PayPal has a huge presence in the global payment industry and has adapted to a variety of markets with its user-focused features and compatibility with ecommerce platforms. As a payment method, PayPal has transformed the way individuals and businesses transact across borders, allowing customers to pay in their local currencies and businesses to accept payments from a diverse customer base.
Despite the complexities of operating across multiple regions, PayPal continues to prioritize the customer experience. Its focus on customer interfaces, security, and trust has contributed to its widespread adoption. The company demonstrates its commitment to these principles in its customer support and fraud protection policies, which have become benchmarks for the industry.
PayPal has a considerable amount of influence worldwide, providing small businesses and entrepreneurs with access to international markets, and impacting trade and the flow of money across the globe. In this article, we’ll explain how PayPal works and how your business can use PayPal to accept payments.
What’s in this article?
- What is PayPal?
- How to accept payments on PayPal
- Requirements for businesses to start accepting PayPal
- PayPal costs and fees
- Business benefits of accepting PayPal
- PayPal security measures
- How PayPal works
- Where is PayPal used?
- Who uses PayPal?
- Alternatives to PayPal
What is PayPal?
PayPal is a digital payments platform that allows users to send and receive money online. It supports transactions for online shopping, personal or peer-to-peer transfers, and business payments.
For customers, PayPal acts as a digital wallet, enabling them to make online purchases without sharing credit card details with multiple businesses. Customers can link their bank accounts, credit cards, or debit cards to their PayPal account, allowing them to send and receive money or pay for goods and services with ease.
How to accept payments on PayPal
When someone sends money to an email address or mobile number linked to PayPal, the account owner will receive a notification letting them know the funds are available. To access the money, they will need to have a PayPal account and confirm their email address.
You can embed PayPal payment buttons and links on your business website or share them directly with customers. Once your business has received a payment, the funds will appear on the business’s PayPal account home page. From there, you can transfer the funds to a bank account or keep them as a balance in PayPal to make purchases or send money.
Most PayPal payments are instant, and users will receive the money in their accounts shortly after the sender completes the transaction. International payments typically appear in users’ PayPal accounts within minutes, though in some cases it may take a few hours depending on the payment method and currency.
Requirements for businesses to start accepting PayPal
1. Set up a PayPal Business account
To start using PayPal, a business must first set up a PayPal Business account, entering legal information such as the business name, business address, and personal details of the business owner. PayPal verifies these details to meet Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations and to ensure only verified businesses are using its services for authentic transactions.
2. Link a bank account
Next, businesses must link a bank account with the PayPal Business account to facilitate fund transfers. PayPal confirms the linked account by depositing small amounts and having the business verify these amounts to confirm the connection.
3. Accept the user agreement
To use PayPal, a business must agree to PayPal’s User Agreement and Acceptable Use Policy. These documents outline the permitted use cases of PayPal’s services as well as prohibited activities.
4. Submit tax information
Tax compliance is non-negotiable for businesses using PayPal. Businesses must submit their tax identification numbers (such as an Employer Identification Number, or EIN, in the US) to PayPal and align with local tax regulations.
5. Verify your email address
A functional email address is required for managing a PayPal account and for PayPal to communicate with the business. This email address must be verified before it can be used, a standard security step for digital payments.
6. Select your transaction currencies
Businesses need to determine the currencies in which they will transact and inform PayPal before processing payments through its platform.
7. Integrate mobile payment
Businesses opting for mobile transactions must integrate PayPal’s mobile payment solutions as well, ensuring system compatibility and a user-friendly experience for their customers.
PayPal costs and fees
For businesses
Transaction fees: Businesses using PayPal incur various transaction fees. These can include a fixed fee for each transaction processed, plus a fee set as a percentage of the transaction amount.
Chargeback and dispute fees: When customers file a dispute or a chargeback, businesses face additional fees. PayPal charges a fee to the business to cover the cost of processing the chargeback, and this amount varies by country.
International and currency conversion fees: For cross-border commercial transactions, PayPal charges a percentage of the transaction amount to compensate for the currency conversion process. There’s also a fixed fee that fluctuates based on the currencies involved and the country where the PayPal account is located.
Withdrawal and receiving fees: Receiving money in a PayPal account is typically free for domestic personal transactions, but it incurs a fee for commercial transactions and international transfers. There’s also a withdrawal fee if the business opts to instantly transfer funds from the PayPal account to a bank account rather than using the standard transfer function.
For customers and individuals
International fees: For individuals, sending money to friends and family within the same country is generally free if funded by a PayPal balance or a bank account linked to the PayPal account. Sending money internationally from a PayPal balance or bank account comes with a fee.
Currency conversion fees: When a transaction involves a currency conversion, PayPal increases the exchange rate, resulting in an additional cost to the customer. This fee is a percentage of the transaction amount and varies depending on the type of transaction.
Credit and debit card fees: Receiving credit or debit card payments incurs fees that PayPal charges to cover the costs imposed by card networks.
ATM withdrawal fees: For customers who use the PayPal debit card, withdrawing cash from an ATM incurs a flat fee per transaction.
Business benefits of accepting PayPal
There are many advantages to using PayPal for your business:
- Access to new markets and tech-focused customers
- Streamlined transactions
- Improved transaction speed and convenience for customers
- Increased customer satisfaction
- High security and compliance standards
- Simplified cross-border transactions
- Increased customer protections
- Enhanced customer trust and boosted brand credibility
- Expanded protections for businesses
- Upgraded customer support for both businesses and customers
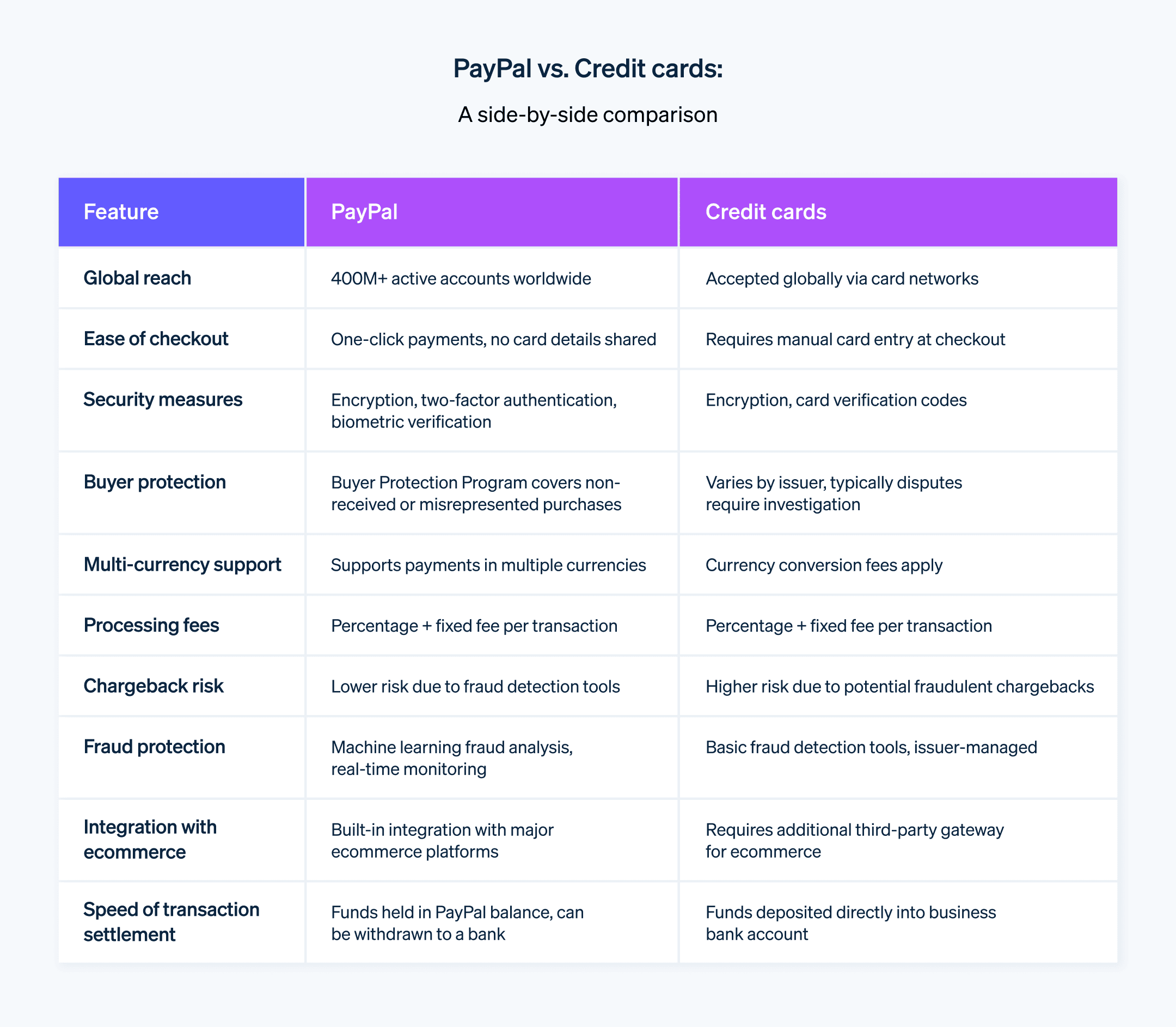
PayPal security measures
PayPal combines new technology, regulatory compliance, and user education to create a safe transaction environment for its users. Here are some of the security measures PayPal implements:
Applies encryption techniques: PayPal secures customer and transaction data in transit using strong encryption protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Uses advanced fraud protection: PayPal monitors transactions in real time for suspicious activity, powered by machine learning algorithms that analyze vast datasets to identify patterns indicative of fraud.
Maintains two-factor authentication: To enhance account security, PayPal supports two-factor authentication (2FA), which requires customers to provide two forms of identification before access is granted.
Conducts biometric verification: The PayPal mobile app can verify a customer’s identity via fingerprint and facial recognition, even if their password is compromised.
Upholds data security standards: PayPal complies with the PCI DSS to protect cardholder data, implementing stringent controls and conducting regular audits to ensure continued compliance.
Complies with security regulations: PayPal adheres to local regulations governing payment security. In Europe, for example, the platform conforms to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
How PayPal works
A diverse range of users worldwide use PayPal, including individual customers, businesses, enterprises, and nonprofits. Here’s how PayPal payments work:
Account setup and user verification
Users begin by creating a PayPal account and linking payment methods such as a bank account or credit card. PayPal verifies the user’s identity before processing payments, a regulatory requirement for added security. Users can receive money with either a personal or business PayPal account, as long as the email address or mobile number is confirmed.Transaction initiation
Buyers initiate payments by selecting PayPal as the payment method at checkout, either on a business’s website or through a peer-to-peer transfer. The buyer enters their PayPal credentials, and the platform then prompts them to select a preferred funding source, such as a bank account, credit card, or PayPal balance.Payment routing
After the funding source is confirmed, PayPal requests the funds from that source. If the source is a PayPal balance, the transaction completes almost instantaneously. For bank transfers or credit card payments, PayPal communicates with the relevant financial institutions through secure channels.Data security and privacy
Throughout the transaction process, PayPal employs advanced encryption standards to maintain data security and privacy. PayPal does not share full financial information with sellers, which reduces the chances of sensitive data being compromised.Fee structure
PayPal charges customers fees for certain transactions, including currency conversions and cross-border payments. It also charges fees to businesses, which are calculated as a percentage of the transaction amount plus a fixed amount.Risk management and fraud protection
PayPal monitors transactions for suspicious activity using proprietary risk models and algorithms. The platform’s fraud prevention measures include two-factor authentication, email confirmations for transactions, and real-time fraud analysis.Dispute resolution and buyer protection
PayPal provides a dispute resolution service, which allows buyers and sellers to file claims if there is an issue with a transaction. PayPal’s Buyer Protection policy offers refunds for purchases that don’t arrive or aren’t as described, reinforcing trust in its payment platform.Clearing and settlement
After a transaction is authorized and processed, PayPal settles the funds, deducting the money from the buyer’s account and crediting it to the seller’s PayPal balance. Sellers can then transfer their PayPal balance to their bank accounts or keep the funds in PayPal for future transactions.Mobile payments
With mobile payment solutions such as PayPal One Touch, customers can make payments on their mobile devices without entering login details for each transaction. This service relies on device authentication for added security.
Where is PayPal used?
PayPal’s customer base spans multiple continents. As of 2024, PayPal had 434 million active consumer and merchant accounts, processing $1.68 trillion in total payment volume across 26 billion transactions. This demonstrates its extensive reach and the trust it has built with customers and businesses.
North America
A substantial portion of PayPal’s revenue comes from its customers in the United States, with 57% of US adults using PayPal, according to a 2022 survey. PayPal is deeply embedded in the US ecommerce industry, providing a trusted and familiar method for digital transactions. The convenience of PayPal’s one-click payment appeals to the fast-paced shopping culture, and its buyer protection policies are a strong draw for customers wary of online fraud.Europe
The platform’s presence in Europe varies by region. Western European countries have high levels of PayPal usage, with PayPal used for online payments more often in Germany and Italy than in the United States in 2023. Eastern European countries are also increasingly adopting PayPal, coinciding with the rise of ecommerce in this region. The company’s compliance with the European Union’s financial regulations makes it a secure choice for cross-border transactions within Europe.Asia Pacific
PayPal usage in the Asia-Pacific region varies widely. In Australia and Japan, PayPal is favored for both domestic and international transactions. In India, the platform is primarily used for cross-border payments, capitalizing on the substantial market of freelancers and businesses with clients across the globe.Latin America
PayPal has become increasingly prevalent in Latin America’s growing online marketplace. In 2023, PayPal usage for point-of-sale payments in Mexico rose to a new high of 63%. PayPal has also partnered with local financial institutions to better align with the specific payment habits of Latin American customers.Middle East
In the Middle East, PayPal usage has increased in countries such as the United Arab Emirates, primarily for international online purchases. The region’s customers and businesses find PayPal’s multicurrency capabilities and security measures conducive to safe and straightforward international trade.
Who uses PayPal?
PayPal serves a wide range of industries and customers across the globe. The payment method’s versatility caters to the needs of small businesses, large corporations, and individuals.
Ecommerce businesses and online retailers: From emerging startups to established marketplaces, online businesses rely on PayPal payments for their reputation and ease of use.
Service providers and freelancers: With the rise of the gig economy, more than 100 million freelancers and service providers have become frequent users of PayPal. It provides a straightforward interface for invoicing and payment tracking, which is important for individuals managing their business finances.
Nonprofit organizations: PayPal’s donation buttons and nonprofit discounts make it a preferred payment solution for charities and foundations. The platform also has features for creating donation campaigns and provides simplified reporting for tracking and compliance.
Digital content creators: Content creators operating on platforms such as YouTube, Twitch, and Patreon frequently use PayPal to receive financial support from their communities. The platform’s ability to handle small, irregular payments makes it ideal for those who rely on the patronage of a dispersed audience.
Subscription-based businesses: Companies with subscription services—such as media streaming, software, or box-of-the-month clubs—often integrate PayPal for recurring payments. Customers can set up automatic payments to make managing their subscriptions easy.
Online shoppers: PayPal is widely popular among customers shopping on the internet. It enables secure transactions that don’t share card details with businesses, and its Buyer Protection Program provides a safety net for purchases made on many ecommerce websites.
Global workforce: As remote work becomes more common, overseas companies increasingly use PayPal to pay their remote employees. The platform’s ability to handle cross-border payments and convert currencies is particularly advantageous for this employee demographic.
Small businesses: Small businesses, including local sellers and artisans selling goods through online marketplaces, often accept PayPal payments using PayPal’s Seller Protection program.
Family and friends: Individuals extensively use PayPal’s personal transfer services for sending money to family and friends. Whether splitting a bill, sharing gifts, or aiding a loved one financially, PayPal’s ease of use makes it a top choice for personal transfers.
Alternatives to PayPal
While PayPal is a popular payment method, several competitors offer comparable services. Businesses choosing which methods to accept should consider convenience, transaction fees, and international capabilities.
Venmo: Owned by PayPal, Venmo has gained popularity as a digital wallet with person-to-person payment features. Increasingly, Venmo is also being adopted by businesses for customer transactions, particularly by the millennial demographic.
Google Pay: Google Pay combines web and in-app payments for Android users. Google Pay integrates with other Google services, creating a smooth payment experience within the Google environment.
Apple Pay: Designed for Apple users, Apple Pay enables transactions via iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch. The platform emphasizes security and privacy, and it uses biometric authentication to approve transactions.
Amazon Pay: Capitalizing on Amazon’s vast customer base, Amazon Pay allows customers to use their Amazon account details to make purchases on third-party websites. This simplifies the checkout process and can increase conversion rates.
Wise: Focused on international payments, Wise (formerly TransferWise) offers borderless payment accounts to easily and cost-effectively send money internationally. Wise is particularly advantageous for businesses that handle foreign currencies.
Learn more about how Stripe Payments can power your online and in-person payments, or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.