหว่างคู่สัญญาทําได้รวดเร็วและปลอดภัย ระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินช่วยอํานวยความสะดวกด้านการค้า สนับสนุนอีคอมเมิร์ซ และส่งเสริมการเติบโตทางเศรษฐกิจ โซลูชันการประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่ธุรกิจเลือกใช้เป็นเครื่องกําหนดว่าธุรกิจนั้นจะสามารถโต้ตอบกับลูกค้าและธุรกิจการค้าในวงกว้างได้ดีเพียงใด
นอกจากนี้ ธุรกิจทุกขนาดต่างก็ต้องพึ่งพาการประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่มีประสิทธิภาพและเชื่อถือได้ซึ่งจะช่วยจัดการกระแสเงินสด ความพึงพอใจของลูกค้า และการปฏิบัติงานทางธุรกิจโดยรวมด้วย การนำเสนอทางเลือกการชําระเงินที่หลากหลายช่วยให้ธุรกิจสามารถรองรับความต้องการที่หลากหลายของลูกค้า ซึ่งจะช่วยเพิ่มความสะดวกสบายและเสริมสร้างความเชื่อมั่นของลูกค้า อีกทั้งระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่ทํางานได้ดียังช่วยลดความเสี่ยงจากการฉ้อโกง เพิ่มความปลอดภัยให้ข้อมูล และช่วยในการปฏิบัติตามระเบียบข้อบังคับและมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้องอีกด้วย
ในช่วงไม่กี่ปีที่ผ่านมา สภาพการณ์ด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินเปลี่ยนแปลงไปอย่างมากจากขับเคลื่อนด้วยความก้าวหน้าในเทคโนโลยี พฤติกรรมของลูกค้าที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป และการเติบโตของผู้ให้บริการรายใหม่ๆ ในตลาด การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ทําให้เกิดโซลูชันการชําระเงินที่เป็นนวัตกรรมใหม่ๆ การเข้าถึงบริการทางการเงินทำได้มากขึ้น และการแข่งขันในตลาดก็มากขึ้นด้วย ด้วยเหตุนี้ ปัจจุบันธุรกิจและลูกค้าจึงได้รับประโยชน์จากตัวเลือกการประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่รวดเร็ว ปลอดภัยมากขึ้น และสะดวกยิ่งขึ้น
องค์ประกอบของการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน
การประมวลผลการชําระเงินมีองค์ประกอบหลายรายการที่ทํางานร่วมกันเพื่อให้ธุรกรรมระหว่างลูกค้ากับธุรกิจทำได้อย่างปลอดภัยและมีประสิทธิภาพ องค์ประกอบเหล่านี้ประกอบด้วย
- ลูกค้า: บุคคลหรือหน่วยงานที่เริ่มต้นการชําระเงินค่าสินค้าหรือบริการ
- ผู้ค้า: ธุรกิจหรือผู้ให้บริการที่รับการชําระเงินจากลูกค้า
- วิธีการชําระเงิน: วิธีที่ลูกค้าใช้ชําระเงิน เช่น บัตรเครดิต บัตรเดบิต กระเป๋าเงินอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ หรือคริปโตเคอร์เรนซี
- ระบบระบบบันทึกการขาย (POS): แพลตฟอร์มจริงหรือดิจิทัลที่มีการทําธุรกรรม เช่น เทอร์มินัลร้านค้าปลีก เว็บไซต์อีคอมเมิร์ซ หรือแอปบนอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่
- เกตเวย์การชําระเงิน: บริการที่บันทึกและส่งข้อมูลการชําระเงินจากระบบ POS ไปยังผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินหรือธนาคารผู้รับบัตรอย่างปลอดภัย ช่วยให้มั่นใจในการเข้ารหัสและความปลอดภัยของข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนระหว่างขั้นตอนการทําธุรกรรม
- ผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน: บริษัทบุคคลที่สามที่ดูแลธุรกรรมในด้านเทคนิค ซึ่งรวมถึงการตรวจสอบข้อมูลการชําระเงิน การขออนุญาต และการจัดการการสื่อสารระหว่างธนาคารผู้รับบัตรและธนาคารผู้ออกบัตร
- ธนาคารผู้รับบัตร หรือสถาบันผู้รับบัตร: สถาบันการเงินที่ถือบัญชีของผู้ค้า รับชําระเงินในนามของลูกค้า ประมวลผลธุรกรรม และชําระเงินในบัญชีของผู้ค้า
- เครือข่ายบัตร: องค์กร (เช่น Visa, Mastercard และ American Express) ที่ก่อตั้งกฎระเบียบ มาตรฐาน และโครงสร้างพื้นฐานสําหรับการประมวลผลธุรกรรม โดยใช้เครื่องมือการชําระเงินในแบรนด์ของตนเอง
- ธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรหรือสถาบันผู้ออกบัตร: สถาบันการเงินที่ออกเครื่องมือการชําระเงินให้กับลูกค้า และมีหน้าที่อนุมัติหรือปฏิเสธธุรกรรม โดยพิจารณาจากสถานะบัญชีของลูกค้า เงินทุนที่ใช้ได้ และปัจจัยอื่นๆ
- ระบบการรักษาความปลอดภัยในการชําระเงิน: เทคโนโลยีและมาตรฐาน เช่น มาตรฐานการรักษาความปลอดภัยข้อมูลสําหรับอุตสาหกรรมบัตรชําระเงิน (PCI DSS) การแปลงเป็นโทเค็น หรือการเข้ารหัส ซึ่งทำให้เกิดความปลอดภัยและความถูกต้องสมบูรณ์ของข้อมูลการชําระเงินตลอดจนป้องกันการฉ้อโกงและการละเมิดข้อมูล
- การชําระเงินและการกระทบยอด: ขั้นตอนการโอนเงินระหว่างธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรและธนาคารผู้รับบัตร ตามด้วยการอัปเดตบัญชีของผู้ค้าและการสร้างบันทึกรายการธุรกรมของลูกค้าและผู้ค้า
องค์ประกอบแต่ละส่วนมีบทบาทสําคัญในขั้นตอน เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าธุรกรรมเสร็จสมบูรณ์อย่างปลอดภัย มีประสิทธิภาพ และเป็นไปตามระเบียบข้อบังคับและมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้อง
การประมวลผลการชําระเงินมีหลักการทํางานอย่างไร
ขั้นตอนนี้มีหลายขั้นตอนและหลายฝ่ายที่เกี่ยวข้อง ต่อไปนี้คือคําอธิบายการทํางานของการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน
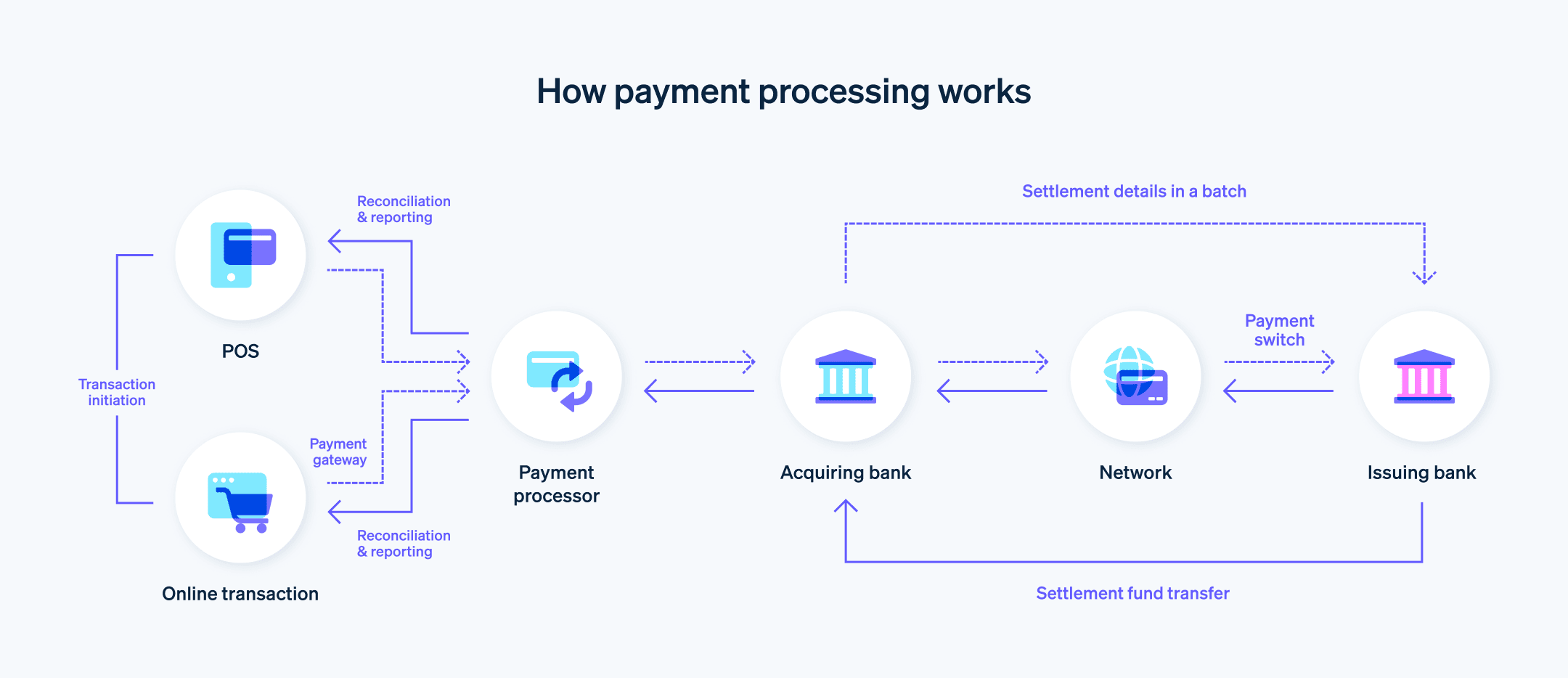
1. การเริ่มต้นธุรกรรม
ลูกค้าเริ่มต้นการชําระเงินโดยแจ้งข้อมูลการชําระเงินของตน (เช่น บัตรเครดิต บัตรเดบิต หรือวิธีการชําระเงินอื่น) ที่จุดขายในร้านค้าจริงหรือผ่านแพลตฟอร์มออนไลน์ เช่น เว็บไซต์อีคอมเมิร์ซหรือแอปบนอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่
2. เกตเวย์การชําระเงิน
เมื่อลูกค้าส่งข้อมูลการชําระเงินแล้ว ระบบจะส่งข้อมูลดังกล่าวอย่างปลอดภัยไปยังเกตเวย์การชําระเงินซึ่งทําหน้าที่เป็นสะพานเชื่อมระหว่างลูกค้า ธุรกิจ และผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน เกตเวย์การชําระเงินมีหน้าที่เข้ารหัสข้อมูลธุรกรรมและตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าข้อมูลนั้นถูกส่งอย่างปลอดภัยไปยังผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินหรือธนาคารผู้รับบัตร
3. การอนุมัติธุรกรรม
ผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินจะได้รับข้อมูลธุรกรรมจากเกตเวย์การชําระเงินและตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของข้อมูล จากนั้นจะส่งต่อรายละเอียดธุรกรรมไปให้ธนาคารผู้รับบัตร ซึ่งจะส่งข้อมูลไปให้เครือข่ายบัตรเพื่อการตรวจสอบและอนุมัติ
4. การยืนยันโดยธนาคารผู้ออกบัตร
เครือข่ายบัตรส่งต่อรายละเอียดธุรกรรมไปยังธนาคารผู้ออกบัตร ธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรยืนยันสถานะบัญชีของลูกค้า ตรวจสอบยอดเงินหรือวงเงินที่ใช้ได้ แล้วประเมินความเสี่ยงที่อาจเกิดขึ้น ธนาคารที่ออกบัตรอาจอนุมัติหรือปฏิเสธธุรกรรมโดยอิงตามปัจจัยเหล่านี้
5. การตอบกลับการอนุมัติ
ธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรจะส่งคำตอบว่าอนุมัติหรือการปฏิเสธผ่านเครือข่ายบัตรไปยังธนาคารผู้รับบัตร ซึ่งจะส่งต่อคำตอบไปยังผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน จากนั้นผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินจะส่งคำตอบไปยังเกตเวย์การชําระเงิน ซึ่งจะสื่อสารผลลัพธ์ไปยังระบบ POS หรือแพลตฟอร์มออนไลน์ของธุรกิจ
6. ธุรกรรมเสร็จสมบูรณ์
หากธุรกรรมได้รับการอนุมัติ ธุรกิจจะทำการขายให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์โดยมอบสินค้าหรือบริการแก่ลูกค้า หากธุรกรรมถูกปฏิเสธ ธุรกิจอาจขอให้ลูกค้าชำระเงินด้วยวิธีการอื่น
7. การชําระค่าธุรกรรม
เมื่อสิ้นสุดแต่ละวัน ธุรกิจจะส่งชุดธุรกรรมที่ได้รับการอนุมัติจํานวนหนึ่งไปยังผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินหรือธนาคารผู้รับบัตรเพื่อ่ชำระค่าธุรกรรม ธนาคารผู้รับบัตรจะส่งคําขอเงินจากธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรผ่านเครือข่ายบัตร ธนาคารผู้ออกบัตรจะโอนเงินไปยังธนาคารผู้รับบัตร ซึ่งจากนั้นจะฝากเงินเข้าบัญชีของธุรกิจ ซึ่งปกติแล้วจะดําเนินการภายใน 2-3 วันทําการ
8. การกระทบยอดและการรายงาน
ธุรกิจจะกระทบยอดธุรกรรมที่ชําระแล้วกับบันทึกการขายและค่าธรรมเนียมธุรกรรมที่เรียกเก็บโดยผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน ธนาคารผู้รับบัตร หรือบุคคลอื่นที่เกี่ยวข้อง ทั้งธุรกิจและลูกค้าจะได้รับบันทึกรายการธุรกรรม เช่น ใบแจ้งหนี้ ใบเสร็จ รับเงิน หรือรายการเดินบัญชี
แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินสําหรับธุรกิจ
การนําแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินมาใช้จะช่วยยกระดับประสบการณ์ของลูกค้า ลดความเสี่ยงจากการฉ้อโกง และช่วยให้การดำเนินงานสอดคล้องกับระเบียบข้อบังคับและมาตรฐานของอุตสาหกรรม นอกจากนี้ การส่งเสริมแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดเหล่านี้ยังเป็นวิธีที่ดีในการปลูกฝังให้มีชุดขั้นตอนภายในเกี่ยวกับการชำระเงินที่มีแบบแผนอย่างดี ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ใช้ทรัพยากรอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพและลดข้อผิดพลาดได้
ต่อไปนี้คือแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินข้อสำคัญสําหรับธุรกิจ
สร้างสภาพแวดล้อมการชําระเงินที่ปลอดภัย
ใช้มาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด เช่น การเข้ารหัส การแปลงเป็นโทเค็น และใบรับรอง Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) เพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลการชําระเงินที่ละเอียดอ่อนระหว่างการส่งและจัดเก็บข้อมูล ปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดของ PCI DSS และมาตรฐานการรักษาความปลอดภัยอื่นๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้อง เพื่อให้เกิดสภาพแวดล้อมการชําระเงินที่ปลอดภัยเสนอทางเลือกการชําระเงินที่หลากหลาย
ตอบสนองความต้องการที่หลากหลายของลูกค้าและยกระดับประสบการณ์การซื้อของลูกค้าด้วยการมอบตัวเลือกการชําระเงินที่หลากหลาย เช่น บัตรเครดิตและบัตรเดบิต กระเป๋าเงินดิจิทัล และวิธีการชําระเงินทางเลือกใช้ผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่มีชื่อเสียง
เลือกผู้ประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่เชื่อถือได้และมีชื่อเสียงซึ่งมีโซลูชันการประมวลผลการชําระเงินแบบครบวงจร มีเครื่องมือป้องกันการฉ้อโกงขั้นสูง ค่าธรรมเนียมใกล้เคียงกับผู้ให้บริการรายอื่น และให้การสนับสนุนลูกค้าที่ยอดเยี่ยมอัปเดตซอฟต์แวร์และฮาร์ดแวร์เป็นประจํา
ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าซอฟต์แวร์ประมวลผลการชําระเงิน ฮาร์ดแวร์ และการผสานการทํางานของคุณเป็นปัจจุบันโดยลงแพตช์ความปลอดภัยและใช้เทคโนโลยีล่าสุด ซึ่งจะช่วยลดช่องโหว่และคงประสิทธิภาพและความปลอดภัยให้กับระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินของคุณฝึกอบรมพนักงาน
ให้ความรู้พนักงานเกี่ยวกับแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดในการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน ระเบียบการรักษาความปลอดภัย และมาตรการป้องกันการฉ้อโกง ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าพนักงานทราบนโยบายและขั้นตอนปฏิบัติในการประมวลผลการชําระเงินของบริษัทแล้ว และสามารถจดจําและรับมือกับภัยคุกคามด้านความปลอดภัยที่อาจเกิดขึ้นได้นําเครื่องมือป้องกันการฉ้อโกงไปใช้งาน
ใช้เครื่องมือป้องกันการฉ้อโกงขั้นสูง เช่น บริการยืนยันที่อยู่ (AVS) การตรวจสอบรหัสยืนยันบัตร (CVV) และการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์แบบ 3D Secure เพื่อลดความเสี่ยงการเกิดธุรกรรมที่เป็นการฉ้อโกงและการดึงเงินคืนตรวจสอบธุรกรรม
ติดตามตรวจสอบกิจกรรมการประมวลผลการชําระเงินของคุณเป็นประจํา เพื่อหารูปแบบที่ผิดปกติหรือสัญญาณการฉ้อโกง ตั้งค่าการแจ้งเตือนเพื่อรับข่าวสารเกี่ยวกับกิจกรรมที่น่าสงสัยแบบเรียลไทม์จัดให้มีนโยบายการคืนเงินและการดึงเงินคืนที่ชัดเจน
พัฒนาและสื่อสารนโยบายการคืนเงินและการดึงเงินคืนกับลูกค้าอย่างชัดเจน เพื่อลดการโต้แย้งการชําระเงินและความเข้าใจผิด ให้บริการลูกค้าที่ครอบคลุมเพื่อแก้ไขปัญหาทันที เพื่อลดความเสี่ยงที่จะถูกดึงเงินคืนเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการกระทบยอดและการรายงาน
นำขั้นตอนการกระทบยอดและการรายงานที่มีประสิทธิภาพมาใช้เพื่อให้การทําบัญชีมีความถูกต้อง มีการชําระเงินที่ตรงเวลา และคอยติดตามดูกิจกรรมการประมวลผลการชําระเงินของคุณอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพรับข่าวสารเกี่ยวกับแนวโน้มอุตสาหกรรมและระเบียบข้อบังคับ
การประมวลผลการชําระเงินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงอย่างต่อเนื่อง ติดตามความคืบหน้าเกี่ยวกับพัฒนาการล่าสุดด้านเทคโนโลยีการประมวลผลการชําระเงิน แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดในอุตสาหกรรม และการเปลี่ยนแปลงระเบียบข้อบังคับเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าธุรกิจของคุณปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดและแข่งขันได้อยู่เสมอ
ผู้ให้บริการประมวลผลการชําระเงินเช่น Stripe สามารถปฏิบัติตามแนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดเหล่านี้ได้อย่างต่อเนื่อง ทำให้ธุรกิจสามารถเข้าถึงระบบประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่มีประสิทธิภาพและใช้งานได้ดีโดยไม่ต้องมีภาระด้านทรัพยากร สําหรับข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมว่า Stripe สามารถตอบสนองความต้องการด้านการประมวลผลการชําระเงินที่ซับซ้อนของธุรกิจสมัยใหม่ได้อย่างไร โปรดเริ่มต้นที่นี่
เนื้อหาในบทความนี้มีไว้เพื่อให้ข้อมูลทั่วไปและมีจุดประสงค์เพื่อการศึกษาเท่านั้น ไม่ควรใช้เป็นคําแนะนําทางกฎหมายหรือภาษี Stripe ไม่รับประกันหรือรับประกันความถูกต้อง ความสมบูรณ์ ความไม่เพียงพอ หรือความเป็นปัจจุบันของข้อมูลในบทความ คุณควรขอคําแนะนําจากทนายความที่มีอํานาจหรือนักบัญชีที่ได้รับใบอนุญาตให้ประกอบกิจการในเขตอํานาจศาลเพื่อรับคําแนะนําที่ตรงกับสถานการณ์ของคุณ