As more and more payment methods have become available worldwide, customer behavior and expectations have shifted. In 2024, global cash usage declined by 4%, with a significant shift toward digital payments.
While the popularity of specific payment methods depends on where customers are located, what they’re buying, and whether they’re making a purchase online or in person, customers still expect businesses to offer fast, secure, and flexible payment options.
Below, we’ll explain how to choose a set of payment options tailored to your business and customers, how to set up a payment system equipped to support those payment methods, and what’s required to accept multiple forms of payment from customers. Here’s what you should know.
What’s in this article?
- Why it’s important to accept multiple payment methods
- How to split a payment onto multiple payment methods
- How to decide which payment methods to accept
- How to set up a payment system for multiple payment methods
- Types of payment methods—and how to accept them
- How Stripe Payments can help
Why it’s important to accept multiple payment methods
As the payments industry continues to evolve, businesses should offer a variety of payment methods to meet rising customer expectations. Here’s why businesses should diversify their payment methods:
Convenience for customers: Customers have different preferences and limitations around payment methods. By accepting multiple methods, businesses cater to a wider range of needs, making it easier for shoppers to complete purchases.
Boosting sales and conversion rates: Accepting more payment options increases sales and improves conversion rates because customers are less likely to abandon their carts.
Enhancing customer experience and satisfaction: By offering a variety of payment options businesses can show they are customer-centric, which improves the overall shopping experience and increases customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reaching a wider customer base: Different demographic groups may prefer different payment methods. For instance, younger customers might favor digital wallets or peer-to-peer (P2P) apps, while older customers might prefer credit cards or bank transfers.
Improving cash flow management: Different payment methods have different processing times. Accepting a mix of payment methods means businesses receive some payments faster than others, which helps cash flow management.
Staying competitive: Accepting multiple payment options is becoming standard practice in many industries. As more businesses adopt a wide array of payment methods, those that don’t adapt may find themselves at a disadvantage.
Adapting to global markets: If a business operates internationally or plans to expand, it should accept payment methods that are popular in different regions and countries.
Reducing dependency on a single payment provider: Relying on one payment method can be risky. If there are technical issues or changes in provider policies, having alternate options preserve business continuity.
Security and fraud prevention: Different payment methods come with different security features and fraud prevention mechanisms. Offering a range of options can help protect the business and its customers.
Responding to technological advances and trends: As technology evolves, so do payment methods. Staying up-to-date with the latest payments technology and trends, such as mobile payments and cryptocurrencies, keeps a business relevant.
Compliance and regulatory requirements: Some payment methods may be better suited to regulatory requirements in certain industries or regions.
How to split a payment onto multiple payment methods
If a customer asks to split a payment across multiple payment methods, businesses should be prepared to handle this smoothly. Here's how a business can split a payment onto multiple payment methods.
1. Confirm your system supports split payments
Check your point-of-sale (POS) system or payment processor to ensure it supports multiple payment types for a single transaction.
2. Ask the customer how they want to split it
Find out how many payment methods the customer wants to use and what amount should go on each method. Confirm that the math adds up to the total amount owed.
3. Enter the first partial payment
Begin processing the first payment by entering it as a partial payment into your POS or payment processor. Wait for confirmation before moving on.
4. Enter the remaining partial payments
After the first successful payment, enter the remaining partial payments one at a time. Make sure each transaction is confirmed.
How to decide which payment methods to accept
Make sure your business is equipped to accept the payment methods your customers like to use. Here’s how to determine what those are:
Advanced customer analytics: Using tools such as Google Analytics, customer relationship management (CRM) software, or specialized fintech analytics platforms, analyze customer data to access customer demographics, purchasing habits, and payment preferences. Segment your customer base and analyze spending patterns.
Industry-specific payment trends: Research payment trends in your industry. You can do this by attending conferences, subscribing to trade journals, and networking with peers. Certain industries may gravitate to specific payment technologies (e.g., near-field communication (NFC) payments in retail, subscription models for software services).
Detailed cost-benefit analysis of payment methods: Consider transaction fees, implementation costs, maintenance expenses, chargeback fees, and the potential impact on cash flow. Use financial modeling to forecast the impact of different payment methods on your bottom line.
In-depth security assessment: Work with information technology (IT) and cybersecurity experts to evaluate the security features of different payment platforms. This includes compliance with standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for credit card transactions, data encryption standards, and fraud detection capabilities.
Technology adoption trends and forecasts: Stay abreast of emerging payment technologies, such as blockchain-based payments, biometrics, and AI-driven payment systems, and predict how they might be adopted in your market. Consider consulting with fintech experts or technology forecasters.
Multichannel sales analysis: Businesses with multiple sales channels can analyze which payment methods work best for each channel. For example, mobile payment options might be more popular for online sales, while traditional methods such as cash or credit cards might dominate in physical stores.
International market analysis: Global businesses should conduct a market-specific analysis. This includes understanding local payment preferences, regulatory environments, currency exchange risks, and partnership opportunities with local providers.
Competitive intelligence gathering: Use advanced tools and services for competitive analysis. Monitor direct competitors as well as industry leaders and innovators. Look for patterns in which payment methods they accept.
Integration capabilities assessment: Evaluate the integration capabilities of different payment methods with your technology stack, including your enterprise resource planning (ERP), CRM, accounting software, and other operational tools. The goal is to create a smooth, automated workflow that minimizes manual intervention.
Structured customer feedback mechanisms: Develop structured methods to gather customer feedback on payment preferences. This could involve advanced survey techniques, focus groups, or social listening.
Experimental pilots and A/B testing: Run experimental pilots with different payment methods in controlled environments. Use A/B testing to compare performance, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
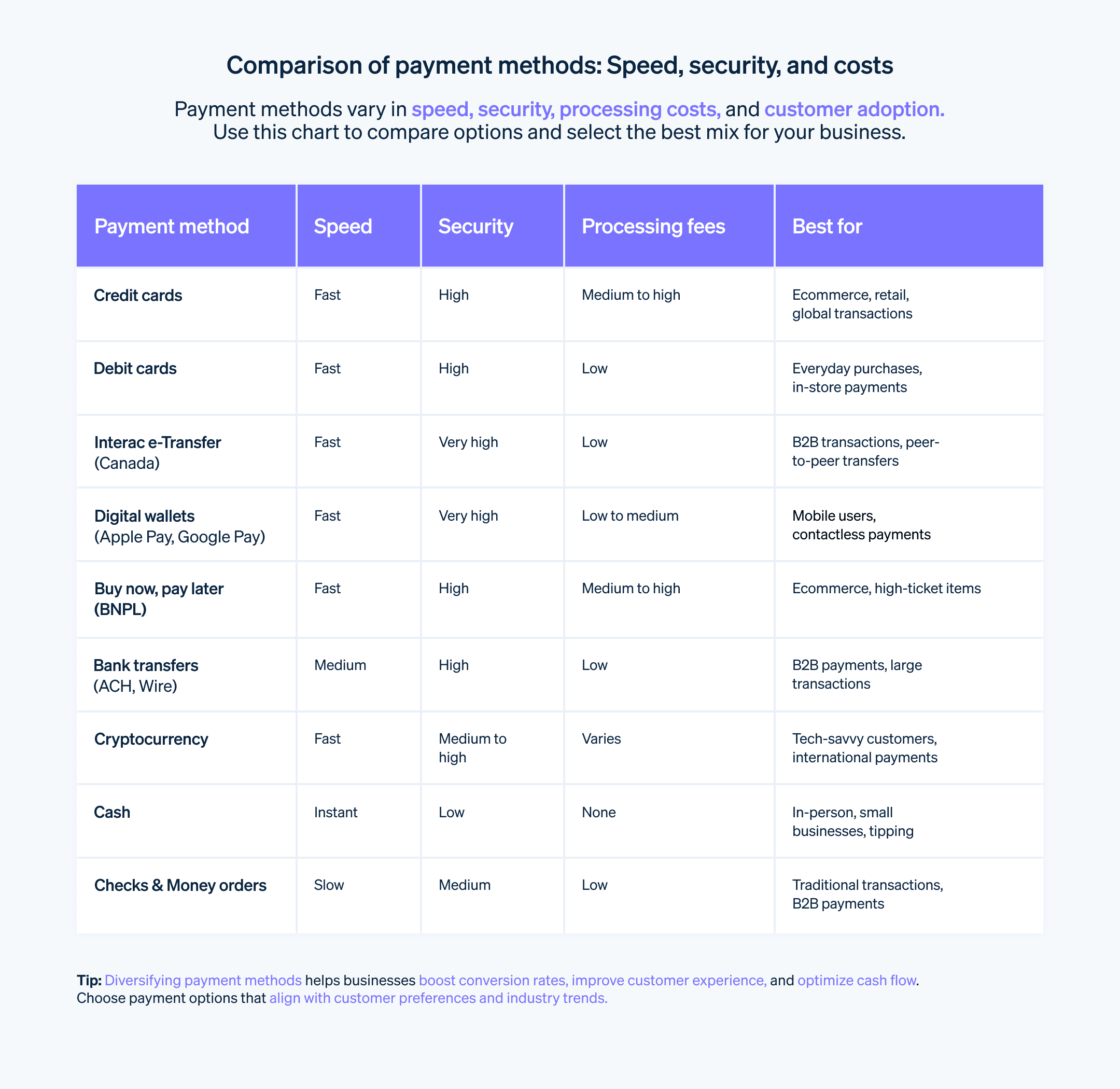
How to set up a payment system for multiple payment methods
Once you know which payment methods you want to offer customers, make sure you can accommodate these methods. Here are the key points to consider when evaluating and setting up your payment processing system:
1. Choose a payment gateway and processor: Your gateway and processor should support your chosen payment methods, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and others. Evaluate their service fees, transaction processing times, and reliability records.
2. Integrate into your existing system: Ensure the payment system works with your business setup, such as ecommerce platforms, financial software, and CRM systems. This will help in automating processes and maintaining accurate records.
3. Adhere to security standards: Your system should comply with security standards, such as PCI DSS for credit card handling, incorporate strong fraud detection and prevention mechanisms, and comply with all relevant data protection laws.
4. Create intuitive user interfaces: The payment interface should be straightforward for customers, with clear payment method options. The backend should be easy to navigate for managing transactions, issuing refunds, and accessing reports.
5. Ensure mobile device compatibility: With the rise in mobile transactions, your system should work on mobile devices and support mobile wallet and app payments.
6. Accept multicurrency and international payments: If your business operates globally, the system should process multiple currencies and adhere to international payment rules.
7. Allow for system scalability: Choose a system that can grow with your business, accommodating increasing transaction volume and new payment methods efficiently.
8. Offer reliable customer support: Select a service provider known for excellent customer support that can help with setup as well as ongoing operational issues.
9. Access comprehensive training and resources: Access to detailed training and resources for you and your team is important for maintaining efficiency and reducing errors.
10. Conduct extensive testing before launch: Test the system thoroughly to identify and resolve issues. This testing should cover all payment methods and include scenarios such as refunds and transaction failures.
11. Implement transaction monitoring and analysis: Use monitoring capabilities to spot trends, manage finances effectively, and make informed business choices.
12. Backup systems and create data recovery plans: Establish backup systems and data recovery procedures in case of system failures and to prevent data loss.
Types of payment methods—and how to accept them
There are many types of payment methods available, and modern payment providers offer a stack of methods you can choose from without needing additional setup. Here are some common methods to know:
Traditional methods
Cash: Though cash is declining in popularity, it remains a widely accepted option, especially for small transactions.
Checks: Checks are still used by certain populations who favor a paper-based payment method, but they have longer processing times and fraud risks.
Money orders: Money orders guarantee funds but have the same drawbacks as checks.
Wire transfers: Wire transfers are often used for large transactions or international payments.
Accepting traditional payment methods
Cash
Equipment: No additional equipment needed—just a cash register or designated secure drawer.
Considerations: Security risks of handling cash, requires manual counting and in-person deposits, is susceptible to theft or loss.
Checks
Equipment: Check imprinter for capturing account information, endorsement stamp, optional check reader to allow for faster processing.
Procedures: Verify identity and signature, check for sufficient funds (which may require calling a bank), endorse and deposit check within a preset time.
Considerations: Processing times can be long, checks can bounce, and there are fraud risks.
Money orders
Equipment: Check imprinter, endorsement stamp, optional check reader.
Procedures: Verify identity, signature, and amount. Endorse and deposit.
Considerations: Checking the issuer and purchase location details can mitigate fraud risks.
Wire transfers
Requirements: Requires customer information, such as bank account details, routing number, amount, and reference code. A bank account is required for receiving transfers.
Considerations: Fees for sender and receiver, plus potential delays depending on banks involved.
Tips for all traditional methods
Clearly display accepted payment methods: Inform customers at checkout or on invoices.
Establish deposit procedures: Securely store and deposit cash/checks regularly.
Train staff on fraud prevention: Identify suspicious activity, and implement verification protocols.
Consider cash management services: These could be armored car services or secure cash drops for larger businesses.
Card-based methods
Credit cards: Credit cards are convenient, widely used, and let customers pay later while accruing interest or rewards.
Debit cards: Similar to credit cards, but debit cards deduct funds directly from a customer’s bank account.
Prepaid cards: Loaded with funds in advance.
Contactless payments: NFC technology enables instant payments with a tap via card or digital wallets.
Accepting card-based payment methods
Credit and debit cards
Equipment and software: Point-of-sale (POS) system with a card reader (physical terminal or mobile reader). Merchant accounts and payment gateways are needed to process transactions securely.
Procedures: Customers swipe, dip, or tap the card. The transaction is authorized and your business receives payment confirmation.
Considerations: PCI compliance for data security, transaction fees, and chargeback management.
Prepaid cards
Accepted by most POS systems through the same process as credit/debit cards.
Considerations: Verify card balance before accepting payment to avoid problems related to insufficient funds. Some prepaid cards have limited functionality.
Contactless payments
Equipment: NFC-enabled reader for tap-to-pay transactions.
Considerations: While the popularity of contactless payments is growing, some customers may still prefer traditional methods.
Digital/online methods
Online payment gateways: Platforms such as PayPal, Stripe, or Square integrate with websites or apps to accept online payments.
Digital wallets: Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay store payment information digitally for quick and secure checkout.
Buy now, pay later (BNPL): BNPL services such as Klarna or Affirm let customers split payments into installments.
Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies have limited acceptance for payment at most businesses.
Accepting digital/online payment methods
Online payment gateways
Choose a provider: Compare the features and fees of popular options, such as Stripe or PayPal, before making your final choice.
Integrate with your website or app: Follow the provider’s instructions for integration.
Set up payment options: Define currencies, accepted cards, and any additional features.
Manage transactions: Access transaction history, reconcile payments, and handle refunds.
Digital wallets
Enable support for major wallets: Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, etc.
POS system compatibility: Make sure your reader or checkout system supports contactless payments.
Customer awareness: Promote the digital wallet payment option during checkout.
BNPL
Partner with a BNPL provider: Choose a service such as Klarna or Affirm that aligns with your target audience and business model.
Integrate with checkout: Offer a BNPL option alongside other payment methods.
Manage installment payments: Set up automatic deductions and procedures for handling potential late fees or defaults.
Cryptocurrency
Choose a cryptocurrency payment processor: Compare security, transaction fees, and supported currencies.
Clearly display accepted cryptocurrencies: Inform customers at checkout or on invoices.
Understand crypto volatility: Be prepared for price fluctuations and potential risks associated with cryptocurrency.
Emerging methods
Open banking: Sharing financial data with third-party providers via application programming interfaces (APIs) to streamline payments.
QR code payments: Scannable codes linked to payment apps facilitate quick and contactless transactions.
Accepting emerging payment methods
Open banking
Partner with an open banking provider: Choose a reputable service that complies with regulations and security standards.
Integrate with your website or app: Follow the provider’s instructions for secure API integration.
Obtain customer consent: Clearly explain the benefits of open banking and obtain explicit consent to access customers’ financial data.
Facilitate account-to-account payments: Enable customers to initiate payments from their bank accounts, often with lower fees than traditional card transactions.
QR code payments
Choose a payment provider or app: Popular options include PayPal, Venmo, Alipay, and WeChat Pay.
Generate QR codes: Create QR codes for each transaction or product, and link them to your payment account.
Display and pay: Place QR codes at checkout counters, on product labels, in invoices, or online. Customers scan codes with their smartphone cameras to initiate payment.
Tips
Partnerships with banks and fintechs: Collaborate with financial institutions to offer innovative payment solutions and services.
Cross-border payments: Explore open banking’s potential for facilitating international transactions with reduced fees and faster processing times.
Integration with loyalty programs: Link QR codes with loyalty points or discounts to increase customer engagement.
Other methods
These payment options include invoice payments and subscriptions.
Accepting other payment methods
Invoice payments
Invoice software or templates: Choose a platform or create invoices detailing services, costs, and due dates.
Payment options: Accept multiple methods such as online payment gateways, credit card processing, bank transfers, or checks.
Delivery channels: Send invoices electronically via email or online portals, or offer printable versions for traditional payment methods.
Payment reminders: Set up automated reminders for approaching due dates, and implement a follow-up system for late payments.
Subscriptions
Subscription management platform: Choose a service, such as Stripe Billing, to manage recurring payments securely.
Subscription plans and pricing: Define different subscription tiers with specific features and pricing options.
Secure customer information: Implement data security measures to protect stored payment details.
Cancellation process: Make it easy for customers to cancel or manage their subscriptions within the platform.
Flexible billing options: Offer annual, monthly, or prorated billing based on your business model.
Tips
Straightforward payment process: Make it simple and convenient for customers to pay invoices or manage their subscriptions.
Payment flexibility: Cater to diverse customer preferences by providing a variety of payment methods.
Clear communication: Clearly communicate invoices, payment terms, and subscription details to avoid confusion.
Task automation: Use software and automation to manage invoices, subscriptions, and payment reminders efficiently.
Payment data analysis: Track payment trends and customer behavior to improve your billing process and pricing strategies.
Partial payments: For larger bills, let customers pay invoices in installments.
Free trials or introductory offers: Attract new subscribers with limited-time free trials or discounted pricing.
How Stripe Payments can help
Stripe Payments provides a unified, global payments solution that helps any business—from scaling startups to global enterprises—accept payments online, in person, and around the world.
Stripe Payments can help you:
- Optimize your checkout experience: Create a frictionless customer experience and save thousands of engineering hours with prebuilt payment UIs, access to 125+ payment methods, and Link, a wallet built by Stripe.
- Expand to new markets faster: Reach customers worldwide and reduce the complexity and cost of multicurrency management with cross-border payment options, available in 195 countries across 135+ currencies.
- Unify payments in person and online: Build a unified commerce experience across online and in-person channels to personalize interactions, reward loyalty, and grow revenue.
- Improve payments performance: Increase revenue with a range of customizable, easy-to-configure payment tools, including no-code fraud protection and advanced capabilities to improve authorization rates.
- Move faster with a flexible, reliable platform for growth: Build on a platform designed to scale with you, with 99.999% uptime and industry-leading reliability.
Learn more about how Stripe Payments can power your online and in-person payments, or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.