Dynamische valutaconversie (DCC) is een financiële dienst die wordt gebruikt bij internationale transacties, wanneer een klant uit het ene land een aankoop met een creditcard of debitcard doet in een ander land. Met DCC kan de transactie bij het verkooppunt worden verwerkt in de valuta van het thuisland van de kaarthouder. De wereldwijde markt voor creditcardbetalingen zal naar verwachting stijgen van $ 524,9 miljard dollar in 2022 naar $ 1,2 biljoen dollar in 2032. En internationale betalingen zijn een belangrijk onderdeel van die groei.
Hieronder leggen we uit wat ondernemingen moeten weten over dynamische valutaconversie: hoe het werkt, hoe het zich verhoudt tot traditionele valutaconversie en wat de voor- en nadelen zijn van het implementeren van dynamische valutaconversie.
Wat staat er in dit artikel?
- Hoe werkt dynamische valutaconversie?
- Dynamische valutaconversie versus traditionele valutaconversie
- Voordelen van dynamische valutaconversie voor ondernemingen
- Uitdagingen van dynamische valutaconversie
- Best practices voor dynamische valutaconversie
- Schakelt Stripe dynamische valutaconversie in?
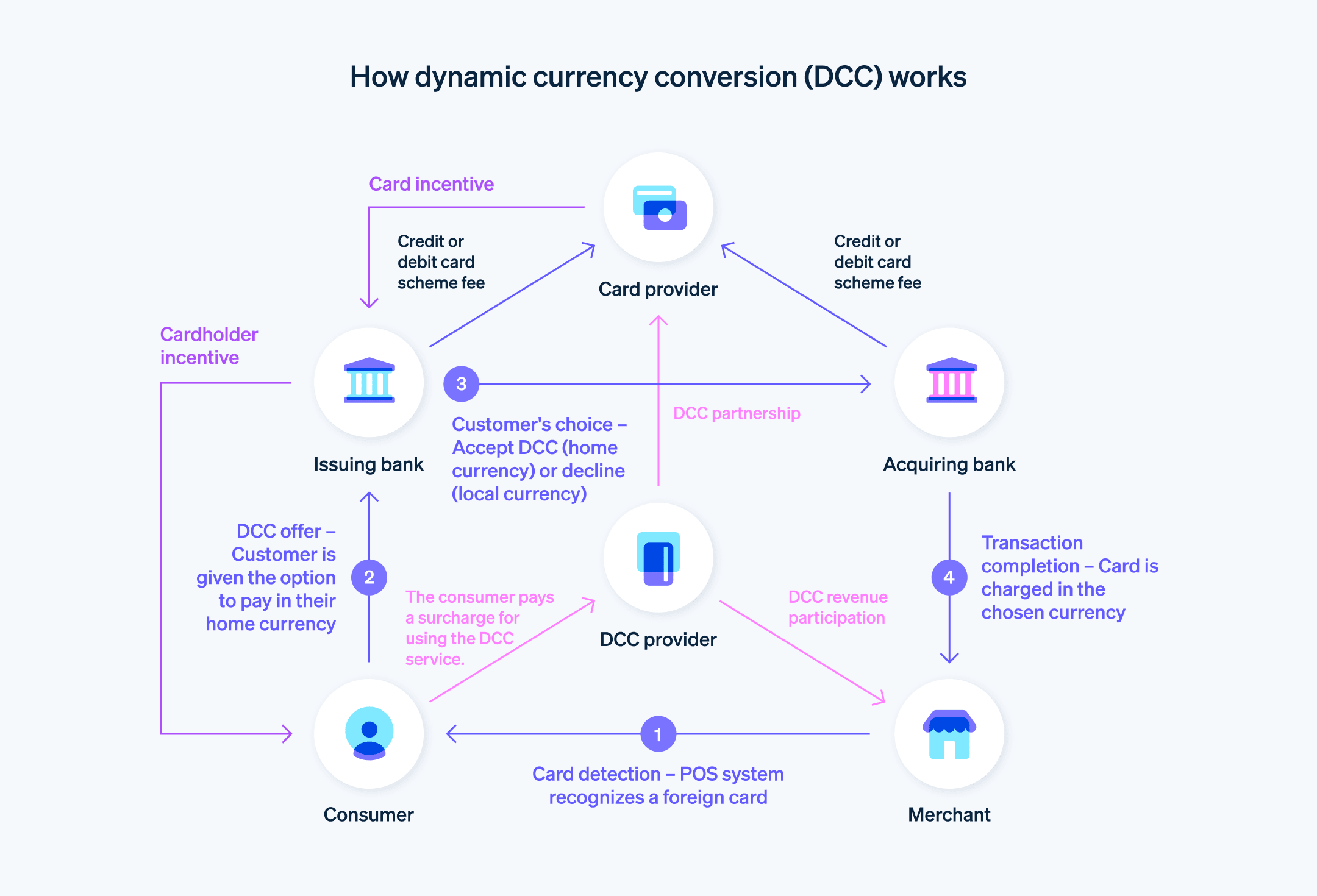
Hoe werkt dynamische valutaconversie?
DCC biedt kaarthouders een gemakkelijk en direct inzicht in de transactiekosten in hun eigen valuta, hoewel dit hogere kosten met zich mee kan brengen vanwege wisselkoerstoeslagen en -kosten. Voor ondernemingen en financiële instellingen biedt DCC een kans om extra inkomsten te verdienen. Zo werkt het:
Het DCC-proces
Kaartdetectie: Wanneer een klant een buitenlandse creditcard of debitcard gebruikt bij het POS-systeem (POS of een e-commerceplatform, identificeert het systeem het land van herkomst van de betaalkaart.
DCC-oplossingen: Het systeem van de onderneming, dat is uitgerust met DCC-technologie, biedt de kaarthouder automatisch de mogelijkheid om de transactie in de eigen valuta te voltooien. Het bedrag is inclusief het conversiepercentage en eventuele extra kosten die aan de conversie zijn verbonden.
Keuze van de klant: De kaarthouder kan het DCC-bod accepteren en in de eigen valuta betalen, of deze afwijzen en in de lokale valuta betalen.
De transactie voltooien: Als de klant DCC kiest, wordt de transactie verwerkt en wordt het bedrag van de betaalkaart afgeschreven in de eigen valuta van de kaarthouder tegen de weergegeven wisselkoers. Als de kaarthouder DCC weigert, wordt de transactie verwerkt in de lokale valuta en zal de bank van de kaarthouder deze converteren op basis van de wisselkoers van de bank.
Rollen en voordelen
Ondernemingen: Ondernemingen profiteren van DCC door extra geld te verdienen via commissies of kosten in verband met het valutaomwisselproces.
Financiële instellingen: Banken of financiële dienstverleners die DCC aanbieden, bepalen de wisselkoersen en vergoedingen. Deze tarieven bevatten vaak een toeslag op de standaardwisselkoers.
Technologische integratie
Betalingsverwerkingstechnologie: DCC-technologie maakt de automatische detectie van buitenlandse betaalkaarten en valutaconversie in real time mogelijk, waardoor DCC een eenvoudige optie is op POS-systemen en online.
POS-systemen en e-commerce-integratie: DCC is geïntegreerd in moderne POS-systemen en online betalingsgateways, zodat ondernemingen deze service kunnen aanbieden aan internationale klanten in de winkel en online.
Denk bijvoorbeeld aan een Amerikaanse toerist in Italië die een item wil kopen dat € 100 kost. Het POS-systeem herkent de creditcard als Amerikaans en biedt aan om $ 120 in rekening te brengen (inclusief de DCC-wisselkoers en kosten). De toerist kan ervoor kiezen om $ 120 te betalen, wetende wat de exacte kosten in diens valuta zijn, of om € 100 te betalen, waarbij de conversie aan zijn bank wordt overgelaten.
Dynamische valutaconversie versus traditionele valutaconversie
Dynamische valutaconversie en traditionele valutaconversie zijn twee verschillende methoden die worden gebruikt bij internationale kaarttransacties. Elke methode heeft haar eigen implicaties voor wisselkoersen, kosten, klantkeuze en de winst van de onderneming. Dit is hoe ze verschillen:
Verschillen in wisselkoersen en kosten
Dynamische valutaconversie
Wisselkoersen: De wisselkoersen in DCC bevatten vaak een toeslag op de dagelijkse bankwisselkoers. Deze toeslag is een combinatie van de kosten voor valutaconversie en een winstmarge voor de onderneming of de DCC-aanbieder.
Kosten: DCC-transacties brengen doorgaans extra kosten met zich mee, die worden gebundeld in de wisselkoers die aan de klant wordt aangeboden. Deze kosten kunnen variëren, afhankelijk van de onderneming en de DCC-serviceprovider.
Traditionele valutaconversie
Wisselkoersen: Bij traditionele valutaconversie wordt de wisselkoers bepaald door de bank van de klant of kaartverstrekker nadat de transactie is verwerkt. Deze koers ligt meestal dichter bij de interbancaire wisselkoers, die meestal gunstiger is voor de klant.
Kosten: Bij traditionele conversies zijn mogelijk buitenlandse transactiekosten in rekening gebracht en worden de bankkosten van de klant in rekening gebracht. Deze kosten zijn meestal een percentage van het transactiebedrag en staan los van de wisselkoers.
Impact op de keuze en ervaring van klanten
Dynamische valutaconversie
Onmiddellijke duidelijkheid: DCC biedt direct duidelijkheid over hoeveel een transactie gaat kosten in de eigen valuta van de kaarthouder. Dit kan met name aantrekkelijk zijn voor diegenen die liever vooraf de exacte kosten weten zonder zich zorgen te hoeven maken over toekomstige wisselkoersschommelingen.
Potentieel voor hogere kosten: Vanwege de hogere wisselkoersen en gebundelde kosten kunnen klanten uiteindelijk meer betalen dan bij traditionele valutaconversie. Uit een onderzoek van de Europese consumentenorganisatie uit 2017 bleek dat klanten die DCC gebruiken in Europa tussen de 2,6% en 12% meer betaalden.
Traditionele valutaconversie
Potentiële besparingen: Klanten kunnen geld besparen vanwege gunstigere wisselkoersen en de mogelijkheid van lagere totale kosten.
Onzekerheid in kosten: De exacte kosten in de eigen valuta zijn onbekend op het verkooppunt en zijn afhankelijk van toekomstige wisselkoersschommelingen en bankkosten.
Voor- en nadelen voor ondernemingen
Voordelen van DCC voor ondernemingen
Extra inkomsten: Ondernemingen verdienen commissies of kosten uit DCC-transacties, wat zorgt voor een extra inkomstenstroom.
Gemak voor de klant: De optie om DCC te gebruiken kan de winkelervaring van klanten verbeteren door ze meer betaalopties en duidelijkheid te bieden over prijzen in hun eigen valuta.
Nadelen van DCC voor ondernemingen
Implementatie en naleving: Het gebruik van DCC vereist integratie met betaalsystemen en naleving van verschillende internationale regels, wat complex en kostbaar kan zijn voor ondernemingen.
Perceptie van de klant: Sommige klanten kunnen DCC ongunstig beoordelen als ze het gevoel hebben dat er een te hoog bedrag in rekening wordt gebracht vanwege hogere wisselkoersen en kosten.
Voor- en nadelen van traditionele valutaconversie
Eenvoud: Voor ondernemingen is traditionele conversie eenvoudiger te beheren omdat er geen integratie van DCC-systemen nodig is.
Minder omzetkansen: In tegenstelling tot DCC levert traditionele conversie geen extra inkomsten uit valutawisselkosten op.
DCC biedt onmiddellijke prijstransparantie in de thuisvaluta van de klant, maar vaak tegen hogere kosten vanwege wisselkoerstoeslagen en gebundelde kosten. Traditionele conversie is misschien kosteneffectiever voor de klant, maar het mist de duidelijkheid van de prijsstelling vooraf van DCC. DCC biedt een extra inkomstenstroom voor ondernemingen en kan handiger zijn voor klanten, maar het brengt ook complexiteit bij de implementatie en mogelijke terughoudendheid van klanten met zich mee vanwege de waargenomen hoge kosten.
Voordelen van dynamische valutaconversie voor ondernemingen
DCC biedt veel voordelen voor ondernemingen die te maken hebben met internationale shoppers, waaronder meer klantgemak en extra inkomsten. Hier gaan we wat dieper op in:
Gemak voor internationale klanten
Gemak van transacties: DCC vereenvoudigt het aankoopproces voor internationale klanten door ze prijzen te laten zien en te laten betalen in hun eigen valuta. Dit elimineert de noodzaak van mentale valutaconversie en zorgt voor een meer intuïtieve winkelervaring.
Vertrouwdheid en comfort: Betalen in een bekende valuta kan geruststellend zijn voor klanten, vooral in een internationale omgeving waar verschillende valuta's een aankoop kunnen bemoeilijken.
Direct inzicht in de kosten: DCC biedt klanten de exacte kosten in hun eigen valuta op het verkooppunt, waardoor onzekerheden in verband met fluctuerende wisselkoersen of onbekende kosten die de bank van de klant in rekening brengt, worden geëlimineerd.
Transparantie in wisselkoersen
Informatie over de wisselkoers vooraf: Bij DCC wordt de wisselkoers op het moment van de transactie aan de klant gepresenteerd, waardoor duidelijk is welke koers wordt gebruikt voor de valutaconversie.
Onderbouwde beslissingen: Door vooraf over deze informatie te beschikken, kunnen klanten weloverwogen beslissingen nemen over de keuze voor DCC of het standaardconversieproces via hun bank.
Vermijden van verborgen kosten: Hoewel DCC-tarieven een toeslag kunnen bevatten, is de algemene structuur van de transactie transparant, zodat klanten verborgen kosten kunnen vermijden die soms voorkomen bij bankconversies.
Potentiële beloningen en voordelen voor ondernemingen
Extra inkomstenstroom: Ondernemingen kunnen extra inkomsten genereren uit DCC-transacties, uit een deel van de conversiekosten of uit het toevoegen van toeslagen aan de wisselkoers.
Betere klantenservice: DCC kan worden gezien als een service met toegevoegde waarde, die de algehele klantervaring verbetert. Dit kan met name gunstig zijn in sectoren waar internationale transacties gebruikelijk zijn, zoals toerisme, horeca en e-commerce.
Concurrentievoordeel: Door DCC aan te bieden, kunnen ondernemingen zich onderscheiden van concurrenten die deze service niet aanbieden, waardoor ze mogelijk meer internationale klanten aantrekken.
Vereenvoudigde boekhouding: Voor ondernemingen wordt het verwerken van transacties in hun eigen valuta vereenvoudigd door de boekhouding en financiële verslaglegging, omdat het niet meer nodig is om buitenlandse verkopen om te zetten in lokale valuta.
Uitdagingen van dynamische valutaconversie
Dynamische valutaconversie biedt verschillende voordelen, maar brengt ook uitdagingen met zich mee voor klanten en ondernemingen. Ondernemingen die DCC overwegen, moeten zich bewust zijn van deze uitdagingen:
Hogere kosten voor klanten
Ongunstige wisselkoersen: DCC gaat vaak gepaard met wisselkoersen die minder gunstig zijn in vergelijking met standaard bankkoersen. Deze toeslag kan leiden tot hogere kosten voor klanten, waardoor aankopen duurder zijn dan ze zouden zijn als ze in de lokale valuta zouden worden verwerkt.
Gebrek aan bewustzijn: Klanten zijn zich mogelijk niet volledig bewust van de extra kosten die DCC met zich meebrengt. Ze kunnen deze optie gebruiken zonder te begrijpen dat deze duurder kan zijn dan hun bank de valutaconversie te laten afhandelen.
Zorgen over transparantie en toestemming
Ontoereikende openbaarmaking: Er zijn gevallen waarin de voorwaarden van DCC (inclusief de wisselkoers en kosten) niet duidelijk aan de klant worden gecommuniceerd, wat leidt tot verwarring en mogelijke ontevredenheid.
Problemen met toestemming: In zeldzame gevallen worden klanten automatisch aangemeld voor DCC zonder uitdrukkelijke toestemming, wat als onethisch wordt beschouwd. Klanten van wie de transacties met DCC worden verwerkt, hadden zelf moeten kiezen boven traditionele conversie.
Wettelijke en compliancevereisten
Complexe regelgeving: Ondernemingen die DCC aanbieden, moeten complexe internationale financiële voorschriften doorlopen en naleven, die veel middelen kunnen vergen.
Constant toezicht: Wisselkoersen fluctueren voortdurend, waardoor ondernemingen concurrerend en eerlijk moeten blijven om de DCC-tarieven voortdurend te monitoren en aan te passen.
Impact op de perceptie van de klant
Negatieve klantervaring: Als klanten het gevoel hebben dat ze zijn misleid of te veel hebben betaald vanwege DCC, kan dit leiden tot een negatieve perceptie van de onderneming, wat van invloed is op de klantloyaliteit en de merkreputatie.
Trainingsvereisten: Ondernemingen die DCC gebruiken, moeten personeel en klanten opleiden. Misverstanden of verkeerde informatie kunnen leiden tot een slechte klantervaring.
Technische en operationele uitdagingen
Integratie met POS-systemen: Het implementeren van DCC vereist integratie met POS-systemen, wat uitdagend en kostbaar kan zijn.
Valutabeheer: Ondernemingen moeten meerdere valuta's efficiënt beheren, wat de boekhoudpraktijken en het financiële beheer kan bemoeilijken.
Variabiliteit van de markt
- Afhankelijkheid van toerisme en internationale handel: Ondernemingen die sterk afhankelijk zijn van DCC, kunnen voor uitdagingen komen te staan tijdens perioden van minder internationale reizen of handelsschommelingen.
Best practices voor dynamische valutaconversie
Begrip en compliance
Naleving van de regelgeving: Je onderneming moet voldoen aan alle relevante lokale en internationale regelgeving met betrekking tot valutaconversie en financiële transacties.
Training: Het personeel moet goed op de hoogte zijn van DCC, inclusief hoe het werkt en de voordelen en implicaties ervan voor de onderneming en de klanten.
Transparante communicatie met de klant
Onderbouwde beslissingen: Bied klanten altijd de keuze tussen betalen in hun eigen valuta of de lokale valuta. Voorkom dat je zonder toestemming standaard gebruikmaakt van DCC.
Duidelijke uitleg: Geef een beknopte en duidelijke uitleg van wat DCC is en hoe het de transactie beïnvloedt.
Tarieven weergeven: Toon vooraf de wisselkoersen en eventuele bijbehorende kosten.
Concurrerende en eerlijke prijzen
Eerlijke wisselkoersen: Gebruik concurrerende wisselkoersen. Te hoge kosten kunnen leiden tot ontevredenheid bij de klant en je reputatie schaden.
Kostenstructuur: Houd de tariefstructuur redelijk en concurrerend. Buitensporige kosten kunnen klanten afschrikken.
Technologie en integratie
Vlotte integratie: Zorg dat DCC geïntegreerd is in je betaalsystemen zonder vertragingen of complicaties in het transactieproces te veroorzaken.
Beveiliging: Implementeer beveiligingsmaatregelen om transactiegegevens te beschermen en te voldoen aan standaarden zoals de Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Monitoring en analyse
Transactiebewaking: Controleer DCC-transacties regelmatig op ongebruikelijke activiteiten of patronen die op fouten of fraude kunnen duiden.
Analyse van de prestaties: Analyseer de prestaties van DCC in je onderneming. Kijk naar de acceptatie door klanten, de gegenereerde inkomsten en eventuele feedback van klanten.
Klantenondersteuning en feedback
Ondersteuningskanalen: Bied eenvoudig toegankelijke klantenondersteuning voor vragen over valutaconversie.
Feedbackmechanisme: Zorg voor een systeem om feedback van klanten te verzamelen en analyseren, specifiek over de ervaringen van klanten met DCC.
Marketing en promotie
Gerichte marketing: Overweeg gerichte marketing die de voordelen van DCC voor specifieke regio's promoot.
Promotionele aanbiedingen: Gebruik DCC als een mogelijkheid voor promotionele aanbiedingen, zoals gereduceerde kosten voor nieuwe gebruikers of tijdens bepaalde periodes.
Voortdurende verbetering
Blijf op de hoogte: Houd rekening met veranderingen in valutamarkten, technologie en regelgeving.
Aanpassing en evolutie: Wees voorbereid om je DCC-praktijken aan te passen op basis van nieuwe technologieën, klantvoorkeuren en markttrends.
Partnerschappen
De juiste partner kiezen: Als je een dienst van derden gebruikt voor DCC, kies dan een gerenommeerde aanbieder met een staat van dienst op het gebied van transparante en eerlijke praktijken.
Onderhandelen over de voorwaarden: Onderhandel samen met je leverancier over voorwaarden die gunstig zijn voor je onderneming en eerlijk voor je klanten.
Schakelt Stripe dynamische valutaconversie in?
Stripe biedt geen dynamische valutaconversie, maar wel een functie voor automatische valutaconversie, op maat gemaakt voor ondernemingen die actief zijn in de VS, Canada, Groot-Brittannië en de eurozone. Met deze functie kunnen ondernemingen prijzen in de lokale valuta van de klant weergeven op basis van de meest recente wisselkoersen van Stripe. Zo werkt het:
Valutaconversie voor meer dan 40 landen: De functie converteert prijzen naar de lokale valuta van een klant voor meer dan 40 landen. Hierdoor kunnen ondernemingen prijzen weergeven in de lokale valuta van de klant, wat de klantervaring verbetert en waarmee ze mogelijk betaalmethoden kunnen toevoegen die lokale valuta vereisen.
Keuze van valuta voor klanten: Klanten hebben de mogelijkheid om prijzen te bekijken in hun lokale valuta of in de oorspronkelijke valuta die door de onderneming is ingesteld. Deze flexibiliteit komt tegemoet aan de uiteenlopende voorkeuren van internationale klanten, zodat ze de meest geschikte optie kunnen kiezen.
Kosten en wisselkoersen: Stripe past de gemiddelde wisselkoers toe en neemt een marge op om deze koers te garanderen voor de duur van de Checkout-sessie door middel van verrekening. De standaardtransactiekosten voor automatische valutaconversie zijn inclusief:
- Kosten voor betaalkaarten of betaalmethoden
- Kosten voor internationale betaalkaarten of betaalmethoden, indien van toepassing
- Kosten voor valutaconversie
- Kosten voor betaalkaarten of betaalmethoden
Gegarandeerde wisselkoers: De wisselkoers is gegarandeerd vanaf het begin van de Checkout- of Payment Links-sessie tot en met de verrekening, op voorwaarde dat de wisselkoers niet meer dan 2% verandert. Als er een aanzienlijke wijziging is boven deze drempel, kan Stripe de meest recente wisselkoers toepassen bij de afwikkeling van de transactie. Deze garantie zorgt voor stabiliteit in de prijsstelling voor ondernemingen en hun klanten.
Afhandeling van terugbetalingen en chargebacks: Terugbetalingen of chargebacks worden gedaan in de valuta die de klant heeft gebruikt voor de betaling. Het automatisch omrekenen van valuta garandeert echter niet dezelfde wisselkoers voor terugbetalingen of chargebacks. De wisselkoers van Stripe die wordt verstrekt op het moment van de terugbetaling of chargeback wordt toegepast, wat kan leiden tot winst of verlies voor de onderneming, afhankelijk van wisselkoersschommelingen.
De functie voor automatische valutaconversie van Stripe biedt een flexibele oplossing voor ondernemingen die internationale klanten willen bedienen. Het vereenvoudigt het valutaconversiesproces, biedt transparantie in prijzen en bevat waarborgen zoals gegarandeerde wisselkoersen. Maar het kan extra kosten met zich meebrengen: ondernemingen moeten zorgvuldig omgaan met terugbetalingen en chargebacks. Lees meer over Stripe Adaptive Pricing.
De inhoud van dit artikel is uitsluitend bedoeld voor algemene informatieve en educatieve doeleinden en mag niet worden opgevat als juridisch of fiscaal advies. Stripe verklaart of garandeert niet dat de informatie in dit artikel nauwkeurig, volledig, adequaat of actueel is. Voor aanbevelingen voor jouw specifieke situatie moet je het advies inwinnen van een bekwame, in je rechtsgebied bevoegde advocaat of accountant.