Payment terms are an important part of any business activity, and most companies have implemented fixed payment terms for their customers. In this article, we explain what payment terms are, what the typical payment conditions and payment deadlines are, and which payment methods are most commonly offered by companies.
What’s in this article?
- What are payment terms?
- What are the different payment terms?
- Additional fees for certain payment terms
- The legal importance of payment terms
What are payment terms?
Payment terms are agreed-upon conditions between two parties that specify how, where, and when the agreed price is to be paid. In addition to the payment amount, the time of payment, and the currency, payments terms include the type of payment, i.e., the means of payment or the payment method. In the case of loan agreements or installment payments, the payment terms also include interest and repayments.
These general conditions are usually set out in a company’s terms of service, and can only be deviated from if both parties agree. The acceptance of the terms of service is assumed, provided that the company has pointed out its terms of service to the customer prior to the conclusion of the contract. In online purchases, it is common for customers to confirm that they have read and agreed to the terms before placing an order. Payment terms should be clearly defined and include all necessary details for both parties to fulfill their part of the agreement. It is also very important that all applicable fees and costs are clearly defined for the customer in order to avoid any misunderstandings.
What are the different payment terms?
There are numerous options for the time of payment and the means of payment:
“Time of payment” payment term
The most common options for the time of payment are advance payment, supplier credit,and immediate payment on delivery. Although an invoice is generally always due immediately, it is common for companies to agree on other payment terms.
In practice, these may be worded as follows:
- “Advance payment on order”
- “The credit card will be charged immediately after the order”
- “Payable immediately upon issuance of the invoice”
- “Payable within 14 days”
- “Payable by (date)”
Some companies offer cash discounts or other reductions if payment is made in advance or promptly to give customers an incentive to pay quickly, which can look like this:
- “Payable within 14 days less 2% cash discount, or within 30 days net without discount.”
- “We offer a 2% cash discount for advance payment.”
- “We offer a 2% cash discount for payment by direct debit.”
Some companies also offer installment purchases. In this case, payment is not made immediately in one lump sum—instead, it is divided into two or more installments or partial payments. Installment purchases allow customers to buy more expensive goods even if their current budget doesn’t allow it, which also helps companies generate more revenue. Installment purchases can either be made through the company itself or handled by service providers.
What is a cash discount?
In commerce, a cash discount is a discount on the purchase price which the seller grants to the customer if payment is made within a certain period. This discount is always optional and the company is not required to offer it.
“Means of payment” payment term
In addition to the traditional payment terms—in this case “means of payment” or payment methods such as advance payment, direct debit, and invoices, there are also digital alternatives such as PayPal or Bitcoin. Companies should always consider the level of risk it should take when choosing payment methods. Below we list the advantages of each of the most commonly used payment methods:
Advance payment
With advance payment, the customer must pay for the goods or services before they are shipped or received. This payment method gives companies greater financial security since they don’t have to wait for payments. Advance payment also minimizes the risk of default, as it is more difficult to cancel an invoice after it has already been paid. However, this payment method does involve a certain risk for customers since they have to pay in advance and trust that they will receive the goods. Many companies try to make this payment method more attractive to customers by offering discounts for choosing this payment method.
Payment on delivery
Payment on delivery means that the customer pays for the goods once they have been delivered. This brings some challenges for companies. The first is that it requires more effort, since the money is not collected until delivery and has to be booked in the accounting system. The second is that there is a higher risk for the company, as it is common for customers to refuse to accept the goods or that they are not at home to accept the delivery. This results in additional costs for return shipping and, if necessary, storage of the goods.
To minimize the risk, companies should ensure that the customer’s address is correct and complete when using payment on delivery. Advance notice of delivery by phone can also be useful to ensure that customers are actually at home. Finally, companies could consider whether charges for payment on delivery can be passed on to the customer or included in the sales price.
Invoice payment
In the case of invoice payment, the customer agrees to pay within a certain period after receipt of the goods or services, usually by bank transfer. This payment term allows customers to pay conveniently and securely and because it is one of the most trusted forms of payment for many people, it enables companies to attract new customers. However, there is a higher risk of non-payment with this payment term. To minimize this risk, you should verify customers in advance or use a payment service provider.
Credit card
Credit cards are issued with a credit limit for the cardholder’s use. When making purchases online, customers enter their credit card details and then authorize the purchase amount. At the point of sale (POS) in a store, the customer simply holds the card up to the card reader or inserts it into the device and confirms it with a PIN. The amount is debited from the customer’s account on the credit card at a later date, and the statement is usually issued at the end of the month.
Credit cards have a chip or magnetic strip system that encrypts all transactions, which minimizes fraud while maintaining the integrity of your business.
PayPal
PayPal is an online payment service that allows customers to make payments by entering their bank account or credit card details in PayPal. When using a credit card, customers don’t even need to create an account. The advantage of this payment term is that customers do not have to share their credit card details with the online store. Although companies have to pay to use PayPal, it is easy to integrate into their online store, and offers fast, secure and simple transactions, as well as protection against fraud and unauthorized purchases.
Direct debit
When paying with SEPA Direct Debit, the customer consents to a company debiting payments from their account by means of a mandate. This is particularly convenient for recurring payments, as the customer only has to enter their bank details once, while the company benefits from less administrative work. The company can also set due dates and collect payments on time.
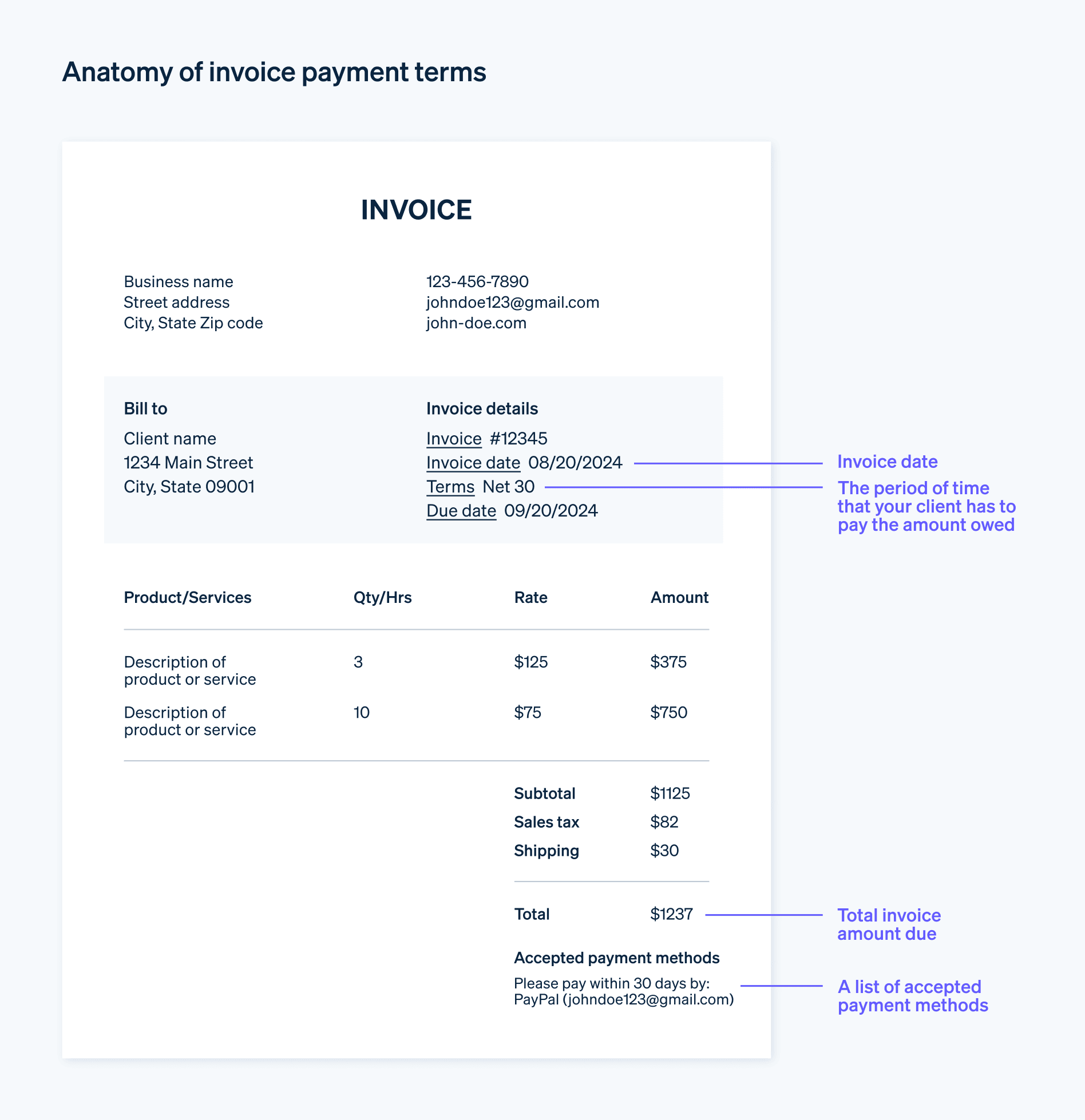
Additional fees for certain payment terms
Businesses are encouraged to offer a wide range of payment terms, allowing customers to find and choose the option that suits them best. Adding fees for specific payment terms is one way to help your business. There are a number of reasons why you may want to charge certain fees, perhaps because some payment methods cost more or take longer than others. It may also be that the cost of risk assessment differs depending on what type of payment method is used.
However, the following regulations must be observed:
Since January 2018, payments by direct debit, bank transfer, and credit card are free of charge if the company is located within the European Union. Therefore, you cannot charge additional fees for these payment methods. This regulation is set out in Article 62(3) of Payment Services Directive 2015/2366/EU (PSD II). In Germany, this regulation was defined in the Payment Services Supervision Act (ZAG) and can also be found in § 270a of the German Civil Code (BGB).
Additional fees are permitted for other payment terms, such as PayPal. However, this fee must correspond to the actual costs incurred by the company for the service.
The legal importance of payment terms
The choice of payment terms can have legal consequences, especially in regards to transfer of ownership and the consequences of default.
Transfer of ownership
Once the ownership of the goods is transferred to the customer, the customer is responsible for any damage or loss and the company no longer has any claim to the goods. According to § 446 BGB, ownership of the goods does not transfer to the customer until the customer has paid the purchase price in full. For this reason, it should be ensured that payment is made promptly and without any delays.
In order to clearly regulate the transfer of ownership, clear provisions should be included in the agreement with the customer. It is particularly important to clearly define the point at which ownership is transferred—for example, when the customer picks up the product or when it is delivered to the customer’s address.
Policies such as the Balance of Payments (BOP) act allow companies to implement control measures that enable them to effectively manage risks, thereby safeguarding the transfer of ownership. Companies must also ensure that they comply with the legal requirements relating to the transfer of ownership.
Consequences of default
Consequences of default are the consequences faced by the customer if they don't fulfill their payment obligation within the agreed period of time. According to § 286(1) BGB, a customer is in default if they don’t pay despite receiving a dunning letter from the company.
In the event of late payment, the creditor may charge the debtor dunning fees and late-payment interest. They may also request the debtor to return the goods and threaten further legal action.
Companies should therefore check in advance that the agreed payment terms have been made sufficiently transparent in the contract and that all parties have been made aware of the possible consequences of failing to meet the agreed deadline. This precautionary measure allows a contractual agreement to be concluded while limiting the risk of consequences of default.
Specifically, the Company has a right to:
- Late-payment interest in the amount of 5% above the base interest rate (§ 288(1) BGB).
- Dunning expenses if the company has sent a dunning notice and the customer has still not paid (§ 288(5) BGB).
- Compensation if the company has incurred any loss as a result of the late payment (§ 280 (1) BGB).
- Withdrawal from the contract if the customer does not pay despite having received a dunning letter and a reasonable deadline for payment being set (§ 323 BGB).
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.