Bank transfers are a routine part of our financial lives, but few people understand how they work. When will a transfer arrive? What will it cost? It's important for business owners to understand the details of accepting bank transfers as a customer payment method. Below, we'll explain the different types of bank transfers and the pros and cons of this payment method.
What's in this article?
- What is a bank transfer?
- Types of domestic bank transfers
- International bank transfer networks
- How long do bank transfers take?
- Benefits of bank transfers for businesses
- Downsides of bank transfers for businesses
- Are bank transfers safe?
- How Stripe Payments can help
What is a bank transfer?
A bank transfer is the electronic movement of funds from one bank account to another. There are many different types of bank transfers, which can be categorised based on where they operate and which network they use to move funds. There are three main types that businesses commonly encounter.
Bank debit transfers
Bank debit transfers occur when an account holder authorises an outside party to "pull" funds from their bank account. The sender provides their name and account details to the recipient, who then uses that information to pull funds from the sender's account into their own. The recipient's bank initiates the funds transfer, not the sender's bank. In customer transactions, the customer gives their bank account information to the business's payment processor, along with authorisation to withdraw the purchase amount from their account.
Bank credit transfers
These transactions use the same network as debit transfers, but the action is reversed: instead of "pulling" money from the sender's account, credit transfers "push" money from the sender's bank account to the recipient's.
Real-time payments
Real-time payments redirect the customer from the business's website to their financial institution's website, where they complete the funds transfer. They're used for domestic purchases in countries such as the US and the Netherlands. India, in particular, is a global leader in the real‑time payment market.
Stripe offers a single integration that supports both domestic and international real-time payments, including Sofort and giropay. Here's how they work with Stripe's checkout experience:
The customer chooses "Pay by Bank" as their payment method during checkout.
They select their bank from a list of supported financial institutions.
They're redirected to their bank's website.
The customer logs in using their bank account credentials.
The customer authorises the payment through their bank.
Once the payment is approved, the customer receives a confirmation.
Finally, they're redirected back to the business's website, where the completed transaction is confirmed.
Types of domestic bank transfers
Bank transfers in the US fall into two categories: ACH transfers and wire (electronic) transfers. These transfers take place on different networks.
Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers
The ACH network allows banks and other financial institutions in the US to send and receive money. It's run by Nacha, an independent organisation that's owned by a large group of banks, credit unions and payment processing companies.
The ACH network bundles together any ACH transactions that come in within a given time frame (usually around four hours on business days) and then periodically settles the transactions in batches throughout the day.
ACH transfers are often used in commercial transactions, but they can be used for many other purposes:
Customer bill payments
Tax refunds
Tax payments
Retirement and investment account contributions
Charity donations
University tuition payments
Funds sent between family and friends
There are two categories of ACH transfers, distinguished by the direction of the funds transfer:
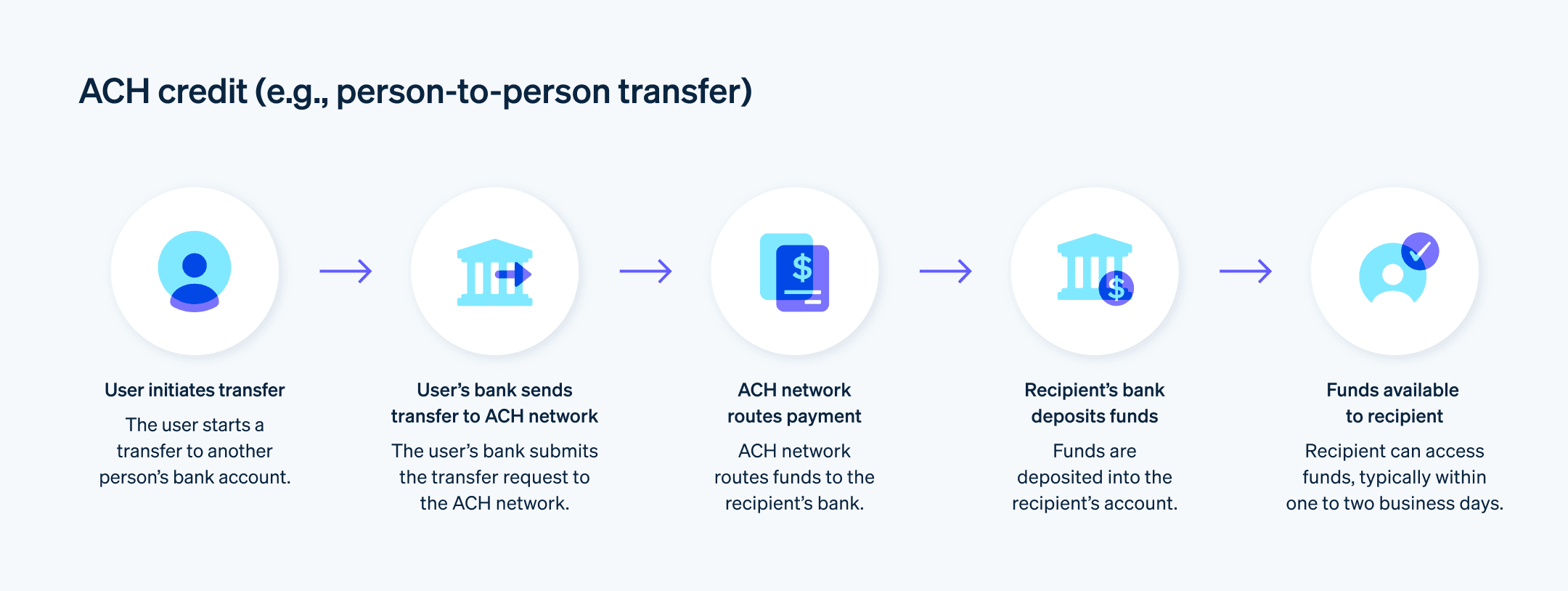
- ACH Credits: With ACH Credits, deposits are initiated by the payer and transferred from their bank account to a payee's account via the ACH network. Employer payroll deposits are a common use case of ACH Credits, with more than 95% of US workers receiving their pay by direct deposit.
- ACH Debits: With ACH Debits, a business initiates the funds transfer from a customer's bank account via the ACH network. Businesses often use these payments for recurring charges (e.g. charging a customer who has set up ACH transfers for a subscription).
Electronic transfers
While ACH transfers transmit funds through the centralised Nacha network, domestic electronic transfers use networks that the Federal Reserve operates. Unlike with ACH transactions, electronic transfers are handled in real time and settled individually. This makes them historically faster than ACH transfers, although recently Nacha has implemented regulatory updates to speed up ACH transfers.
There are two main electronic transfer systems backed by the Federal Reserve: the Fedwire Funds Service and the Clearing House Interbank Payments System (CHIPS). These systems handle the majority of domestic funds transfers and international transactions that use US dollars:
Fedwire: The Fedwire is a real-time settlement system that uses central bank money to electronically transfer funds between businesses, customers, banks and government agencies. Fedwire transfers are very popular in the US. In April 2025 alone, more than 18.6 million Fedwire transfers were sent.
CHIPS: Each financial market has a clearing house that validates and finalizes transactions between buyers and sellers. CHIPS is the clearing house in the US for large bank transfers; the average CHIPS transfer is over $3 million.

International bank transfer networks
International bank transfers between the US and other countries most often use the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network. SWIFT was founded in 1973 to connect more than 11,000 banks and financial institutions in more than 200 countries. This network is managed by central banks in G10 countries, including Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, the UK, the US and Switzerland.
International electronic transfers and currency exchanges that use the SWIFT network require SWIFT codes, which are a type of business identifier code (BIC).
Outside the US, other countries have their own systems for conducting bank transfers within their borders. Here are a few examples:
- Clearing House Automated Payment System (CHAPS): CHAPS is the UK equivalent of ACH. This network is used to process same-day sterling pound payments.
- Bacs: Bacs is a membership organisation made up of 16 top UK banks. In 2023, there were more than 4.8 billion direct debit transactions made through Bacs and more than 1.9 billion direct credit payments.
- Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA): SEPA is an integrated payment system that allows bank account holders in the EU, European Economic Area and the UK to easily transfer funds between different European banks.
How long do bank transfers take?
Wherever you're sending funds to or from, most bank transfers are processed and delivered within a few days. Here's a closer look at the timing that you can expect from different types of bank transfers, domestically and internationally:
USD bank transfers: Same-day settlement enables most ACH transactions to be completed within the same business day. ACH credit transfers are typically delivered within one to two business days, and ACH debit transfers must be processed and delivered by the next business day. Some banks might hold on to funds delivered via ACH transfer for a few days, but this varies by financial institution.
Electronic transfers: Domestic electronic transfers are processed in real time and usually delivered within one business day. But if a electronic transfer is initiated late on a Friday, it might not be delivered until the following Monday.
International electronic transfers: SWIFT bank transfers between the US and other countries typically take one to five business days to be processed and delivered. They're slower than ACH and wire transfers because they have more mitigation measures against fraud and money laundering.
Benefits of bank transfers for businesses
Here are a few key benefits for businesses that accept bank transfers.
No payment reversals or chargebacks
The biggest benefit of bank transfers is that customers can't reverse them. Unlike with credit card payments, which always carry the risk of chargebacks, the customer can't call back bank transfers once they're initiated.
If the customer is dissatisfied with their purchase after paying with a bank transfer, they must contact the business and request a refund instead. This scenario gives the business the best possible opportunity to solve the issue and possibly avoid a funds reversal. Even if a situation warrants the return of the customer's funds, refunds are preferable to chargebacks as they give businesses more control over the funds reversal process.
Greater security
Bank transfers tend to be very secure for businesses and their customers, while credit card payments carry a relatively higher risk of fraud.
Stripe customers have additional layers of protection for these payment types. We provide you with a virtual bank account number that your customers submit bank transfer payments to. This virtual account number automates reconciliation and prevents businesses from exposing their real account details to customers.
Appealing to consumer preferences
Businesses should accept as many payment methods as possible. The more payment types you accept, the more customers you're likely to convert and retain. Bank transfers, in particular, are attractive to customers who prefer not to use credit or debit cards for certain purchases.
Higher conversion rates in Europe and Asia Pacific
Many customer transactions in Europe and Asia Pacific occur via bank transfer. Accommodating this payment type will make your business more favourable to customers who are used to paying this way.
Downsides of bank transfers for businesses
While most businesses find bank transfers to be a reliable, secure and easy way to send and receive payments, they're not without their drawbacks. Here are a few potential drawbacks of bank transfers to consider.
Reconciliation
If customers don't include invoice reference numbers with their payments or they pay a different amount from what's listed on the invoice, those bank transfers will require manual effort to match incoming payments with invoices. This can cause delays or errors and increase administrative costs as finance teams investigate mismatched or unidentified transactions.
General lack of support for recurring payments
This lack of support could be burdensome or prohibitive, if your business sells subscriptions or otherwise works with recurring payments.
No control over payment amount
Because customers often initiate the transaction, it's possible they could send the wrong amount. There are ways to work around this: for example, Stripe holds customers' bank transfers for up to 90 days and allows businesses to reconcile discrepancies, in most cases. But you'll still need to devote extra time and resources to overpayment or underpayment issues when you accept bank transfers from customers.
Chance of incomplete payment
Because the transfer process varies across financial institutions, it's difficult for businesses to give universal bank transfer instructions to their customers. A customer might think they've completed a payment, when they actually need to contact their bank to complete it.
Stripe's checkout experience mitigates some of this risk. But businesses might still have some risk of incomplete payment, since accepting a bank transfer means relying on the customer to complete the transaction.
Higher possibility of delays
Bank transfer networks sometimes have processing delays. Depending on the banks involved in the transaction, funds received might be held for days. Holds and delays become more likely with international transfers. Bank transfer networks are becoming more dependable and faster every year, but delays still happen more frequently than they do with credit and debit card payments.
Here's a simplified list of the pros and cons of bank transfers for businesses:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
No chargebacks: Customers can't reverse payments |
No recurring payments: Not ideal for subscriptions |
|
More control over refunds: Businesses decide when and how to issue a refund |
No control over payment amount: Customers can send the wrong amount |
|
Highly secure: Lower risk of fraud than card payments |
Possibility of incomplete payments: Confusing process for some customers |
|
Virtual account numbers: Businesses won't expose their bank details |
Payment delays: Bank processing can take days, especially for international transfers |
|
Preferred by some customers: Appealing especially to those who avoid cards |
|
|
Better conversion in Europe and Asia Pacific: Bank transfers are common in these regions |
Are bank transfers safe?
Bank transfers are usually a very safe way to accept payment from customers, with less risk for businesses compared to credit card payments. On the customer side, however, there's a risk of electronic transfer fraud. To stay protected, customers should always verify the recipient's details through a trusted source before they send money, especially when they make large or first-time transfers.
How Stripe Payments can help
Stripe Payments provides a unified, global payments solution that helps any business – from scaling startups to global enterprises – accept payments online, in person and around the world.
Stripe Payments can help you:
- Reconcile payments automatically: Easily reconcile electronic transfers to a specific payment or invoice with an automatic reconciliation engine that uses virtual bank accounts for each customer and tools for troubleshooting.
- Simplify refunds: Make refunds or return excess funds to the customer.
- Optimise your checkout experience: Create a frictionless customer experience and save thousands of engineering hours with prebuilt payment UIs, access to 125+ payment methods and Link, a wallet built by Stripe.
- Expand to new markets faster: Reach customers worldwide and reduce the complexity and cost of multi-currency management with cross-border payment options, available in 195 countries across 135+ currencies.
- Unify payments in person and online: Build a unified commerce experience across online and in-person channels to personalise interactions, reward loyalty and grow revenue.
- Improve payment performance: Increase revenue with a range of customisable, easy-to-configure payment tools, including no-code fraud protection and advanced capabilities to improve authorisation rates.
- Move faster with a flexible, reliable platform for growth: Build on a platform designed to scale with you, with 99.999% uptime and industry-leading reliability.
Learn more about how Stripe Payments can power your online and in-person payments or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.