According to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, businesses lose an average of 5% of their annual revenue to fraud each year, and a substantial portion of this can be attributed to irregularities in financial records. Payment reconciliation plays a key role in identifying and addressing these irregularities by aligning internal accounting records with bank statements and transactions.
In addition to safeguarding against errors and fraud, payment reconciliation contributes to informed and data-driven decisions, positive relationships with clients and partners, and adherence to legal and financial standards.
We’ll cover the different aspects of payment reconciliation, dissecting its mechanics, best practices, and the practical benefits it offers businesses.
What’s in this article?
- What is payment reconciliation?
- How does payment reconciliation work?
- Types of payment reconciliation
- Why payment reconciliation matters for businesses
- Payment reconciliation best practices
- Payment reconciliation with Stripe
What is payment reconciliation?
Payment reconciliation is a financial process that involves matching and comparing transaction records to ensure that the payments made or received are accurate and consistent with what is recorded in the business’s accounting books or financial statements. This process is essential for verifying the accuracy of financial transactions, avoiding errors or discrepancies, and maintaining the integrity of financial records.
How does payment reconciliation work?
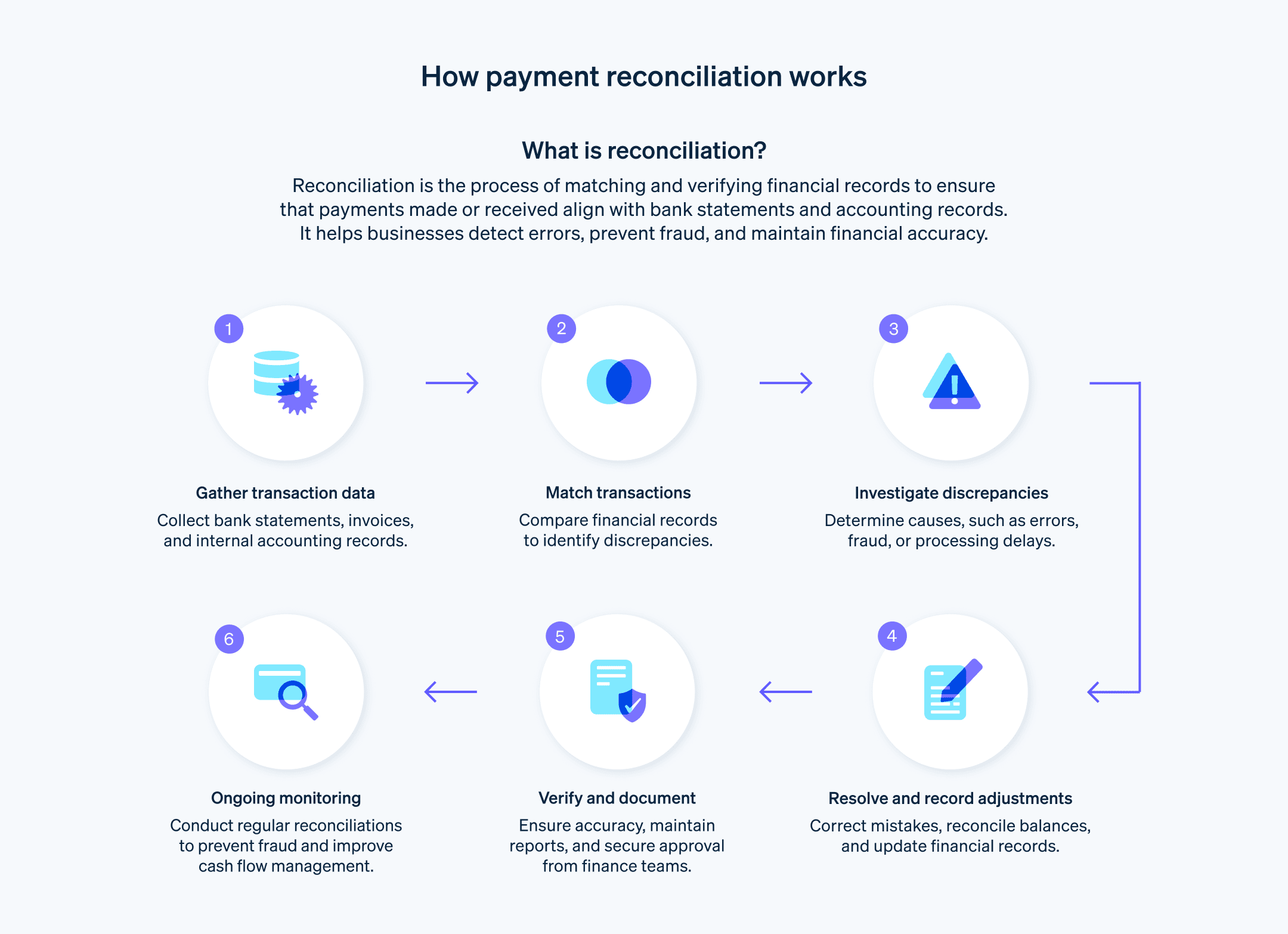
Payment reconciliation involves several steps that help ensure the payments recorded in the financial statements are consistent with the payments made or received. The exact process varies from business to business, but generally includes the following steps:
Gather data
Collect all the relevant financial documents and records, such as bank statements, invoices, receipts, and the records in the accounting system. You will use this data to verify the accuracy of the payments.Match transactions
Compare the records from the bank statements with the entries in the accounting system. Ensure that the dates, amounts, and descriptions of the transactions match.Identify discrepancies
During the matching process, you might find transactions that don’t align. These discrepancies might come from differences in timing, errors, or fraud. Make a list of these discrepancies for further investigation.Resolve discrepancies
Investigate the discrepancies to determine their causes. This could involve contacting the issuing bank, checking the original transaction documents, or reviewing the accounting entries. Once you have identified the reasons for the discrepancies, make the necessary corrections or adjustments in the accounting records.Record adjustments
Sometimes, you may find that certain transactions are recorded incorrectly in the accounting system or are missing entirely. Record any adjustments needed to reconcile the account, such as bank fees, interest earned, or correcting errors.Verify balances
After you have made all the adjustments, verify that the adjusted balance in the accounting records matches the ending balance on the bank statement.Document the process
Keep a record of the reconciliation process, including any discrepancies and adjustments. This documentation is important for audit purposes and for ensuring accountability and transparency.Review and approve
Depending on the size and structure of your organization, a supervisor or manager may need to review and approve the payment reconciliation process, to ensure it was conducted properly.
Payment reconciliation is usually performed on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly.
Types of payment reconciliation
Specific transactions or records call for different types of payment reconciliation. Here are some examples:
Bank reconciliation
Bank reconciliation involves matching the transactions recorded in the company’s cash account with the transactions shown on the bank statement. Businesses use bank reconciliation to ensure that the cash balance in the accounting records is consistent with the balance the bank reports.Credit card reconciliation
Credit card reconciliation is similar to bank reconciliation but meant specifically for credit card accounts. It involves matching transactions recorded in the accounting system against the credit card statements to ensure accuracy and detect any unauthorized or fraudulent transactions.Accounts receivable reconciliation
Accounts receivable reconciliation involves matching customer payments and credit notes against the invoices issued. It helps businesses ensure that records of customer payments are correct and allows them to identify and resolve any discrepancies, such as underpayments or overpayments.Accounts payable reconciliation
Accounts payable reconciliation is the process of matching supplier invoices, credit notes, and payments made to the records in the accounts payable ledger. It helps businesses verify that the amounts they owe suppliers are accurate and that they are making payments in a timely manner.Intercompany reconciliation
For businesses with multiple subsidiaries or divisions, intercompany reconciliation involves matching and reconciling transactions that occur between different entities within the same corporate group. This ensures that businesses record intercompany transactions consistently across the different entities.Payroll reconciliation
Payroll reconciliation involves verifying the accuracy of payroll transactions, including wages, deductions, and taxes, by comparing payroll records to bank statements and other supporting documents. It helps ensure that businesses are paying employees correctly and accounting for payroll taxes and other deductions in the proper manner.General ledger reconciliation
General ledger reconciliation is a broader type of reconciliation that can encompass several of the aforementioned types. In general ledger reconciliation, businesses reconcile individual accounts within the general ledger with the corresponding sub-ledgers or supporting documents. This ensures that all transactions are accurately recorded in the general ledger.
Each type of payment reconciliation serves a specific purpose, and all are important for maintaining the accuracy and integrity of financial records. The exact type of reconciliation you use will depend on a number of factors relating to the nature of your business and the type of transactions you process.
Why payment reconciliation matters for businesses
For any business, financial accuracy and accountability are paramount. But the vast array and volume of transactions that businesses process on a daily basis make the financial landscape complex. Payment reconciliation is an important tool in navigating this complexity. It serves as a compass, guiding businesses in verifying the accuracy of financial records, ensuring compliance, and making informed decisions. Here are some key reasons why payment reconciliation is so significant for businesses:
Detecting errors and discrepancies
Through payment reconciliation, businesses can pinpoint errors or discrepancies between accounting records and actual transactions. Errors and discrepancies can range from minor data entry mistakes to more serious issues like missing transactions.Preventing fraud
Regular account reconciliation acts as a safeguard, helping businesses detect unauthorized transactions or irregularities, which may signal fraud. Identifying these issues early on is necessary for damage control.Improving cash flow management
Payment reconciliation helps businesses understand their true cash position. With an accurate understanding of the cash at hand, businesses can make smart decisions related to investments, expenses, and debt management.Ensuring accurate financial reporting
The reconciliation process ensures that financial statements mirror the business’s financial status. This accuracy is essential not only for internal decision-making but also for transparent communication with investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.Compliance with laws and regulations
Regular payment reconciliation plays a key role in ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, thereby mitigating the risk of penalties and legal challenges.Enhancing relationships with stakeholders
When financial records are precise and up-to-date, stakeholders, including investors, suppliers, and customers, are more likely to trust the business. This trust helps maintain strong and mutually beneficial relationships.Facilitating audits
An organized and thorough payment reconciliation process eases the auditing process. Auditors can review reconciliation documentation and processes in an efficient manner, reducing the likelihood of audit adjustments or concerns.Optimizing operational efficiency
Payment reconciliation helps businesses highlight areas in need of process enhancements, such as payment procedures or internal controls. Optimizing these areas can lead to increased efficiency and cost reductions.Supporting budgeting and forecasting
Accurate financial data obtained through reconciliation is fundamental for effective budgeting and forecasting. It empowers businesses to make realistic predictions and plan for future financial requirements.
In addition to protecting a business against errors and possible fraud, payment reconciliation builds a foundation for strategic, fact-based decision-making, compliance, and trust-based stakeholder relationships. The impact of payment reconciliation on a business’s current and future health cannot be overstated.
Payment reconciliation best practices
Payment reconciliation is a fundamental financial process for businesses. To make it as effective and efficient as possible, businesses should adopt these best practices:
Conduct payment reconciliation regularly
Businesses should conduct payment reconciliation regularly, typically on a monthly basis. Regular reconciliation helps businesses detect and resolve errors and discrepancies in a timely manner.Segregate duties
To minimize the risk of errors and fraud, the person who records transactions should not be the same person who reconciles accounts. This segregation of duties serves as a system of checks and balances for businesses.Use reconciliation software or tools
Businesses can use specialized software or tools to automate much of the reconciliation process. This not only increases efficiency but also minimizes manual errors and provides better tracking and reporting.Standardize the reconciliation process
Establishing standardized procedures for reconciliation ensures consistency and accuracy. Document these procedures and make sure the relevant staff understand and follow them closely.Document thoroughly
Maintain detailed records of the reconciliation process, including explanations for any adjustments made. This documentation is needed for audits and for understanding the historical context of transactions.Investigate discrepancies promptly
Investigate discrepancies immediately. Taking quick action is essential for correcting errors, recovering funds if necessary, and preventing similar issues in the future.Train employees
Ensure that all employees involved in the reconciliation process are properly trained. They must be well-versed in accounting practices, regulations, and how to use any applicable reconciliation tools or software.Create a review and approval process
A supervisor or manager should review and approve reconciliation reports. This additional layer of oversight helps to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the reconciliation process.Maintain security and access controls
Limit access to financial records and systems to authorized personnel only. Implement strong security measures to protect sensitive financial information.Benchmark progress and strive for improvement
Evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of your reconciliation process on a regular basis. Compare your practices with industry standards and look for ways to improve your system.Establish clear communication channels
Maintain clear lines of communication with banks, vendors, and other parties involved in financial transactions. These channels will help resolve issues and obtain necessary information or clarifications.
By following these best practices for payment reconciliation, businesses can enhance the accuracy and integrity of their financial records, which contributes to better financial management, informed decision-making, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Payment reconciliation with Stripe
Stripe’s suite of financial solutions helps businesses understand their money movement while automating much of the payment reconciliation process. This feature is tailored to ensure that revenue is captured accurately and a business’s system of record remains in sync with the transactions processed through Stripe, including both charges and refunds.
Here’s how Stripe can streamline the reconciliation process for businesses:
Automation
Stripe reconciliation automates the often arduous task of comparing internal records, such as invoices and fees, with external records like settlement files, payout files, and bank statements. This significantly reduces manual effort and minimizes errors.Daily cash tracking
One of the benefits of using Stripe for reconciliation is the ability to track cash on a daily basis. This gives businesses a real-time understanding of their cash position, which is important for effective financial management.Identifying discrepancies
Stripe allows businesses to swiftly identify any gaps in fund flows or data discrepancies. By detecting these issues early, businesses can resolve them faster, preventing revenue leakages and ensuring accurate financial records.Transaction life cycle visibility
With Stripe reconciliation, businesses gain visibility into the complete life cycle of each transaction. From the moment a transaction is initiated to the moment it is settled, businesses can track every stage, ensuring thorough monitoring and control.Implementing financial controls
Stripe helps implement strong financial controls by automating reconciliation and providing detailed transaction tracking, which ensures that financial records are accurate and businesses are protected from errors and fraud.Scalability
As businesses grow, their financial operations become more complex. Stripe’s reconciliation solutions are scalable, capable of accommodating the increasing transaction volumes and complexities that come with growth. This makes Stripe particularly valuable for businesses with high transaction volumes, multiple payment methods in a single transaction, or long transaction life cycles.
Stripe’s reconciliation functionality acts as a bridge between Stripe-processed transactions, including payments and refunds, and your internal accounting records. Stripe automatically matches and verifies each transaction and highlights any discrepancies for further investigation. Learn more about how Stripe facilitates payment reconciliation for businesses here.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.