With help from a range of digital tools, systems, and platforms, businesses can now reach customers through online stores, mobile payment platforms, and social media. Payment transaction processing has adapted to fit the ever-changing needs of customers and their payment preferences.
As digital payment transactions continue to grow in number, businesses should understand how up-to-date payment processing systems can help them stay competitive. In this article, we’ll cover the key aspects of payment transaction processing, the parties and components involved, and helpful insights to guide businesses through the challenges of digital commerce.
What’s in this article?
- What is payment processing?
- Payment transaction processing: Key players and components
- How does payment transaction processing work?
- Why does payment transaction processing matter for businesses?
What is payment processing?
Payment processing is the manner in which buyers and sellers handle financial transactions. It consists of many steps and involves the authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions.
Payment transaction processing: Key players and components
Payment transaction processing is a complex system that involves multiple players and components that work together to facilitate the secure and efficient transfer of funds during financial transactions. Here’s an overview of the parties involved in payment transactions:
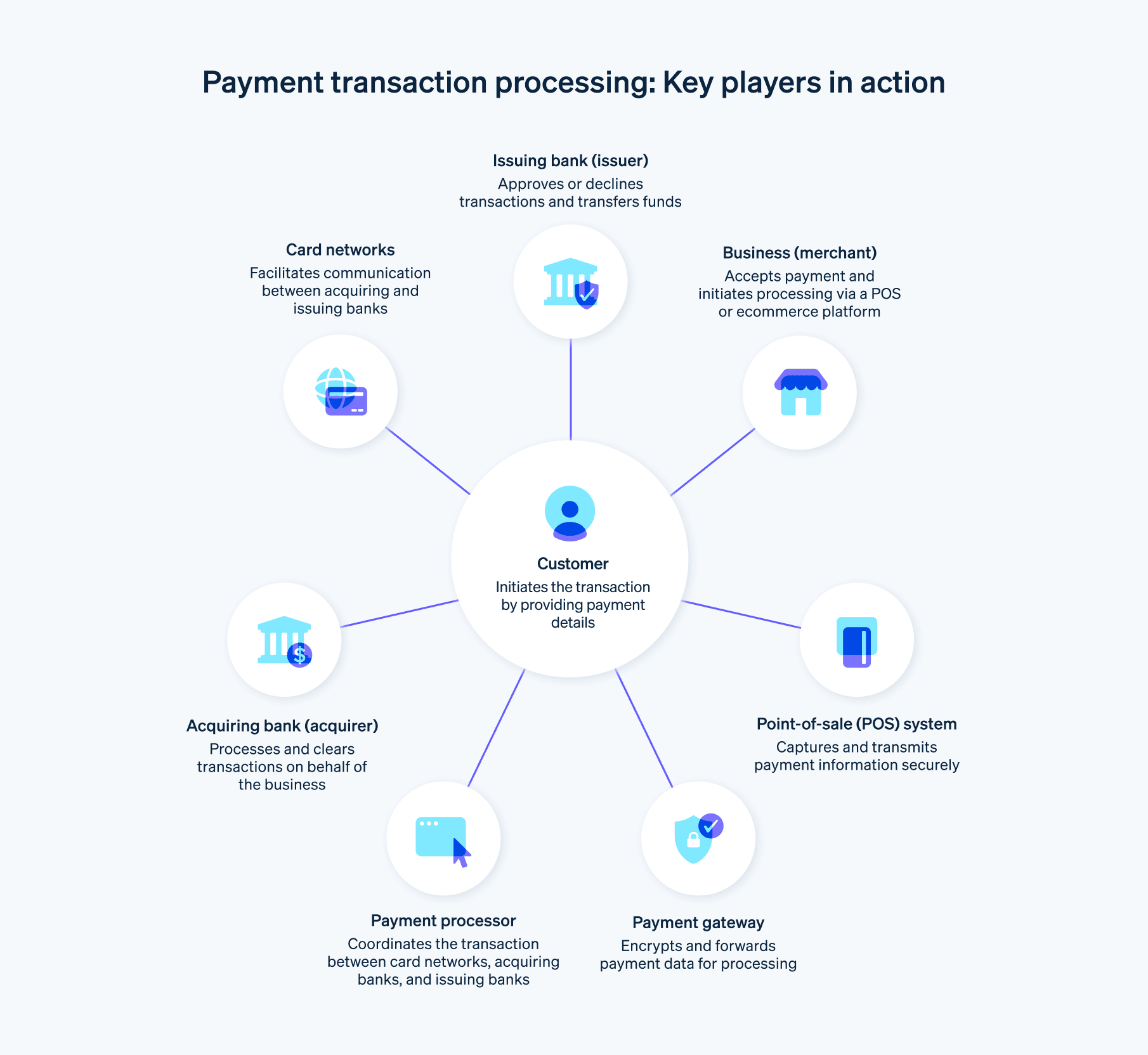
Cardholder
The cardholder is the individual or entity that initiates the payment by providing their payment information (credit card, debit card, or bank account details) for a purchase or service.Business
The business is the merchant or service provider that accepts payment from the customer in exchange for goods or services.Acquiring bank, or acquirer
The acquiring bank, or acquirer, is the financial institution that holds the merchant account and receives the transaction information from the payment processor. The acquiring bank is responsible for the authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions.Issuing bank, or issuer
The issuing bank, or issuer, is the financial institution that issued the credit or debit card to the customer. The issuing bank validates the customer’s available funds or credit and either approves or declines the transaction.Card networks
Card networks are organizations like Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover that establish the infrastructure and guidelines for processing credit card transactions. Card networks serve as a conduit between acquiring banks and issuing banks, ensuring smooth communication, authorization, and settlement of transactions.Payment gateway
A payment gateway is a tool that safely transfers payment data from the business’s point-of-sale (POS) system or ecommerce platform to the acquiring bank for processing. It encrypts the cardholder’s information and verifies that the transaction adheres to security standards.Payment processor
A payment processor, or payment processing provider, is a company that oversees the transaction process on behalf of the acquiring bank. A payment processor’s responsibilities include tasks such as communicating with payment networks, obtaining authorization, and managing the settlement process.Point-of-sale (POS) system
The point-of-sale system is the physical or digital interface where the customer’s payment information is captured and transmitted for processing. In physical stores, this may include card readers or mobile payment devices, while in online settings, this includes ecommerce platforms, mobile apps, or websites.
These parties work together to guarantee that credit card transactions are secure, efficient, and in compliance with regulations and industry standards, ensuring a seamless and swift payment experience for both customers and businesses.
How does payment transaction processing work?
Payment transaction processing is the series of steps that occur when a customer initiates a financial transaction with a business, typically for the purchase of goods or services. The process involves multiple entities and components that work together to securely and efficiently authorize and settle the transaction. The process may look different depending on factors such as:
- Payment environment (in-person, online, or mobile)
- Payment channel (website, mobile app, brick-and-mortar retail location, mobile retailer, in-home service provider, etc.)
- Payment method (credit or debit card, bank transfer, digital wallet, etc.)
Despite these differences, the general process is similar. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
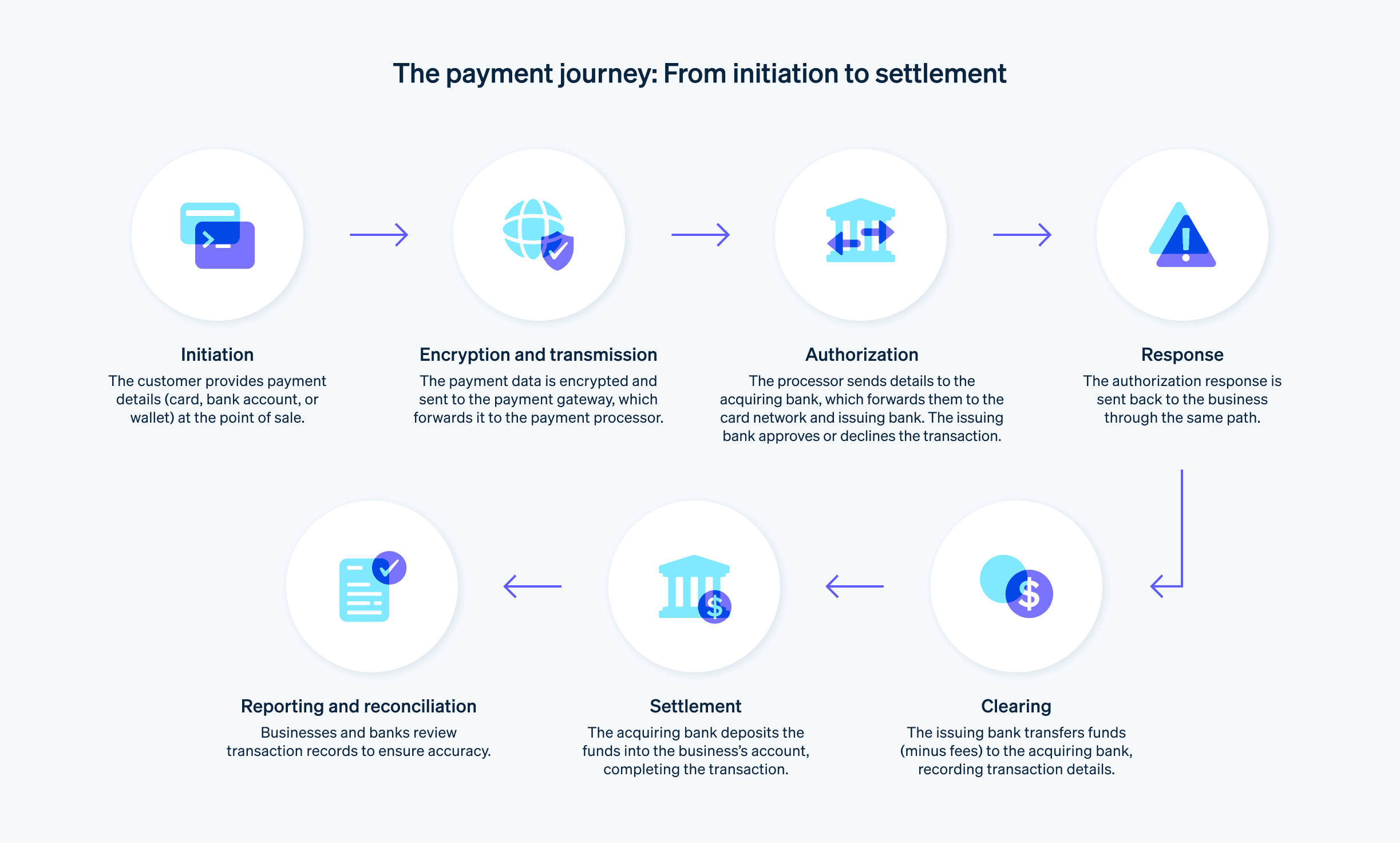
Initiation
The customer provides their payment details—like card number or bank account information—at the business’s POS, card reader, or ecommerce checkout.Encryption and transmission
The payment information is securely transmitted to a payment gateway, which encrypts the data and forwards it to the payment processor.Authorization
The payment processor sends the transaction details to the acquiring bank (the business’s bank), which forwards the information to the issuing bank (the customer’s bank) through the relevant card network. The issuing bank verifies the customer’s account and checks if they have sufficient funds or credit to complete the transaction. At this point, the issuing bank sends an approval or decline message back through the card networks and acquiring bank to the payment processor.Response
The payment processor relays the transaction’s approval or decline status to the business, which then informs the customer of the outcome. If the transaction is approved, the business may proceed with providing the goods or services. If the transaction is declined, the business will receive a decline code indicating why the transaction couldn’t be approved, and they notify the customer.Clearing
Once the transaction is authorized, the clearing process begins. The issuing bank transfers the transaction amount (minus any applicable fees) to the acquiring bank through the card networks. The details are recorded and reconciled among the parties involved.Settlement
During the settlement process, the acquiring bank deposits the funds into the business’s account. The business receives the payment, and the transaction is considered complete.Reporting and reconciliation
The business and financial institutions review and reconcile their transaction records, ensuring accuracy and addressing any discrepancies.
Why does payment transaction processing matter for businesses?
Payment transaction processing is important for businesses for several reasons:
Customer convenience
Payment processing plays a significant role in shaping the customer experience for businesses. When customers shop or use a service, they expect a smooth and hassle-free payment process. By offering efficient and user-friendly payment options and accepting a variety of electronic payment methods, businesses can make sure their customers have a positive experience, which in turn builds trust and loyalty.Expanded sales opportunities
Accepting electronic payments allows businesses to reach a broader customer base—including customers who prefer cashless transactions, online shoppers, and international customers—which can result in increased sales and revenue.Improved cash flow
Electronic payments are typically processed and settled faster than traditional methods, such as checks. This helps businesses maintain a healthy cash flow, which is important for covering operational expenses and supporting growth.Enhanced security
Payment transaction processing systems employ advanced security measures, such as encryption and fraud detection, to protect sensitive data and minimize the risk of unauthorized transactions.Simplified record-keeping
Electronic payment processing systems automatically generate transaction records, reducing the workload involved with tracking sales, managing inventory, and monitoring financial performance.Reduced human error
Automated payment processing minimizes the ever-present risk of human error associated with manual handling of cash or check transactions, ensuring greater accuracy in financial management.Regulatory compliance
Payment processors help businesses comply with industry regulations and standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which governs the handling of cardholder information.Scalability
As businesses grow, electronic payment processing systems can easily scale to accommodate higher transaction volumes, ensuring continued efficiency and reliability.
Payment transaction processing might seem like a straightforward technical consideration for businesses that need to accept payments from customers. But like many aspects of building and running a business, it’s far more complicated than it looks.
Working with an exceptional provider in this area is a smart way to cut through some of the complexity and set up a system of solutions that fits your needs and goals—and to uphold a competitive customer experience that’s highly secure, efficient, and compliant. To learn more about how Stripe approaches this challenge for businesses, get started here.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.