การถือหุ้นของธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ (QSBS) จะเปลี่ยนเกณฑ์การรับผิดทางภาษีสำหรับผู้ก่อตั้งธุรกิจสตาร์ทอัพและนักลงทุนระยะแรกเริ่มได้อย่างมาก คนกลุ่มนี้จะได้รับการยกเว้นภาษีกำไรของรัฐบาลกลาง 100% จำนวนสูงถึง 10 ล้านดอลลาร์หรือ 10 เท่าของเงินลงทุนครั้งแรก ผู้ประกอบการที่มีประสบการณ์นิยมใช้ QSBS มากขึ้นเพื่อเพิ่มผลตอบแทนทางการเงิน
ตามรายงานของ National Venture Capital Association ระบุว่ามูลค่าการขายเฉลี่ยสําหรับธุรกิจสตาร์ทอัพในสหรัฐอเมริกาในปี 2022 ต่ำกว่า 200 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ ซึ่งเป็นมูลค่าการขายที่เหมาะสําหรับซึ่งจะได้รับการยกเว้นหรือการลดภาษีของ QSBS อย่างมีนัยสําคัญ แต่ไม่ใช่ว่าธุรกิจขนาดเล็กและผู้ถือผลประโยชน์ร่วมทุกรายที่ทราบวิธีใช้ประโยชน์ด้านภาษีนี้อย่างสมบูรณ์ ตั้งแต่การถือหุ้น QSBS ไปจนถึงการขายในขั้นตอนสุดท้าย
ด้านล่างนี้ เราจะอธิบายวิธีการทำให้มีสิทธิ์รับ QSBS, ประโยชน์ทางภาษี และเงื่อนไขที่อาจทําให้หุ้นไม่เข้าเกณฑ์การเป็น QSBS เราจะอธิบายวิธีการประเมินที่คุณควรใช้ขณะนําหุ้นออกจําหน่าย การตรวจสอบการปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดอย่างต่อเนื่อง รวมถึงขีดจํากัดและความเสี่ยงที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการถือ QSBS สิ่งที่ผู้ก่อตั้งและนักลงทุนระยะแรกต้องรู้มีดังนี้
บทความนี้ให้ข้อมูลอะไรบ้าง
- หุ้นธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ (QSBS) สำหรับผู้ก่อตั้งคืออะไร
- เกณฑ์การมีสิทธิ์ของ QSBS
- วิธีรับ QSBS
- วิธีขาย QSBS
- ประโยชน์ทางภาษีของ QSBS
- ขีดจำกัดและความเสี่ยงของ QSBS
หุ้นธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ (QSBS) สําหรับผู้ก่อตั้งคืออะไร
หุ้นของธุรกิจขนาดเล็กที่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ (QSBS) เป็นหุ้นประเภทหนึ่งที่ออกโดยบริษัทประเภท C (C corp) ที่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดของประมวลรัษฎากรภายในประเทศ โดยเฉพาะมาตรา 1202 และ 1045 QSBS มอบประโยชน์ทางภาษีจํานวนมากให้แก่ผู้ถือหุ้น โดยเฉพาะผู้ก่อตั้ง และนักลงทุนระยะแรก หากคุณถือหุ้นประเภทนี้แล้วขาย คุณสามารถหลีกเลี่ยงการจ่ายภาษีรายรับของรัฐบาลกลางเป็นจำนวนเงินที่ขายได้ตามขีดจำกัดที่กำหนด
เกณฑ์การมีสิทธิ์ของ QSBS
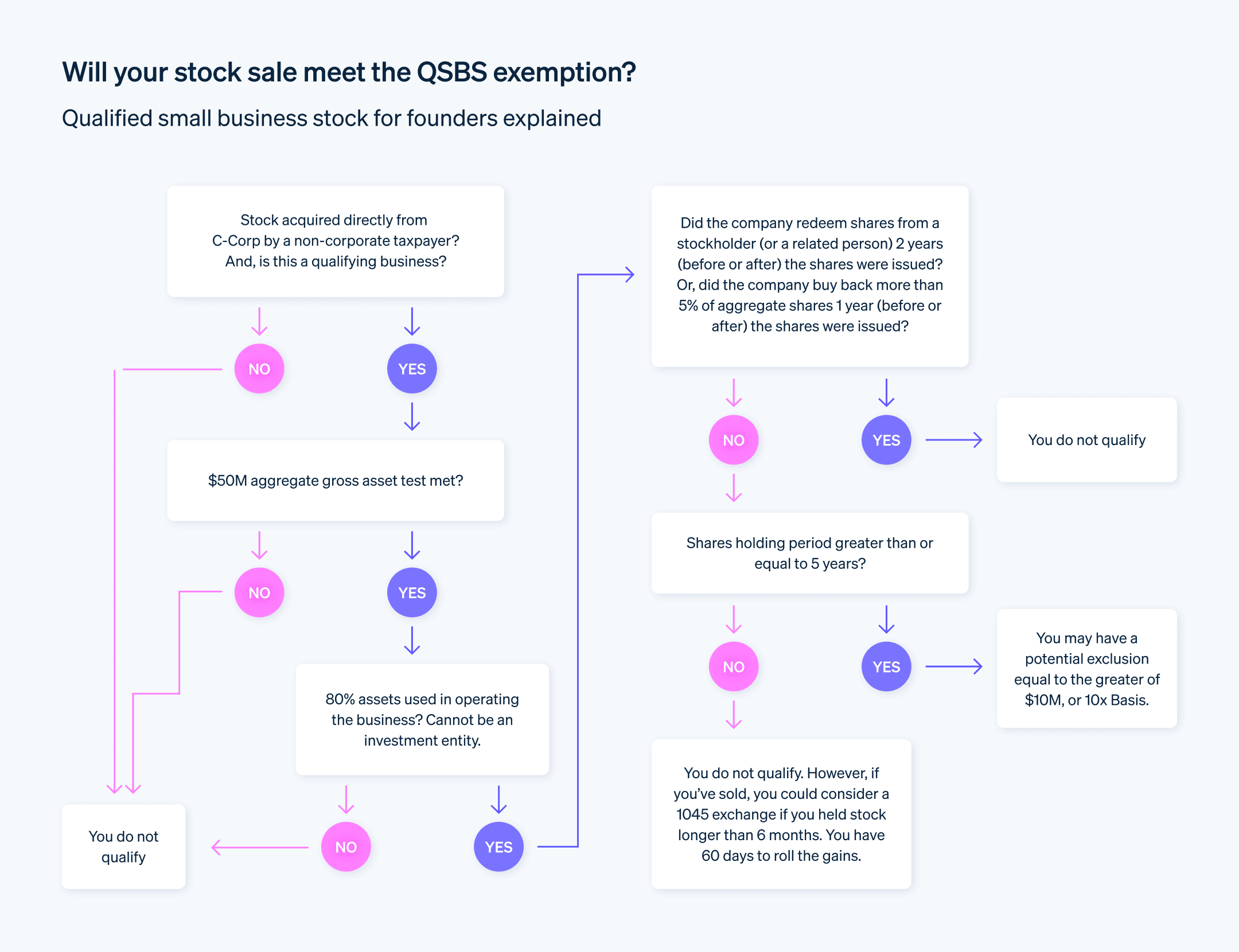
เพื่อให้มีสิทธิ์รับประโยชน์ทางภาษีจํานวนมากภายใต้ QSBS ทั้งบริษัทผู้ออกบัตรและนักลงทุนต้องปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดโดยละเอียด กฎเหล่านี้มีตัววัดเฉพาะเจาะจง และการไม่ปฎิบัติตามกฎแม้เพียงข้อเดียวอาจส่งผลให้เสียผลประโยชน์ด้านภาษีไปได้ ต่อไปนี้คือภาพรวมเกี่ยวกับข้อกําหนดในการมีสิทธิ์
ประเภทของธุรกิจ
- บริษัทประเภท C: หุ้นจะต้องออกโดยบริษัทประเภท C บริษัทประเภท S และ LLC ไม่เข้าเกณฑ์การออก QSBS
- อยู่ภายในประเทศ: บริษัทควรจัดตั้งขึ้นในสหรัฐอเมริกา บริษัทต่างประเทศจะไม่มีสิทธิ์
การตรวจสอบสินทรัพย์
- สินทรัพย์ขั้นต้น: สินทรัพย์ขั้นต้นของบริษัทจะต้องมีมูลค่าไม่เกิน 50 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐ ณ เวลาที่ออกหุ้นและหลังจากนั้นทันที รวมถึงเงินสดและสินทรัพย์อื่นทั้งหมดที่มีมูลค่าตามต้นทุนเดิมด้วย
เกณฑ์การปฏิบัติงาน
- ข้อกําหนดทางธุรกิจที่ดำเนินอยู่: มูลค่าสินทรัพย์ของบริษัทอย่างน้อย 80% ต้องนําไปใช้ในการดําเนินธุรกิจที่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ตั้งแต่ 1 รายการขึ้นไป ไม่รวมกิจกรรมรายได้แบบทางอ้อม เช่น การเป็นเจ้าของอสังหาริมทรัพย์ที่ปล่อยเช่าเช่า
เกณฑ์การออกหุ้น
- การออกหุ้นเดิม: นักลงทุนจะต้องซื้อหุ้นโดยตรงจากบริษัท หุ้นที่ซื้อต่อมาจากผู้ถือหุ้นคนอื่นๆ ถือว่าไม่มีสิทธิ์
- ประเภทหุ้น: หุ้นสามัญหรือหุ้นบุริมสิทธิจะถือว่าเข้าเกณฑ์หากตรงตามข้อกำหนดด้านอื่นไ
ระยะเวลาการถือหุ้น
- กฎ 5 ปี: นักลงทุนจะต้องถือหุ้นเป็นเวลาขั้นต่ำ 5 ปี เพื่อให้ได้ประโยชน์อย่างเต็มที่จากการยกเว้นภาษีของ QSBS อย่างไรก็ตาม พวกเขาสามารถใช้กลยุทธ์การขายหุ้นปัจจุบันแล้วไปซื้อหุ้นอื่นที่มีการถือเป็นระยะเวลาที่สั้นกว่าได้
ขีดจํากัดในการยกเว้น
- ขีดจํากัดในการยกเว้น: จํานวนผลกำไรที่มีสิทธิ์ในการยกเว้นภาษีจํากัดอยู่ที่ 10 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐหรือ 10 เท่าของราคามาตรฐานของหุ้น
เอกสารประกอบ
- การเตรียมเอกสาร: ทั้งบริษัทผู้ออกบัตรและผู้ถือหุ้นควรบันทึกข้อมูลอย่างละเอียด รวมถึงใบรับรองหุ้นและงบการเงินเพื่อให้มีสิทธิ์สำหรับ QSBS
ซึ่งมีรายการข้อกําหนดแบบเฉพาะเจาะจงที่ละเอียดมาก แต่สําหรับผู้ก่อตั้งและนักลงทุนระยะแรกแล้ว ประโยชน์ทางการเงินมักจะมีแรงจูงใจเพียงพอในการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดดังกล่าว
วิธีรับ QSBS
การรับ QSBS ต้องใช้ขั้นตอนการพิจารณาอย่างรอบถอบ การปฏิบัติตามกฎด้านภาษีคือกุญแจสำคัญ แต่ก็ยังมีข้อควรพิจารณาเชิงกลยุทธ์ที่อาจเป็นตัวกําหนดภาระทางภาษีและการเติบโตของสินทรัพย์ในระยะยาวได้ ประโยชน์ทางภาษีที่สําคัญของการได้รับ QSBS ถือว่าคุ้มค่ากับงานการจัดการด้านการเงิน กฎหมาย และการบริหารจัดการอย่างมาก
ภาพรวมของกระบวนการรับ QSBS มีดังนี้
ก่อตั้งบริษัทประเภท C
สถานที่ที่คุณเลือกจัดตั้งธุรกิจอาจส่งผลกระทบต่อการปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดและความยืดหยุ่นในการดําเนินงานอย่างมีนัยสําคัญ ตัวอย่างเช่น รัฐเดลาแวร์เป็นตัวเลือกยอดนิยมเนื่องจากกฎหมายบริษัทมีการร่างขึ้นมาเป็นอย่างดี ทำให้คาดการณ์ได้และเป็นประโยชน์ต่อธุรกิจ
ไม่ว่าจะจัดตั้งบริษัทประเภท C ที่รัฐใด คุณก็จะต้องยื่นเอกสารการจดทะเบียนจัดตั้งบริษัทกับสำนักงานรัฐมนตรีบริหารกิจการรัฐ โดยเอกสารควรระบุองค์ประกอบสําคัญขององค์กรอย่างชัดเจน เช่น วัตถุประสงค์ทางธุรกิจ จํานวนหุ้นที่ได้รับอนุญาตทั้งหมด และมูลค่าหุ้นแต่ละหน่วย นอกจากนี้ คุณจะต้องสร้างกฎข้อบังคับขององค์กรที่ครอบคลุมเพื่อควบคุมระเบียบข้อบังคับภายในด้วย เช่น การดําเนินการประชุมคณะกรรมการบริหาร สิทธิ์ในการออกเสียง รวมถึงบทบาทและความรับผิดชอบของเจ้าหน้าที่
การตรวจสอบทางการเงิน
การตรวจสอบทางการเงินโดยละเอียดเป็นข้อกําหนดเบื้องต้นเพื่อให้มีสิทธิ์เกี่ยวกับ QSBS โปรดทํางานอย่างใกล้ชิดกับที่ปรึกษาทางการเงินหรือผู้ตรวจสอบเพื่อประเมินสินทรัพย์ของคุณ ซึ่งปกติแล้วจะแสดงโดยงบดุลที่ครอบคลุม คุณจะต้องยืนยันว่าสินทรัพย์รวมของบริษัทไม่เกิน 50 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐทั้งก่อนและทันทีหลังจากออกหุ้น ขั้นตอนนี้อาจต้องมีการประเมินค่าสินทรัพย์ของบุคคลที่สามหรือแม้แต่การตรวจสอบอย่างเต็มรูปแบบเพื่อให้ถูกต้องแม่นยำสูงสุด
ที่ปรึกษาทางกฎหมาย
ติดต่อทีมกฎหมายที่มีความเชี่ยวชาญด้านกฎหมายหลักทรัพย์ เพื่อทำความเข้าใจความซับซ้อนของการออกหุ้นและการปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนด QSBS จัดทำเอกสารที่ระบุวิธีการทำงานร่วมกันอย่างเป็นทางการและกำหนดขอบเขตของงานให้ชัดเจน ทีมนี้จะทําการตรวจสอบการปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของการออกหุ้นเป็นไปตามข้อบังคับของรัฐบาลกลางและระดับรัฐ โดยมักต้องใช้การตรวจสอบการยกเว้นด้านหลักทรัพย์และเตรียมการยื่นเอกสารที่จําเป็น
เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับหุ้น
ร่างสัญญาต่างๆ เช่น สัญญาซื้อขายหุ้น (SPA) และข้อตกลงของผู้ถือหุ้น เพื่อมอบข้อกําหนดของการขายหุ้นและการมีกรรมสิทธิ์ในภายหลัง โดย SPA จะระบุราคาซื้อ จํานวนหุ้น และข้อจํากัดอื่นๆ เช่น กําหนดการขายหุ้นตามเงื่อนไขเวลา โดยข้อตกลงของผู้ถือหุ้นสามารถคุ้มครองผลประโยชน์ได้โดยการให้รายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับสิทธิในการออกเสียง สิทธิในการรับหุ้นใหม่ก่อนคนอื่น และข้อกําหนดของสัญญาพ่วงซื้อขายหุ้น (Tag-along และ Drag-along)
การใช้รายการบันทึกหุ้นและตารางแสดงสัดส่วนการถือหุ้นนั้นจําเป็นสําหรับการติดตามกรรมสิทธิ์หุ้นและเป็นการเตรียมพร้อมหากมีการตรวจสอบบัญชีโดย IRS
การอนุมัติจากคณะกรรมการบริหาร
การออกหุ้นจะต้องได้รับอนุมัติจากคณะกรรมการและวาระการประชุมนี้ควรระบุรายการดําเนินการที่เกี่ยวข้องอย่างชัดเจน หลังจากอนุมัติการออกหุ้นแล้ว คณะกรรมการบริษัทต้องยื่นมติเหล่านี้ในการประชุม โดยจะจัดเก็บไว้ตามบันทึกข้อมูลอย่างเป็นทางการในลำดับถัดไป
การออกหุ้น
จัดทำเอกสารหุ้นที่ออกแต่ละหน่วยได้อย่างแม่นยำ ใบรับรองหุ้นแบบดั้งเดิมเป็นหลักฐานการเป็นเจ้าของและต้องมีรายละเอียดต่างๆ เช่น วันที่ออกหุ้น มูลค่าตามหุ้นที่ตราไว้ และข้อจํากัดใดๆ อย่างไรก็ตาม บริษัทบางแห่งเลือกใช้โทเค็นดิจิทัลซึ่งใช้เทคโนโลยีบล็อกเชนเพื่อแสดงสิทธิ์การเป็นเจ้าของที่ปลอดภัยและโอนได้ง่าย
การปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดอย่างต่อเนื่อง
คุณต้องติดตามการปฏิบัติตามเกณฑ์ QSBS อย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยทําการประเมินทางการเงินเป็นประจําเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่ามูลค่าสินทรัพย์ของบริษัทยังคงเป็นไปตามขอบเขตที่กําหนด นอกจากนี้ คุณยังต้องปรึกษาที่ปรึกษาทางกฎหมายเป็นระยะเพื่อยืนยันว่ากิจกรรมทางธุรกิจยังคงมีคุณสมบัติตาม QSBS เนื่องจากกิจกรรมเหล่านี้อาจเปลี่ยนแปลงได้เมื่อธุรกิจเติบโตขึ้น
วิธีขาย QSBS
เมื่อขาย QSBS โปรดวางแผนอย่างรอบคอบและทําตามขั้นตอนอย่างละเอียดเพื่อให้รักษาสิทธิประโยชน์ทางภาษีทั้งหมดที่มีและทําธุรกรรมได้อย่างราบรื่น กระบวนการขายมีข้อผูกพันทางกฎหมาย กรอบกฎหมายที่ซับซ้อน และผลกระทบทางภาษีที่ซับซ้อนมากมาย แต่คุณสามารถทําได้ด้วยการวางแผนและการสนับสนุนที่เหมาะสมจากที่ปรึกษาด้านภาษี วิธีขาย QSBS มีดังนี้
การยืนยันระยะเวลาการถือครอง: ขั้นตอนแรกคือการยืนยันว่าคุณพอใจกับข้อกําหนดการถือครอง 5 ปี ระยะเวลานี้จะเริ่มตั้งแต่วันที่ออกหุ้นครั้งแรกและสิ้นสุดในวันที่ขาย การคํานวณนั้นตรงไปตรงมา แต่จําเป็นต่อการมีคุณสมบัติในการได้รับประโยชน์ทางภาษีของ QSBS เป็นอย่างมาก ทํางานอย่างใกล้ชิดกับที่ปรึกษาด้านภาษีเพื่อยืนยันระยะเวลาการถือครองและพูดคุยเกี่ยวกับผลกระทบทางภาษีที่อาจเกิดขึ้น
การวิเคราะห์ภาษี: ขั้นตอนต่อไป ให้ตรวจสอบผลทางภาษีที่มาจากยอดขายอย่างละเอียด ทําความคุ้นเคยกับอัตราภาษีที่ใช้กับ QSBS เนื่องจากอัตราภาษีเหล่านี้แตกต่างจากอัตราภาษีเงินได้แบบปกติอย่างมาก พิจารณาปัจจัยด้านสิทธิประโยชน์ทางภาษีที่อาจได้รับ เช่น การยกเว้นจากภาษีรายรับสูงสุดถึงวงเงินที่กำหนด โดยทำควบคู่กับการวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่าย-ประโยชน์
การตรวจสอบเอกสาร: ก่อนเริ่มต้นการขาย โปรดตรวจสอบเอกสารทั้งหมดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกรรมสิทธิ์ในหุ้น ซึ่งรวมถึงสัญญาซื้อหุ้น สัญญาผู้ถือหุ้น และใบรับรองหุ้น ระบุและจัดการข้อจํากัดหรือสิทธิ์ใดๆ ที่ส่งผลกระทบต่อการขายหุ้น เช่น สิทธิ์การซื้อหุ้นก่อนผู้ถือหุ้นคนอื่นๆ
การขอคำปรึกษาด้านกฎหมาย: ติดต่อกับทีมกฎหมายที่มีประสบการณ์ในด้านธุรกรรมหลักทรัพย์เพื่อเตรียมและตรวจสอบเอกสารทั้งหมดที่จําเป็นสําหรับการขายหุ้น ส่วนนี้มักรวมข้อตกลงการซื้อและการขายที่ระบุข้อกําหนดของข้อตกลง ตั้งแต่ราคาขายไปจนถึงเงื่อนไขการปิดบัญชี ตลอดจนตัวแทนและการรับประกันใดๆ จากทั้งสองฝ่าย
การตรวจสอบวิเคราะห์สถานะสําหรับผู้ซื้อ: หากการขายหุ้นมีผู้ซื้อจากภายนอก ก็คาดว่าผู้ซื้อจะดําเนินการตรวจสอบสถานะของตัวเอง โปรดเตรียมพร้อมส่งเอกสารที่จําเป็นทั้งหมด ซึ่งอาจมีตั้งแต่งบการเงินไปจนถึงข้อตกลงทรัพย์สินทางปัญญา และให้ความร่วมมืออย่างเต็มที่เมื่อทำตามขั้นตอนที่เหมาะสมเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลละเอียดอ่อน
การอนุมัติครั้งสุดท้าย: ขั้นตอนสุดท้ายของการขายจะต้องมีอนุมัติอย่างเป็นทางการจากคณะกรรมการบริษัท และอาจมีการออกเสียงจากผู้ถือหุ้น โดยขึ้นอยู่กับกฎข้อบังคับของบริษัทและกฎหมายของรัฐ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าได้บันทึกกระบวนการอนุมัติเพื่อสร้างหลักฐานที่เป็นเอกสาร
การปิดธุรกรรม: สรุปการขายโดยดําเนินการเอกสารที่จําเป็นทั้งหมด ซึ่งมักประกอบด้วยข้อตกลงการซื้อหุ้น มติองค์กรที่ยืนยันการขาย และการโอนเงินเพื่อชำระ คู่สัญญาแต่ละฝ่ายจะต้องจัดเก็บสําเนาเอกสารทั้งหมดในขั้นสุดท้ายที่ดําเนินการ เพื่อเป็นการจัดทำบันทึกและใช้สำหรับการตรวจสอบบัญชีในอนาคต
การยื่นและการแจ้งเตือนหลังการขายหุ้น: หลังจากสรุปการขายแล้ว ให้อัปเดตบัญชีแยกประเภทหุ้นของบริษัทเพื่อแสดงถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงการมีกรรมสิทธิ์ คุณจะต้องทําการยื่นเอกสารทางกฎหมายที่จําเป็นเพื่อบันทึกการขายและอัปเดตข้อมูลผู้ถือหุ้น
การยื่นภาษี: สุดท้ายนี้ คุณจะต้องรายงานการขาย QSBS ในแบบแสดงรายการภาษี โดยมักจะต้องใช้แบบฟอร์ม 8949 และ Schedule D ของแบบฟอร์ม 1040 เพื่อจัดทำเอกสารเกี่ยวกับธุรกรรมเงินทุน ติดต่อที่ปรึกษาด้านภาษีที่เชี่ยวชาญเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าคุณได้รับรายละเอียดทั้งหมดที่เหมาะสม
แต่ละขั้นตอนของกระบวนการขาย QSBS มีความซับซ้อน และการข้ามขั้นตอนใดขั้นตอนหนึ่ง อาจส่งผลเสียต่อประโยชน์ด้านภาษีได้ การปฏิบัติตามข้อกําหนดตลอดกระบวนการและการรับผลลัพธ์ทางการเงินที่ดีที่สุดจะเป็นเรื่องง่ายขึ้นด้วยการสนับสนุนจากที่ปรึกษาทางกฎหมายและภาษี
สิทธิประโยชน์ทางภาษีของ QSBS
ถึงแม้ว่าการจัดการ QSBS เป็นเรื่องที่ยุ่งยาก แต่ก็คุ้มค่าที่จะดำเนินการเพราะมีประโยชน์ทางการเงินหลายประการ โดยประกอบไปด้วย
การยกเว้นผลกำไรจากเงินลงทุน
หนึ่งในแง่มุมที่น่าดึงดูดที่สุดของ QSBS คือการยกเว้นผลกําไรส่วนใหญ่จากการเก็บภาษีของรัฐบาลกลาง IRS อนุญาตให้ยกเว้นผลกําไรสูงสุดถึง 10 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐได้ 100% หรือ 10 เท่าของจํานวนหุ้นที่ปรับมูลค่าแล้ว ขึ้นอยู่กับว่ากรณีใดสูงกว่าทางเลือกในการลดภาษีขั้นต่ำ (AMT)
AMT เป็นการคํานวณภาษีเงินได้แบบแยกกันซึ่งทำให้บุคคลทั่วไปและบริษัทที่มีรายได้สูงไม่สามารถหลีกเลี่ยงภาระทางภาษีในระดับขั้นต่ำผ่านการหักภาษีและการยกเว้นได้ โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ข้อยกเว้นผลกําไรจากเงินทุนอาจทำให้ต้องพิจารณาเกี่ยวกับ AMT แต่ข้อยกเว้นสําหรับ QSBS ก็มีผลบังคับใช้กับวัตถุประสงค์ของ AMT เช่นกัน เพื่อช่วยลดภาระของนักลงทุนสองต่อข้อกําหนดการขายหุ้นปัจจุบันเพื่อซื้อหุ้นอื่น
หากคุณตัดสินใจที่จะขาย QSBS และนำเงินมาลงทุนกับ QSBS อื่นภายใน 60 วัน ก็สามารถเลื่อนการรับรู้ผลกําไรจากเงินทุนได้ การทําเช่นนี้จะช่วยส่งเสริมการลงทุนใหม่ที่มีภาษีต่ำลงและเป็นการปรับพอร์ตโฟลิโออย่างมีประสิทธิภาพโดยที่ไม่ต้องเสียภาษีในทันทีประโยชน์ด้านภาษีของรัฐ
หลายรัฐปฏิบัติตามกฎ QSBS ของรัฐบาลกลาง โดยมอบประโยชน์ด้านภาษีของรัฐที่คล้ายกับประโยชน์ด้านภาษีของรัฐบาลกลาง อย่างไรก็ตาม ประโยชน์อาจจะแตกต่างกันออกไป และคุณจำเป็นต้องทำการวิเคราะห์ตามรัฐเพื่อให้ประหยัดภาษีได้มากขึ้นสิทธิ์ในการลดอัตราภาษีของรัฐบาลกลาง
หากหุ้นไม่ตรงตามเกณฑ์การยกเว้นอย่างเต็มรูปแบบ ผลกําไรอาจยังมีสิทธิ์ได้รับอัตราภาษีของรัฐบาลกลางที่ลดลงซึ่งอาจต่ำกว่าอัตราภาษีเงินได้ทั่วไปเงินปันผลแบบปลอดภาษี
บริษัทที่ออก QSBS มักจะอยู่ในระยะการเติบโตและมีแนวโน้มที่จะนำผลกำไรไปลงทุนใหม่ แทนที่จะต้องจ่ายเป็นเงินปันผล ซึ่งเปลี่ยนกลยุทธ์ไปเป็นการเพิ่มเงินทุนในระยะยาว ซึ่งทำให้ไม่ต้องเสียภาษีจนถึงขีดจำกัดการยกเว้นความสามารถในการโอนข้อยกเว้น
ในบางสถานการณ์ บริษัทสามารถโอนประโยชน์ทางภาษีของ QSBS ให้กับทรัสต์หรือส่งต่อให้กับทายาทเพื่อให้คนรุ่นอื่นๆ ไม่ต้องเสียภาษีจำนวนมากได้การจัดการกับการขาดทุน
ในขณะที่แง่มุมหลักของ QSBS คือผลกำไร แต่การขาดทุนก็ได้รับการจัดการแบบพิเศษเช่นกัน ในบางกรณี การขาดทุนจากการขาย QSBS ก็อาจเข้าเกณฑ์เป็นการขาดทุนปกติแทนที่จะเป็นการขาดทุนจากเงินลงทุน ทําให้มีการดําเนินการด้านภาษีที่เอื้อประโยชน์มากขึ้นการลงทุนผ่านนิติบุคคลที่เป็นตัวกลาง
คุณยังสามารถถือครอง QSBS ผ่านนิติบุคคลที่เป็นตัวกลางบางประเภทได้ เช่น ห้างหุ้นส่วนหรือบริษัทประเภท S ประโยชน์ทางภาษีสามารถหมุนเวียนไปให้สมาชิกแต่ละคน โดยอาจมีความซับซ้อนและข้อจํากัดบางอย่าง
ประโยชน์ที่แท้จริงของ QSBS มาจากการเชื่อมโยงประโยชน์เหล่านี้เข้ากับกลยุทธ์ด้านภาษีแบบหลายระดับที่มีความสอดคล้องกัน ประโยชน์แต่ละอย่างจะเพิ่มขึ้นเมื่อใช้ร่วมกับประโยชน์ด้านอื่นๆ ซึ่งช่วยเร่งการเติบโตของสินทรัพย์และลดความเสี่ยงได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
ขีดจํากัดและความเสี่ยงของ QSBS
แม้ว่า QSBS มีประโยชน์ทางการเงินมากมาย แต่ก็มีข้อเสียที่ต้องพิจารณา สิ่งที่คุณควรรู้เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงข้อผิดพลาดเมื่อได้รับ ถือครอง และขาย QSBS มีดังนี้
ระยะเวลาการถือครอง
หนึ่งในข้อจํากัดหลักคือข้อกําหนดระยะเวลาถือครองที่ 5 ปี หากต้องการรับสิทธิประโยชน์จาก QSBS คุณต้องถือหุ้นนานกว่า 5 ปี ระยะเวลาที่สั้นกว่านี้อาจะทำให้คุณเสียประโยชน์ด้านภาษีได้ขีดจํากัดสินทรัพย์
สถานะ QSBS ใช้กับบริษัทที่มีสินทรัพย์ขั้นต้นมูลค่าไม่เกิน 50 ล้านดอลลาร์สหรัฐทันทีหลังการออกหุ้น หากเกินขีดจํากัดนี้ อาจทําให้สถานะ QSBS ของหุ้นใหม่ไม่เข้าเกณฑ์ธุรกิจที่มีสิทธิ์
บางอุตสาหกรรมไม่มีสิทธิ์เกี่ยวกับ QSBS ธุรกิจด้านบริการ เช่น การดูแลสุขภาพ กฎหมาย และการเงินมักจะไม่มีคุณสมบัติตามเกณฑ์ที่กําหนด ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับประเภทธุรกิจที่ไม่มีสิทธิ์การเปลี่ยนแปลงอัตราภาษี
ประโยชน์ของ QSBS จะผูกกับรหัสภาษีซึ่งอาจมีการเปลี่ยนแปลง หน่วยงานด้านกฎหมายสามารถแก้ไขหรือยกเลิกประโยชน์เหล่านี้ได้ ทําให้การวางแผนในระยะยาวไม่แน่นอนเปอร์เซ็นต์การมีกรรมสิทธิ์
มีขีดจํากัด QSBS ที่บุคคลทั่วไปสามารถยกเว้นออกจากรายได้ขั้นต้นได้ ซึ่งมักจะขึ้นอยู่กับเปอร์เซ็นต์ของกรรมสิทธิ์ในบริษัท นักลงทุนควรตระหนักถึงความแตกต่างเหล่านี้เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงเหตุการณ์ที่ไม่คาดคิดในระหว่างการยื่นภาษีภาษีของรัฐ
แม้ QSBS จะมอบประโยชน์ทางภาษีระดับรัฐบาลกลาง แต่การดําเนินการด้านภาษีของแต่ละรัฐก็อาจแตกต่างกันออกไป บางรัฐปฏิบัติตามกฎของรัฐบาลกลาง ในขณะที่บางรัฐยังไม่ให้ประโยชน์ของ QSBS เลย ตัวอย่างเช่น รัฐแคลิฟอร์เนียการขาดทุนจากเงินทุน
หากธุรกิจล้มเหลว การขาดทุนจาก QSBS จะถือว่าเป็นการขาดทุนจากเงินทุน ซึ่งมีชุดกฎและข้อจํากัดด้านภาษีเป็นของตัวเอง ขาดทุนจากเงินทุนที่มีข้อจํากัดเกี่ยวกับการลดหย่อนภาษีซึ่งแตกต่างจากการขาดทุนทางธุรกิจทั่วไป
Stripe Atlas ช่วยอะไรได้บ้าง
Stripe Atlas สร้างรากฐานด้านกฎหมายของบริษัทเพื่อให้คุณสามารถระดมทุน เปิดบัญชีธนาคาร และรับชำระเงินได้ภายใน 2 วันทำการจากทุกที่ทั่วโลก
ร่วมเป็นส่วนหนึ่งกับบริษัทกว่า 75,000 แห่งที่จดทะเบียนจัดตั้งโดยใช้ Atlas ซึ่งรวมถึงสตาร์ทอัพที่ได้รับการสนับสนุนจากนักลงทุนชั้นนำอย่าง Y Combinator, a16z และ General Catalyst
การสมัครใช้งาน Atlas
การสมัครเพื่อจัดตั้งบริษัทกับ Atlas ใช้เวลาไม่ถึง 10 นาที คุณจะเลือกโครงสร้างบริษัทของคุณ จากนั้นจะยืนยันได้ทันทีว่าชื่อบริษัทของคุณใช้งานได้หรือไม่ และเพิ่มผู้ร่วมก่อตั้งได้ไม่เกิน 4 คน นอกจากนี้ คุณยังตัดสินใจได้ว่าจะแบ่งหุ้นอย่างไร สำรองหุ้นบางส่วนไว้สำหรับนักลงทุนและพนักงานในอนาคต แต่งตั้งเจ้าหน้าที่ และลงนามเอกสารทั้งหมดแบบอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ จากนั้นผู้ร่วมก่อตั้งจะได้รับอีเมลเชิญให้ลงนามในเอกสารทางอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ด้วยเช่นกัน
การรับชำระเงินและการธนาคารก่อนที่จะได้รับ EIN ของคุณ
หลังจากจัดตั้งบริษัทแล้ว Atlas จะยื่นขอหมายเลขประจำตัวนายจ้าง (EIN) ให้คุณ โดยผู้ก่อตั้งที่มีหมายเลขประกันสังคม ที่อยู่ และหมายเลขโทรศัพท์มือถือของสหรัฐอเมริกาจะมีสิทธิ์ได้รับการดำเนินการแบบเร่งด่วนจาก IRS ส่วนผู้ก่อตั้งที่ไม่มีข้อมูลดังกล่าวก็จะได้รับการดำเนินการแบบมาตรฐาน ซึ่งอาจใช้เวลานานขึ้นเล็กน้อย นอกจากนี้ Atlas ยังรองรับการชำระเงินและการธนาคารก่อนมี EIN ด้วย คุณจึงเริ่มรับชำระเงินและทำธุรกรรมต่างๆ ได้ก่อนที่จะได้รับ EIN
การซื้อหุ้นของผู้ก่อตั้งแบบไร้เงินสด
ผู้ก่อตั้งสามารถซื้อหุ้นเริ่มต้นโดยใช้ทรัพย์สินทางปัญญา (เช่น ลิขสิทธิ์หรือสิทธิบัตร) แทนเงินสดได้ โดยหลักฐานการซื้อจะได้รับการจัดเก็บไว้ในแดชบอร์ด Atlas ทรัพย์สินทางปัญญาของคุณจะต้องมีมูลค่าไม่เกิน 100 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐจึงจะใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ได้ หากคุณมีทรัพย์สินทางปัญญาที่มีมูลค่าสูงกว่านั้น โปรดปรึกษาทนายความก่อนที่จะดำเนินการต่อ
การยื่นเอกสารการเลือกสถานะภาษี 83(b) อัตโนมัติ
ผู้ก่อตั้งสามารถยื่นเอกสารการเลือกสถานะภาษี 83(b) เพื่อลดหย่อนภาษีเงินได้บุคคลธรรมดาได้ โดย Atlas จะยื่นเอกสารให้คุณ (ไม่ว่าจะเป็นผู้ก่อตั้งในสหรัฐอเมริกาหรือนอกสหรัฐอเมริกา) โดยใช้ USPS Certified Mail และติดตามข้อมูล คุณจะได้รับเอกสารการเลือกสถานะภาษี 83(b) ที่ลงนามและหลักฐานการยื่นเอกสารโดยตรงในแดชบอร์ด Stripe
เอกสารทางกฎหมายของบริษัทระดับโลก
Atlas ให้บริการเอกสารทางกฎหมายทั้งหมดที่คุณจำเป็นต้องใช้ในการเริ่มดำเนินบริษัท โดยเอกสารสำหรับบริษัทประเภท C ของ Atlas ได้รับการสร้างขึ้นโดยร่วมงานกับ Cooley ซึ่งเป็นหนึ่งในสำนักงานกฎหมายการร่วมลงทุนชั้นนำของโลก เอกสารเหล่านี้ออกแบบมาเพื่อช่วยให้คุณระดมทุนได้ทันทีและช่วยให้มั่นใจว่าบริษัทของคุณจะได้รับการคุ้มครองตามกฎหมาย โดยครอบคลุมถึงแง่มุมต่างๆ เช่น โครงสร้างการเป็นเจ้าของ การแจกจ่ายหุ้น และการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดด้านภาษี
Stripe Payments ฟรีหนึ่งปี พร้อมเครดิตและส่วนลดสำหรับพาร์ทเนอร์มูลค่า 50,000 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
Atlas ร่วมงานกับพาร์ทเนอร์ระดับแนวหน้าเพื่อมอบส่วนลดและเครดิตสุดพิเศษกับผู้ก่อตั้ง ซึ่งได้แก่ส่วนลดสำหรับเครื่องมือที่จำเป็นสำหรับการทำงานด้านวิศวกรรม ภาษี การเงิน การปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนด และการปฏิบัติงานจากผู้นำอุตสาหกรรมอย่าง AWS, Carta และ Perplexity เรายังมอบตัวแทนที่จดทะเบียนในรัฐเดลาแวร์ให้คุณโดยไม่เสียค่าใช้จ่ายในปีแรกด้วยเช่นกัน นอกจากนี้ ในฐานะผู้ใช้ Atlas คุณยังได้รับสิทธิประโยชน์เพิ่มเติมจาก Stripe เช่น การประมวลผลการชำระเงินแบบไม่เสียค่าใช้จ่ายสูงสุด 100,000 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นเวลาสูงสุด 1 ปี
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่ Atlas ช่วยคุณจัดตั้งธุรกิจใหม่ได้อย่างรวดเร็วและง่ายดาย และเริ่มใช้งานได้เลยวันนี้
เนื้อหาในบทความนี้มีไว้เพื่อให้ข้อมูลทั่วไปและมีจุดประสงค์เพื่อการศึกษาเท่านั้น ไม่ควรใช้เป็นคําแนะนําทางกฎหมายหรือภาษี Stripe ไม่รับประกันหรือรับประกันความถูกต้อง ความสมบูรณ์ ความไม่เพียงพอ หรือความเป็นปัจจุบันของข้อมูลในบทความ คุณควรขอคําแนะนําจากทนายความที่มีอํานาจหรือนักบัญชีที่ได้รับใบอนุญาตให้ประกอบกิจการในเขตอํานาจศาลเพื่อรับคําแนะนําที่ตรงกับสถานการณ์ของคุณ