Bulk Electronic Clearing System (BECS) Direct Debit is a popular Australian bank transfer system for recurring payments. It allows businesses to automatically collect authorized payments directly from customers’ bank accounts, a method known as direct entry.
Since its inception in 1989, BECS has become a go-to method for managing regular bills, subscriptions, and memberships. The system is an important part of the economy in Australia, where direct entry carries an average value of $15 trillion Australian dollars (AUD) each year—the majority of customer payments in the country, based on value.
Below, we’ll discuss what businesses need to understand about BECS Direct Debit, including how it works, which customer segments use it and why, and what’s required to start using this system as a payment method.
What’s in this article?
- How does BECS Direct Debit work?
- How to accept BECS Direct Debit as a payment method
- Benefits of accepting BECS Direct Debit
- What’s driving BECS Direct Debit adoption in Australia?
- Who uses BECS Direct Debit?
- How Stripe Payments can help
How does BECS Direct Debit work?
BECS Direct Debit simplifies the payment process for businesses and customers. Here’s how it works.
For customers
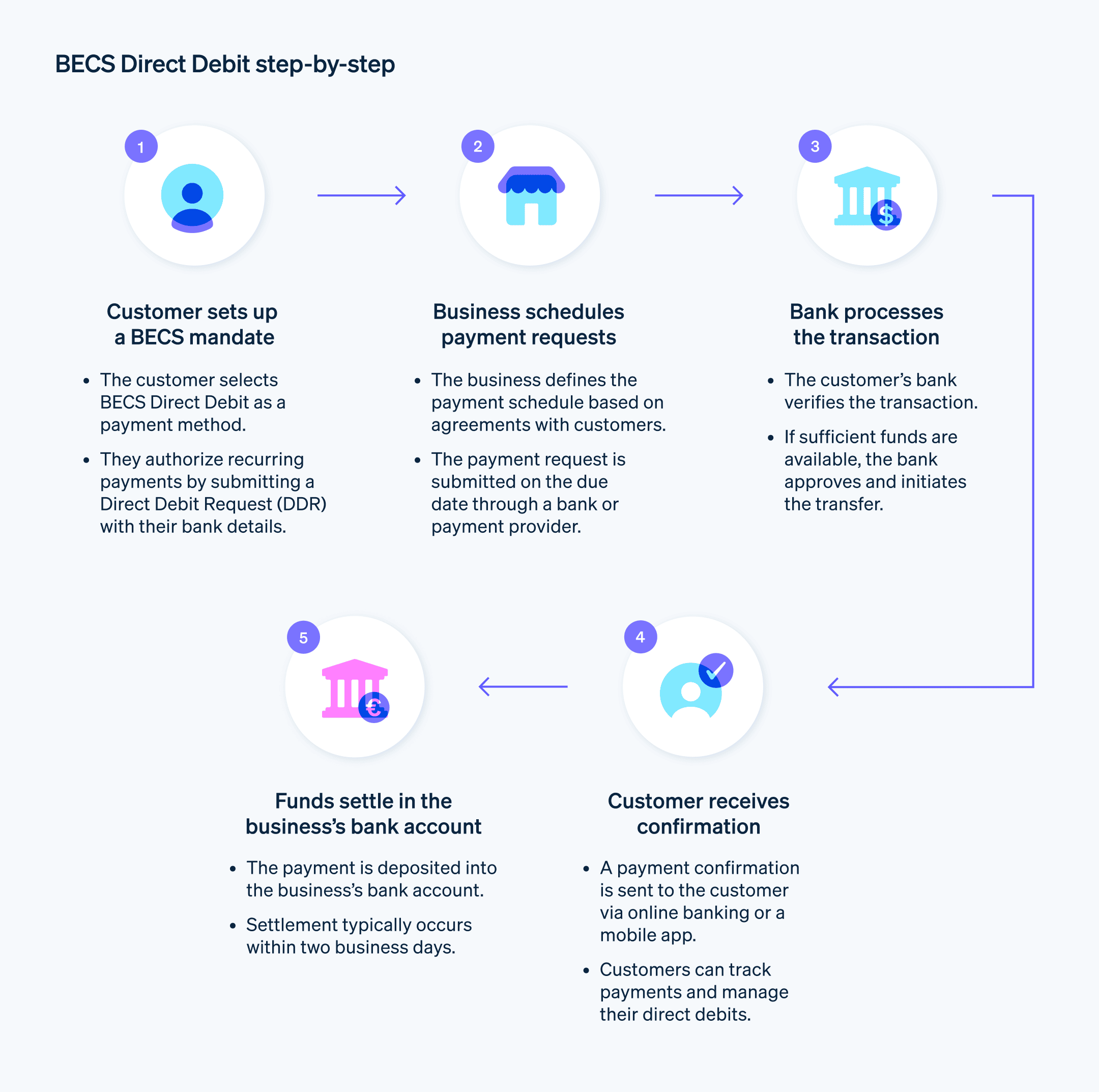
- Mandate setup: The customer chooses BECS Direct Debit as their preferred payment method at a business’s checkout or through a separate agreement. They provide their bank with a Direct Debit Request (DDR), which includes their bank account details and authorizes the business to debit specific amounts at predetermined intervals.
- Payment processing: If everything is in order, the funds move from the customer’s account to the business’s account. The customer receives a notification, usually through the online banking portal or a mobile app, that the payment has been made.
- Mandate management: The customer has complete control over their BECS mandate. They can choose to cancel it to stop future payments altogether. They can also initiate a dispute about unauthorized or incorrect transactions with their bank or the business.
For businesses
BECS setup: The business integrates BECS into its payment system by partnering with a bank or a payments service provider. The company defines the payment schedule and amount for each customer based on their agreement.
Direct Debit Instruction (DDI): On the due date(s), the business submits a DDI to its payment provider. This contains information about the customer, payment amount, and bank account, as well as a reference number.
Automatic payment collection and reconciliation: The payment provider processes the DDI and facilitates the fund transfer from the customer to the business. The company receives automated notifications and transaction records for reconciliation purposes.
Dispute resolution: Businesses are responsible for resolving any disputes that customers raise about unauthorized or incorrect BECS payments. Businesses must work with the customer and their bank to reach a resolution within an agreed time frame.
How to accept BECS Direct Debit as a payment method
Accepting BECS Direct Debit comes with specific requirements for both Australian and non-Australian businesses. Stripe offers a pathway for non-Australian businesses to integrate BECS. Here are the requirements for accepting BECS payments.
For businesses based in Australia
Business registration: Your business must be registered and have an Australian Business Number (ABN).
Local bank account: You need a valid Australian bank account to receive BECS payments.
BECS service provider: You should partner with a BECS service provider to handle the technical aspects of clearing and settlement.
DDR service agreement: You and your BECS service provider need to sign a DDR agreement that outlines the terms and conditions for processing direct debit payments.
Compliance: You must comply with the relevant BECS rules and regulations of the Australian Payments Network (AusPayNet).
For businesses based outside Australia
Australian partnership: You need to partner with an Australian entity, such as a subsidiary or a trusted partner, which acts as your BECS recipient and holder of the bank account that will receive deposits.
Stripe BECS Direct Debit integration: You can use Stripe’s BECS Direct Debit functionality to initiate BECS payments from Australian customers. This requires:
- A Stripe account with BECS Direct Debit capability
- A payment configured with
au_becs_debitas a payment method type - The
currencyset toAUD
- A Stripe account with BECS Direct Debit capability
Steps for accepting BECS
BECS integration: Configure your software or payment gateway to accept BECS payments. Stripe offers simple integration for its business clients.
BECS as a payment option: Make BECS available during checkout alongside your other chosen payment methods.
Customer authorization: Customers provide their bank account details and accept the DDR, thereby authorizing the payment.
Payment processing: Your BECS service provider submits the payment request to the customer’s bank through the network.
Settlement: Funds are transferred to your account.
Additional considerations
Fees: BECS service providers typically charge fees for processing direct debit payments.
Minimum payment amount: Some BECS service providers set minimum payment amounts.
Dispute resolution: Understand the dispute resolution process in the event of any payment issues.
Benefits of accepting BECS Direct Debit
Accepting BECS Direct Debit as a payment method offers businesses many advantages, including the following.
Increased efficiency and reduced costs
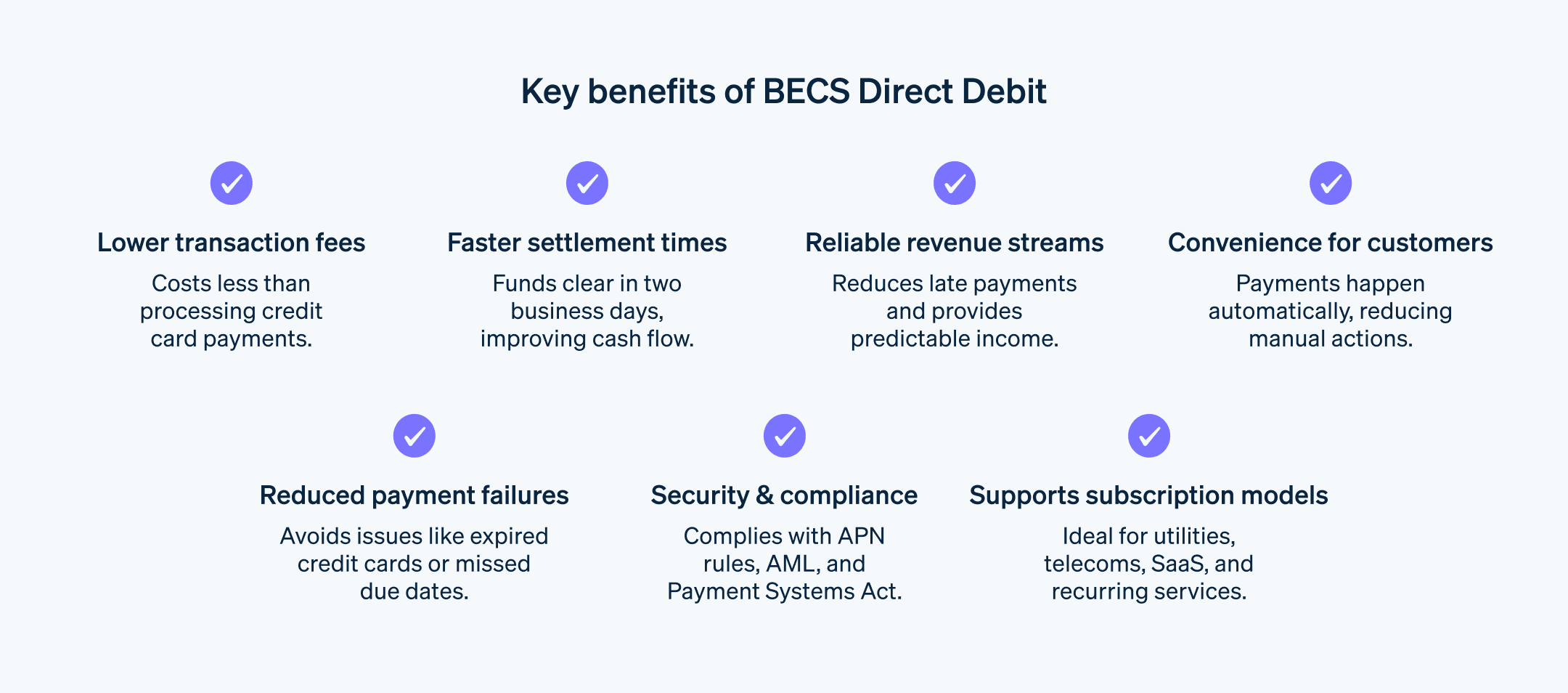
Reduced administrative burden: BECS reduces manual invoicing and eliminates the need to chase payments, freeing up time and resources.
Lower transaction fees: BECS charges significantly lower transaction fees compared to credit cards.
Faster settlement times: Typically, funds arrive in business accounts within two business days, compared to five to seven days for credit card payments.
Improved cash flow and predictability
Fewer late payments: Direct debits in general boast an extremely high success rate for authorized transactions, significantly reducing late payments compared to traditional methods.
Predictable revenue streams: Regular BECS payments provide businesses with reliable income forecasting and cash flow management.
Improved budgeting and financial planning: Predictable recurring income allows businesses to plan expenses and investments more effectively.
Enhanced customer experience and retention
Convenience for customers: BECS offers a convenient way for customers to pay their bills automatically, increasing overall customer satisfaction.
Reduced churn: Automated payments can decrease the customer churn that comes from missed payments or expired cards, raising customer retention rates.
Subscription growth: By making recurring payments easier to set up and use, BECS can boost a business’s subscription volume.
What’s driving BECS Direct Debit adoption in Australia?
Several national trends and advantages of BECS Direct Debit have contributed to increased adoption of the payment system in Australia. Here are some major factors:
Digital shift: In a 2021 survey, more than 80% of Australians said they preferred to check their account balances, make bill payments, and transfer money online. The high adoption rate for online payments contributes to BECS’s popularity, as customers can easily set up and manage mandates through online portals or banking apps.
Fewer cash payments: Australia has seen a shift away from cash payments; the amount of cash withdrawals each month declined from about $115 billion in 2018 to about $78 billion in 2024. BECS supports this trend by reducing the need for cash or checks.
Subscription boom: The rise of subscription services such as streaming platforms, meal kit services, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) products has fueled demand for the type of automated payments that BECS offers.
Convenience and ease of setup: Setting up a BECS mandate for recurring payments on Stripe is simple and straightforward, and it allows customers to avoid the hassle of initiating payments manually.
Transparency and visibility: Users can track their BECS payments through web banking or banking apps and access detailed transaction history. This transparency fosters trust and empowers informed decision-making.
Ability to manage personal finances: BECS provides users with the tools and information they need to manage their recurring payments effectively.
BECS follows or is directly subject to many governmental policies. This helps it gain traction among businesses and customers. These are some of the important drivers:
AusPayNet rules: These standards, which govern BECS’s operations, set limited rules for consumer protection, security, and dispute resolution to ensure processes are fair and transparent.
Competition and Consumer Act 2010: This consumer protection legislation, which is enforced by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission, prohibits unfair practices and establishes that customers must have access to clear, accurate information about their rights and obligations.
Payment Systems (Regulation) Act 1998: This rule established the framework for regulating payment systems in Australia. It requires BECS to operate in the public’s interest, in a manner that is safe, efficient, and transparent.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CTF): This legislation helps combat money laundering and the financing of terrorism. BECS complies with these requirements to safeguard the integrity of the financial system.
Who uses BECS Direct Debit?
BECS Direct Debit’s versatile, user-centric approach to automating, simplifying, and securing financial transactions makes it a popular choice for a wide range of businesses and individuals in Australia. Here’s a rundown of who uses the system and why.
Business users and industries
Utilities: Gas, water, and electricity providers in Australia rely heavily on BECS payments. The system facilitates timely bill collection and lowers processing expenses.
Telecommunications: BECS Direct Debit is ideal for phone, internet, and cable providers that collect monthly bills. It offers timely payments, simplifies administrative tasks, and can reduce customer churn.
Financial services: Banks and lenders use BECS for loan repayments and mortgages. The system’s efficiency and accuracy in managing fixed payments are key advantages.
Insurance companies: The convenience of BECS payments helps with handling insurance payments.
Subscription services: Streaming platforms, SaaS providers, and online publications use BECS to collect recurring subscription fees.
Charitable organizations: BECS simplifies regular donations, allowing organizations to count on sustained support. Its ease of setup and management makes it an effective tool for fundraising.
Government agencies: Local and national bodies use BECS for tax collection, fees, and benefit disbursements. Its efficiency and transparency are ideal for managing finances in the public sector.
Retail and ecommerce: While BECS is used less often for one-off transactions, the system facilitates recurring deliveries and subscription models in retail.
B2B transactions: BECS’s simplified approach supports regular payments between businesses for services and supplies. These direct debit payments can minimize the administrative workload and improve cash flow.
Customer segments
Budget-conscious individuals: For budget-conscious Australians, the system’s predictability aligns with their focus on financial planning and cost control. More than a quarter (27%) of Australians surveyed in 2022 said they planned to set up direct debits for regular payments in an effort to save on missed payment fees.
Subscription services: Many Australians use BECS to pay for gym memberships, streaming services, and other recurring payments due to its reliability and convenience. This contributes to higher customer retention for businesses.
Utility bill payments: Australian households often automate their utility bill payments through BECS to avoid late fees and simplify bill management.
How Stripe Payments can help
Stripe Payments provides a unified, global payment solution that helps any business—from scaling startups to global enterprises—accept payments online, in person, and around the world.
Stripe Payments can help you:
- Optimize your checkout experience: Create a frictionless customer experience and save thousands of engineering hours with prebuilt payment UIs, access to 100+ payment methods, and Link, Stripe’s digital wallet.
- Expand to new markets faster: Reach customers worldwide and reduce the complexity and cost of multicurrency management with cross-border payment options, available in 195 countries across 135+ currencies.
- Unify payments in person and online: Build a unified commerce experience across online and in-person channels to personalize interactions, reward loyalty, and grow revenue.
- Improve payment performance: Increase revenue with a range of customizable, easy-to-configure payment tools, including no-code fraud protection and advanced capabilities to improve authorization rates.
- Move faster with a flexible, reliable platform for growth: Build on a platform designed to scale with you, with 99.999% uptime and industry-leading reliability.
Learn more about how Stripe Payments can power your online and in-person payments, or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.