In order for businesses to offer their increasingly digital-first customers simple and secure transactions, they have to examine the distinctions and interplay between payment processors and payment gateways.
Understanding how these components work together is a key part of delivering smooth and reliable payment experiences. Below, we’ll cover the main differences between payment processors and payment gateways, their respective roles, how they work together, and how Stripe approaches their functions in a unified, comprehensive way for platforms and businesses.
What’s in this article?
- What is a payment processor?
- What is a payment gateway?
- What are the differences between payment processors and payment gateways?
- How do payment processors and payment gateways work together?
- How Stripe handles payment processing and payment gateways
What is a payment processor?
A payment processor is a company or service that facilitates electronic transactions between customers and businesses by processing and authorizing credit card, debit card, and other digital payment methods. A payment processor acts as an intermediary between the customer’s bank (issuing bank, or issuer) and the business’s bank (acquiring bank, or acquirer), ensuring that funds move securely from the customer’s account to the merchant account.
Payment processors play an important role in ecommerce and retail by verifying the customer’s payment details, checking for fraud, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations, and, ultimately, authorizing or declining the transaction. Typically, they charge the business a fee for their services, which may include a per-transaction fee or a percentage of the transaction amount.
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is a technology or service that securely transmits payment information between the customer, the business, and the payment processor. It acts as a bridge between the parties involved in a transaction, enabling the exchange of information required for processing payments. A payment gateway is the digital equivalent of a point-of-sale (POS) terminal found in physical retail stores.
Using a payment gateway ensures that sensitive payment information is handled securely, as payment gateways adhere to strict security standards and encryption protocols such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
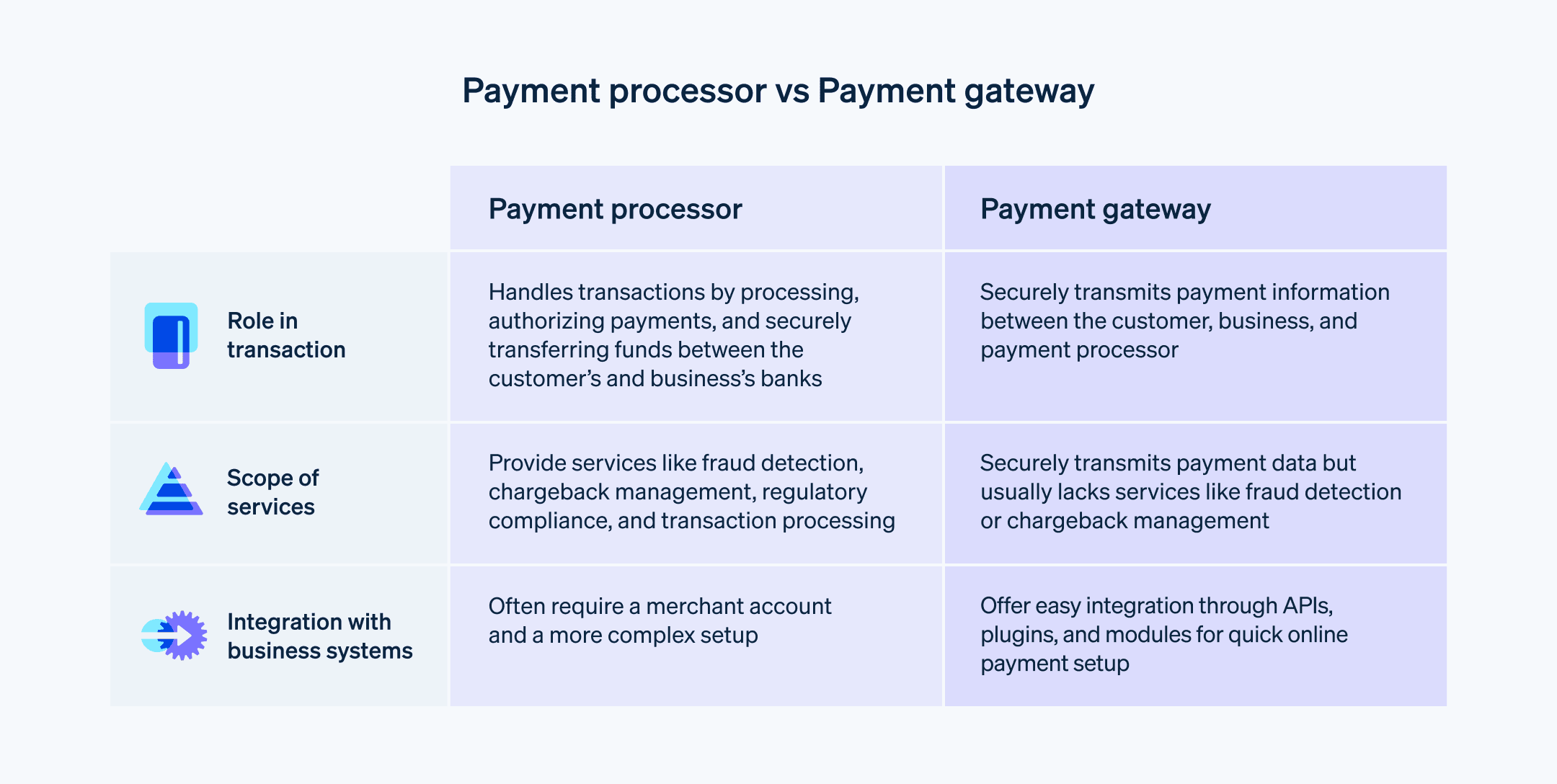
What are the differences between payment processors and payment gateways?
Both payment processors and payment gateways are important components of the electronic payment ecosystem, but they serve different functions. Here are the key differences between them:
Role in the transaction process
Payment processor: A payment processor is responsible for facilitating the transaction by processing and authorizing payments, as well as ensuring the secure transfer of funds between the customer’s bank and the business’s bank.
Payment gateway: A payment gateway is the connective component responsible for facilitating communication and securely transmitting payment information between the customer, the business, and the payment processor.
Scope of services
Payment processor: Payment processors offer a broad range of services, including fraud detection, chargeback management, and compliance with payment regulations, in addition to processing transactions.
Payment gateway: Payment gateways focus primarily on the secure transmission of payment data and typically do not provide additional services like fraud detection or chargeback management.
Integration with business systems
Payment processor: Payment processors usually require businesses to establish a merchant account to process transactions and may involve more complex setup procedures.
Payment gateway: Payment gateways often provide easier integration options for businesses, including APIs, plugins, and prebuilt modules, allowing businesses to start accepting online payments quickly.
Some companies offer both payment processing and payment gateway services as part of an integrated solution. For example, Stripe provides end-to-end payments services for businesses, making it easier for businesses to manage their online transactions. Further below, we’ll go into more detail about how Stripe handles these aspects of payment functionality.
How do payment processors and payment gateways work together?
Payment processors and payment gateways play different but complementary roles in facilitating secure and efficient electronic transactions for businesses and customers. Together, they enable frictionless communication and data transfer between parties.
Here’s a step-by-step overview of how payment processors and payment gateways collaborate during an online transaction:
Customer initiates the transaction
When a customer is ready to make a purchase, they enter their credit card information (or other payment information) on the business’s website or app.Payment gateway’s role
The payment gateway securely encrypts the customer’s payment data and sends it to the payment processor.Payment processor’s role
The payment processor receives the encrypted payment data from the payment gateway and forwards it to the customer’s bank (the issuing bank) to request authorization for the transaction.Issuing bank’s response
The customer’s bank verifies the payment details, checks for available funds, and either approves or declines the transaction based on its assessment. The issuing bank sends this response to the payment processor.Processor to gateway communication
The payment processor shares the bank’s response (approval or denial of the transaction) with the payment gateway.Gateway to business communication
The payment gateway relays the response to the business’s website or app, which displays the appropriate message to the customer (transaction approved or declined).Settlement of funds
If the transaction is approved, the payment processor coordinates the transfer of funds from the customer’s bank account to the business’s bank account. This process, called settlement, typically takes a few business days to complete.
Throughout this process, the payment gateway and payment processor work together to handle sensitive payment information securely and efficiently, while adhering to industry standards and encryption protocols such as PCI DSS.
How Stripe handles payment processing and payment gateways
Stripe is an all-in-one payment services provider that offers businesses and platforms combined payment processing and payment gateway functionality. By integrating both components into a single, streamlined platform, Stripe eliminates the need for businesses to find and acquire these services separately. This approach generates numerous benefits for businesses, including:
Simplified setup
With Stripe, businesses can set up and start accepting payments quickly, without the need to establish separate relationships with payment gateways and processors. This reduces the complexity of getting started with online transactions.Seamless integration
Stripe offers well-documented APIs, plugins, and prebuilt modules, making it easy for businesses to integrate Stripe’s payment solution into their websites, apps, and ecommerce platforms. This enables businesses to focus on their core business operations rather than spend time dealing with the technical aspects of payment processing.Enhanced security
Stripe adheres to the highest security standards, including PCI DSS compliance, and uses advanced encryption techniques to protect sensitive payment data. By consolidating the payment gateway and processor functions, Stripe ensures a consistent level of security across the entire transaction process.Unified reporting and management
With Stripe’s integrated solution, businesses can access and manage all transaction data, customer information, and payment analytics from a single Dashboard. This simplifies the tracking and reconciliation of transactions, making it easier for businesses to monitor their performance and make data-driven decisions.Reduced costs
Since Stripe combines payment gateway and processor services, it’s possible for businesses to save on fees by working with a single provider. Stripe offers transparent and competitive pricing, which can be more cost-effective for businesses when compared to the expenses of managing separate relationships with gateways and processors.Scalability and flexibility
Stripe supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies, enabling businesses to easily expand their operations globally. The platform is designed to scale with businesses as they grow and ensure that their payments infrastructure can handle increased transaction volumes and complexity.Continuous improvements
The Stripe platform benefits from regular updates that include new features, enhancements, and additional payment options. This ensures that businesses using Stripe can stay ahead of industry trends and offer their customers the best possible payment experience.
To learn more about payment processing with Stripe and to get started, go here.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.