在当今全球化的世界里,越来越多的企业在多个州或国家/地区开展业务。这为企业带来了在更多市场上获得成功的机会,但也引发了复杂的税务问题。
了解两个重要的税务术语——关联和销售税关联——对于那些需要遵守销售税义务的扩展型企业至关重要。未能遵守相关规定可能会导致严重的财务罚款,且未能妥善管理销售税义务的企业还可能面临声誉损害甚至法律诉讼。此外,了解销售税关联可以帮助企业确定其需要在哪些地区征收和缴纳销售税,从而准确计算在不同管辖区开展业务的成本,并遵守税法要求。
本文将介绍关联和销售税关联的定义,包括哪些活动可以触发销售税关联、不同类型的关联,以及企业如何判断在特定管辖区内是否存在销售税关联。您还将了解帮助企业管理销售税义务、保持合规并避免潜在处罚或法律行动的最佳实践。
目录
- 什么是关联税?
- 销售税关联的类型
- 销售税关联
- Stripe 能提供什么帮助
Stripe 在 IDC MarketScape 中被评为领导者
《IDC MarketScape:2024 年全球 SaaS 和云端支持的 SaaS 销售与使用税自动化软件中小型市场供应商评估报告》赞誉了 Stripe 在集成便利性、可靠性以及平台和交易市场支持等方面的实力,并将其评选为税自动化软件领域的“领导者”。了解更多。
什么是关联税?
关联税,也称为“关联费”或“关联附加费”,是州或司法管辖区对在其境内有销售税联结的企业征收的一种税费。当企业在某个州或管辖区内有足够的联系或存在(如物理存在或经济活动),从而触发了销售税收义务时,就会形成销售税关联。
关联税是根据企业具有销售税关联的州或管辖区的具体规则和税率计算的。通常,关联税是企业在该州或管辖区内总销售额或收入的一定百分比。具体百分比会因州或管辖区的不同而有很大差异,有些州还可能征收额外的费用或附加费。
例如,有销售税关联的企业需要对在以下州内进行的应税销售收取和缴纳州和地方销售税:
加利福尼亚州
加利福尼亚州的州销售税率目前为 7.25%,但当地销售税率可能从 0.1% 到 2.5% 不等,具体取决于具体地点。纽约州
纽约州的销售税率目前为 4%,但当地销售税率从 3% 到 4.875% 不等,具体取决于具体地点。德克萨斯州
德克萨斯州的州销售税率目前为 6.25%,但当地销售税率可能从 0.5% 到 2% 不等,具体取决于具体地点。
销售税关联的类型
销售税关联是企业与产生销售税义务的州或司法管辖区之间的联系或关系。有不同类型的销售税关联可以触发征收和上缴销售税的要求,包括:
物理联系
当企业在某个州或管辖区内有物理存在(如商店、仓库或办公室)时,就会形成物理关联。这种关联类型是销售税征收的传统标准,并通过各种法院案例得到了确立。物理关联的例子包括企业在某个州拥有的物理地点、雇员或库存。经济关联
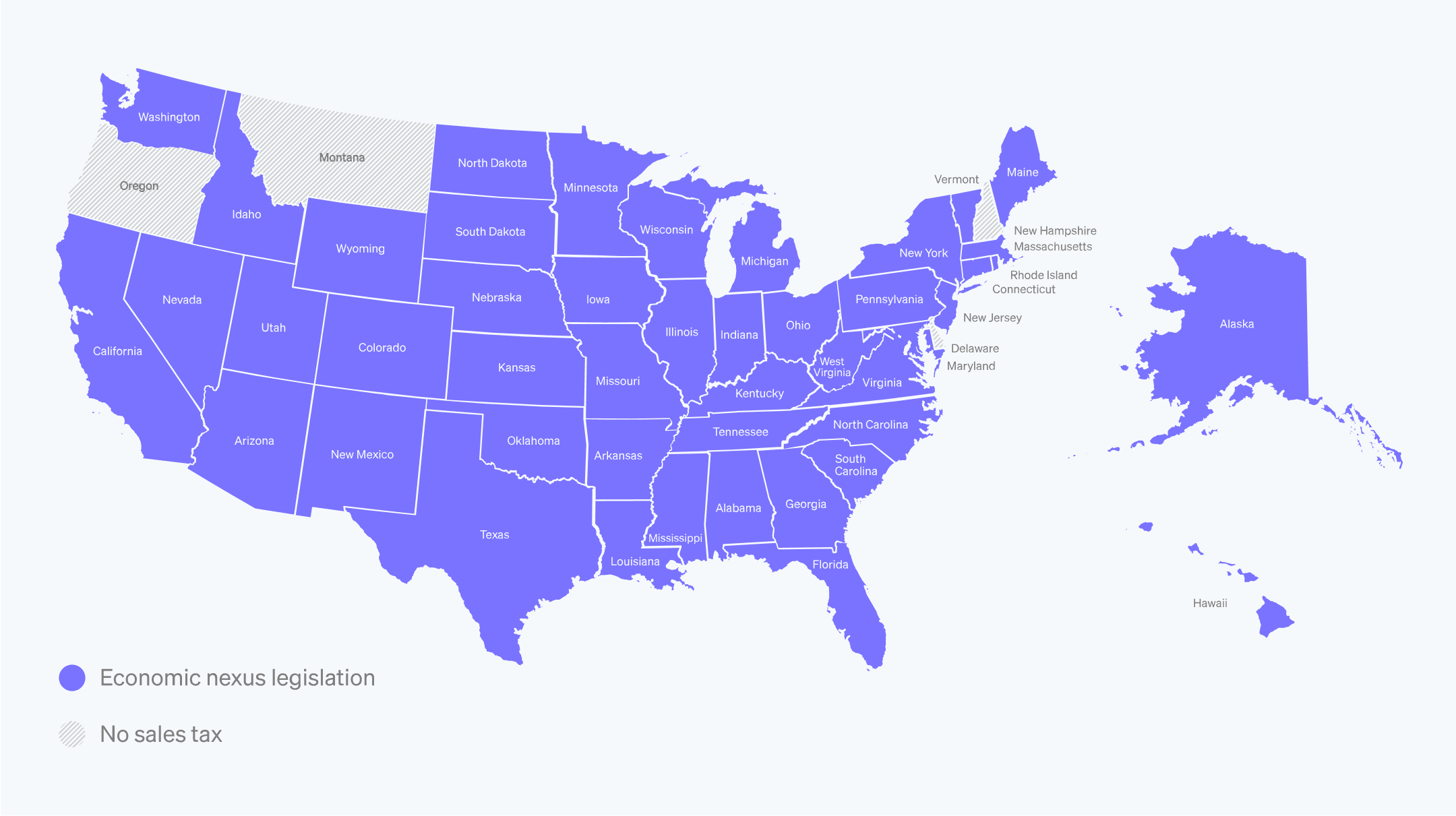
当企业在某个州或管辖区内有一定程度的经济活动,即使没有物理存在,也会形成经济关联。经济关联法律通常设定一个销售、交易或收入的阈值;如果达到或超过该阈值,企业就需要征收和缴纳销售税。近年来,许多州为了响应南达科他州诉 Wayfair 案的最高法院裁决,制定了经济关联法律,该裁决要求企业在任何州进行的交易超过 200 笔或销售额超过 10 万美元时,即使没有物理存在,也必须征收和上缴销售税。联盟关联
联盟关联是指企业与另一家在某个州有物理存在的企业之间存在关系时产生的。这种情况可能发生在企业在某个州拥有关联公司或子公司(例如拥有共同的所有者或品牌)时。关联关联法律通常要求,如果关联企业在该州有物理存在,企业就需要征收和上缴销售税。点击 (Click-through) 关联
点击关联是在企业与某个州的第三方卖家或推荐代理之间存在关系时形成的。这种情况可能发生在企业支付佣金或推荐费给第三方,以换取通过其网站或营销活动达成的销售。点击关联法律通常要求,如果第三方在该州有物理存在,企业就需要收取并缴纳销售税。
销售税关联
销售税关联是指企业与州或地方政府之间的联系,这种联系会触发企业收取并上缴销售税的要求。关联代表企业在某个州达到的最低活动阈值,当满足这一阈值时,企业有义务在该州收取并上缴销售税。
例如,假设您经营一家销售手工蜡烛的在线商店。您的企业位于亚利桑那州,但您也在加利福尼亚州、德克萨斯州和纽约州销售蜡烛。每个州都有各自的销售税法律和税率,所以您需要确定是否在这些州符合销售税关联的标准。
在加利福尼亚州,如果您在当前或上一日历年度的销售额超过 50 万美元,就会形成销售税关联。2019 年 4 月 25 日起,加州取消了之前关于交易次数的阈值。而在科罗拉多州,如果企业在任何一年中的销售额超过 10 万美元,就符合销售税关联的标准。
销售税关联可以通过多种活动或因素产生,例如在某个州或管辖区内有物理存在、经济活动、联盟关联或点击关联。一旦形成销售税关联,企业就需要对该州或管辖区内的应税销售收取并上缴销售税。各州和管辖区的销售税关联规则和要求各不相同,企业需要了解其销售税关联义务,并遵守所有适用的税法,以避免潜在的罚款或法律诉讼。
建立销售税关联的标准
虽然没有统一的标准来设立销售税关联,但通常在确定企业是否在某个州或管辖区有销售税义务时,会考虑多个因素。以下是设立销售税关联的一些常见标准:
物理存在
在某个州或管辖区有物理存在可以形成销售税关联。这包括在该州有物理办公地点、商店、仓库或其他物业,或有员工或独立承包商在该州工作。经济活动
许多州已制定经济关联法律,这些法律为在某州满足一定销售、交易或收入阈值的企业建立销售税义务。这些阈值在各州之间差异很大,并且可能会发生变化。这里有美国各州经济关联标准的完整列表。联盟关系
一些州有关联关联法律,对于在州内拥有关联公司或子公司的企业,这些法律会建立销售税义务。当企业与该州的附属公司或子公司有共同所有者、品牌或其他联系时,就会发生这种情况。点击关系
一些州有点击关联法律,对于与州内第三方卖家或推荐代理存在关系的企业,这些法律会建立销售税义务。这种情况可能发生在企业支付佣金或推荐费给第三方,以换取通过其网站或营销活动达成的销售。
销售税关联对企业的影响
销售税关联对企业的影响可能很大,这取决于各州或管辖区的具体情况和要求。企业了解在哪些州和管辖区存在销售税关联及其影响非常重要,包括:
合规成本
销售税关联对企业的最显著影响之一是遵守州和地方税法的成本。在多个州或管辖区有销售税关联的企业,可能需要注册销售税许可证、收取并上缴应税销售的销售税、定期提交销售税申报表,并保存销售和已收税款的详细记录。罚款和利息
企业未能遵守销售税关联要求,可能会因延迟或错误的申报或付款而面临罚款和利息。这些罚款可能非常高,且累积速度很快,会为企业带来额外的成本和财务负担。竞争劣势
没有妥善管理销售税义务的企业,相较于遵守税法的企业可能面临竞争劣势。合规企业可以准确计算在不同管辖区的经营成本,而不合规企业可能在价格或其他方面难以与之竞争。声誉损害
未能遵守销售税关联要求也会导致企业的声誉受损。客户可能不愿与有税务合规问题历史的公司进行业务往来,负面宣传或法律行动会损害企业的声誉和品牌形象。
企业遵守销售税关联法律的步骤
遵守销售税关联法律对于企业,尤其是那些在多个州或管辖区有销售税义务的企业来说,可能是一个复杂而具有挑战性的任务。以下是一些企业可以采取的措施,以遵守销售税关联法律:
确定您的销售税关联所在
遵守销售税关联法律的第一步是确定企业在哪些地方有销售税义务。这涉及识别企业在哪些地方有物理存在、经济活动、关联关系或点击关系,并了解您有业务活动的每个州或管辖区的销售税关联要求。注册销售税许可证
一旦确定了销售税义务所在,就需要在每个有关联的州或管辖区注册销售税许可证。这通常包括填写申请表,并提供有关企业的信息,例如联邦税号、企业类型和联系方式。为简化改流程,可以让 Stripe 管理您在美国的税务注册流程,并可特享预先填写申请细节的简化流程,从而节省您的时间并确保符合当地法规。征收并上缴销售税
注册销售税许可证后,需要对在每个有关联的州或管辖区内的应税销售征收并上缴销售税。这通常包括向客户收取适当的销售税税率、跟踪销售和已收税款,并定期提交销售税申报表并向州或管辖区上缴销售税。保持详细记录
保存所有销售和已收税款的详细记录对于遵守销售税关联法律至关重要。这包括保留销售账单、收据和其他支持销售税收取和上缴的文档。及时了解销售税关联的最新要求
销售税关联要求经常变更,因此了解每个有关联的州或管辖区的销售税法律和法规的最新情况非常重要。这包括监控销售税税率、阈值和规则的变化,并与合格的税务专业人士合作,确保遵守所有适用的税法。
Stripe 能提供什么帮助
对于希望以最有效的方式处理税务、合规以及持续监测法律和法规变化的企业,科技驱动的解决方案可以消除传统上管理这些问题所需的手动工作。Stripe Tax 是一个全面的税务解决方案,帮助企业通过单一集成自动计算、收取和报告全球支付的税款。这包括帮助企业知道在哪里注册并自动收取正确的税款,还生成企业所需的所有申报报告。
以下是 StripeTax 在销售税关联问题上能为企业带来的具体益处:
自动化销售税计算
Stripe Tax使用实时的销售税率和规则自动计算每笔交易的销售税,考虑到企业在每个有销售税义务的州或管辖区的特定销售税关联要求。这有助于企业确保准确收取正确的销售税,避免潜在的合规问题。全面的销售税覆盖
Stripe Tax 覆盖了美国 50 个州及华盛顿特区的销售税关联要求,以及多个国际管辖区,使得使用 Stripe Tax 的企业在多个州和管辖区的销售税合规变得更加容易。简化的申报和上缴流程
Stripe Tax 可以使申报和上缴过程更加简便。通过我们值得信赖的全球合作伙伴,用户可以从与您的 Stripe 交易数据相关联的无缝体验中受益,让我们的合作伙伴管理您的报税工作,以便您可以专注发展您的业务。可扩展的销售税解决方案
Stripe Tax 设计成可随着企业的成长和业务扩展而扩展。企业可以轻松增加新的销售税义务,不用担心自己管理销售税合规。
Stripe Tax 是简化和自动化企业销售税合规义务的强大解决方案,尤其是在销售税关联问题上。使用 Stripe Tax,企业可以确保在每个有销售税义务的州或管辖区准确征收和上缴销售税,而无需自己处理复杂的销售税规则和要求。请点击此处了解更多信息。
本文中的内容仅供一般信息和教育目的,不应被解释为法律或税务建议。Stripe 不保证或担保文章中信息的准确性、完整性、充分性或时效性。您应该寻求在您的司法管辖区获得执业许可的合格律师或会计师的建议,以就您的特定情况提供建议。