管理经常性付款(无论是家庭账单、订阅还是商业发票)可能非常耗时且容易出错。逾期支付、人工处理和不可预测的现金流也会给企业和消费者带来挑战。
直接借记是一种流行的无现金支付方式,它简化了支付交易。根据皮尤研究中心的数据,大约十分之四的美国人 (41%) 表示,在正常的一周内,他们的购物没有一笔是用现金支付的,这反映出人们对数字和自动支付方式的偏好日益增强。
在本文中,你将了解什么是直接借记,这些年来它发生了哪些变化,它与银行转账有何不同等等。
本文内容
- 什么是直接借记?
- 这些年来直接借记发生了哪些变化?
- 直接借记有哪些好处?
- 直接借记和银行转账有什么区别?
- 客户要求退还直接借记款项的期限是多久?
- 如果无法收取直接借记款项会怎样?
- Stripe Payments 如何提供帮助
什么是直接借记?
直接借记是一种安全的无现金支付方式,企业可以用它来处理付款。人们经常使用“直接借记”这个术语来指代单一欧元支付区 (SEPA) 直接借记支付。
直接借记允许企业在付款到期日从客户的银行账户中收取款项。与其他需要客户手动发起转账的支付方式不同,直接借记授权企业自动提取资金,最大限度地减少了付款延迟。
要处理直接借记交易,企业需要一份直接借记指令,也称为单一欧元支付区 (SEPA) 直接借记委托书。这代表着客户书面同意从其账户中扣除相应金额。直接借记为企业提供了按时收到付款的保障,而且企业不会产生任何费用。
直接借记支付对于订阅服务或会员资格等经常性付款尤其有益。自动处理直接借记加快了计费流程,改善了现金流,减轻了管理工作量,并使整个支付流程更加高效。
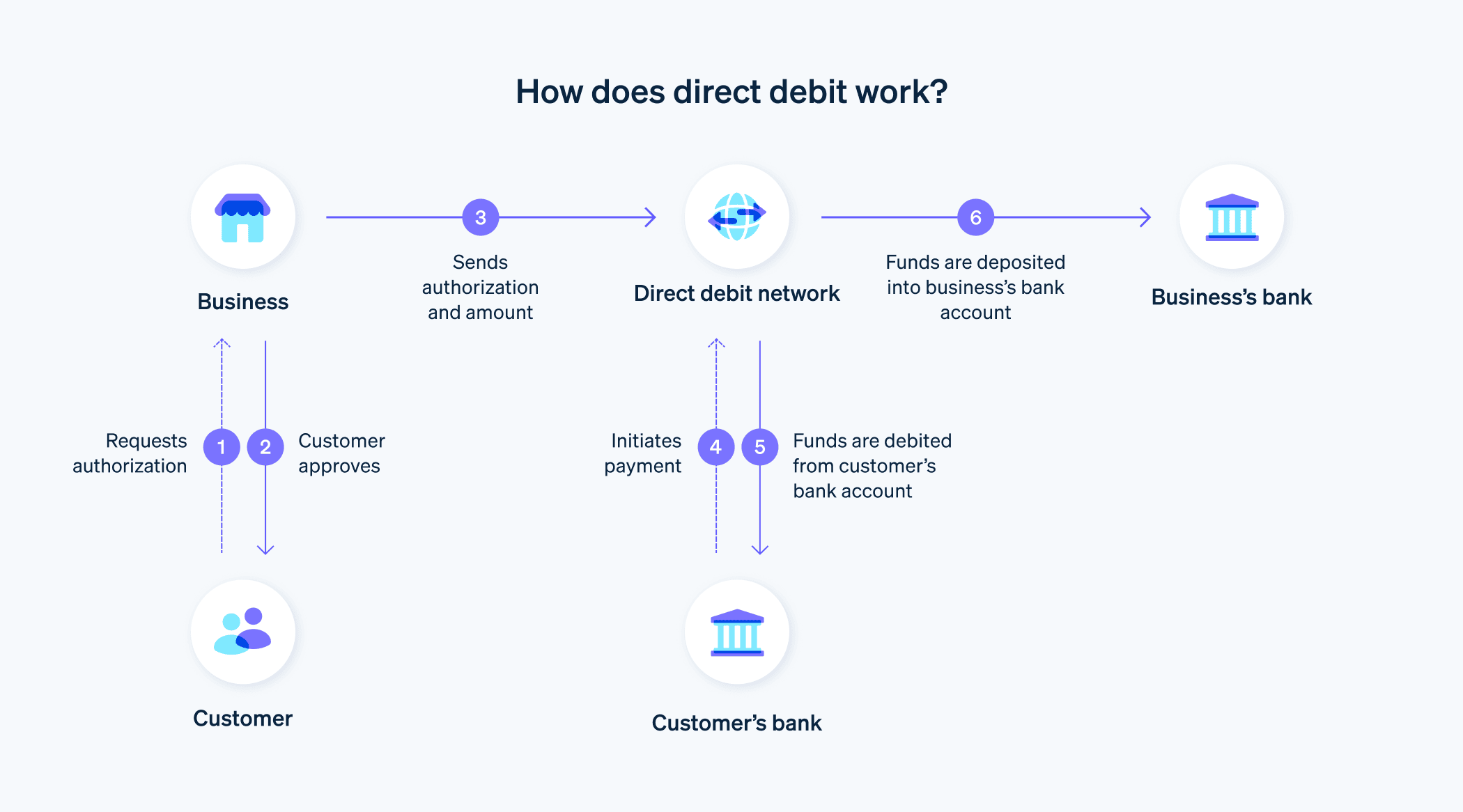
这些年来,直接借记发生了哪些的变化?
在 2009 年引入单一欧元支付区 (SEPA) 直接借记计划之前,直接借记是通过直接借记机构和借记进行的,处理支付时通常需要纸质表格。
单一欧元支付区 (SEPA) 直接借记计划的推出,使得自动清算所 (ACH) 借记交易能够在一个标准化框架下跨多个国家进行处理。这使得企业首次能够在国际范围内收取直接借记款项,扩大了支付服务的覆盖范围并提高了效率。
直到 2014 年 2 月 1 日,直接借记授权和手动借记仍在使用。然而,从那时起,单一欧元支付区直 (SEPA) 接借记计划完全取代了这些旧方法。现有的直接借记指令自动转换为符合开放银行和金融法规的单一欧元支付区 (SEPA) 直接借记授权书。
直接借记有哪些好处?
直接借记为企业提供了一种安全且自动化的方式来向客户收款。以下是企业从这种支付方式中获得的好处:
- 经济高效的收款方式: 消除了手动开票的需要,从而降低了管理成本并改善了运营。
- 自动化支付: 确保在到期日收款,降低了逾期或未付款的风险。
- 改善现金流管理: 按时收到付款,使企业能够更有效地规划财务。
- 简化会计工作: 交易自动记录,降低了出错的可能性,使对账更加容易。
- 减轻工作量: 无需手动处理付款、发送提醒或跟进未付发票。
- 灵活接受付款: 与信用卡和借记卡、银行转账以及网上银行服务兼容。
客户也能享受到直接借记带来的自动化、无烦恼的付款便利。具体方式如下:
- 方便无忧的支付: 无需记住家庭账单、订阅服务或会员资格的付款到期日,也无需手动发起转账。
- 安全的交易: 银行账户详细信息经过加密,降低了欺诈或未经授权访问的风险。
- 防止未经授权的借记: 客户可以监控直接借记交易,如果出现任何差异,可以要求退款。
- 无需重新输入支付详情: 经常性付款会自动处理。
- 高效可靠的支付处理: 付款处理无缝衔接,无需纸质发票或手动审批。
通过自动化直接借记,企业可以优化现金流,减轻管理负担,并增强财务安全性,而客户则能从更简单、更快捷、更可靠的交易中受益。
直接借记和银行转账有什么区别?
直接借记和银行转账的关键区别在于交易的发起方。
对于银行转账,付款人负责手动发起支付。他们必须输入收款人的详细信息,指定付款金额,并通过网上银行系统授权转账。
通过直接借记,付款人授权企业自动收款。一旦他们通过直接借记授权书给予了许可,企业就可以在无需客户进一步操作的情况下提取商定的金额。
客户要求退还直接借记款项的期限是多久?
退还直接借记款项的时间期限取决于该交易是核心直接借记(个人与企业之间)还是企业直接借记(两个企业之间或个体经营者之间)。
- 核心直接借记: 客户自借记日期起有八周时间可以要求退款 — 无需说明理由。
- 延长退款期限: 如果客户未收到借记的事先通知、使用了错误的账户详细信息,或者怀疑存在欺诈行为,退款期限将延长至 13 个月。
- 企业直接借记: 除非授权书无效或怀疑存在欺诈活动,否则不会自动给予退款。在这种情况下,客户有 13 个月的时间对费用提出异议。
拒付给企业带来巨大的成本,并影响公司的声誉。为避免任何问题,企业应确保每笔借记的所有信息都是正确的,并提前通知客户。这样可以防止客户在没有任何理由的情况下退还直接借记。
如果无法收取直接借记款项会怎样?
直接借记未能成功可能有多种原因,包括:
- 客户账户中的资金不足
- 转账过程中出现银行错误或技术问题
- 账户详细信息不正确或过时
- 由于账户限制或欺诈疑虑导致直接借记被拒绝
在这种情况下,企业应迅速采取行动并联系客户解决问题。也可以安排通过银行转账或其他支付方式进行付款。
Stripe Payments 如何提供帮助
Stripe Payments 提供一体化的全球支付解决方案,帮助各种商家(从初创公司到全球企业)在全球范围内接受线上和线下付款。
Stripe Payments 可以帮您:
- 优化结账体验: 通过预构建的支付用户界面、超过 125100 种支付方式以及 Stripe 构建的钱包 Link,营造顺畅的客户体验,并节省数千个工程小时。
- 更快地拓展新市场: 借助跨境支付选项,触达全球客户,降低多币种管理的复杂性与成本,业务覆盖 195 个国家/地区,支持超过 135 种货币。
- 实现线下与线上付款一体化: 整合线上与线下渠道,打造一体化商务体验,实现个性化互动、奖励客户忠诚度并提升收入。
- 优化支付性能: 通过一系列可定制、易于配置的支付工具提升收入,包括无代码的欺诈保护功能与提高授权率的高级功能。
- 依托灵活可靠的平台加速业务增长: 采用专为弹性扩展设计的平台架构,提供 99.999% 正常运行时间与业界领先的可靠性保障。
了解关于 Stripe Payments 如何为您的线上与线下付款提供支持的更多信息,或立即开始使用。
本文中的内容仅供一般信息和教育目的,不应被解释为法律或税务建议。Stripe 不保证或担保文章中信息的准确性、完整性、充分性或时效性。您应该寻求在您的司法管辖区获得执业许可的合格律师或会计师的建议,以就您的特定情况提供建议。