The SA, SAS, and SARL are some of the most common commercial legal forms in France. But did you know there is also a legal form dedicated to noncommercial activities? This is known as the société civile, or civil company. It differs from the commercial company in several respects: its purpose, the taxation of its profits, and the liability of its members. Read the article below to learn more about the unique features of a civil company.
What’s in this article?
- What is a civil company?
- What are the types of civil companies?
- How does a civil company function?
- What is the fiscal regime of a civil company?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a civil company?
- How do you create a civil company?
- What are the differences between a civil company and a commercial company?
What is a civil company?
A civil company is a noncommercial enterprise, formed by a minimum of two partners who pursue a common goal. The partners of a civil company can be natural persons or legal entities. The number of partners is not limited.
What are the types of civil companies?
Civil companies are suitable for most agricultural, liberal, real estate, and intellectual activities. There are many types, including:
- Civil real estate companies (SCI)
- Professional civil companies (SCP)
- Nontrading private companies (SCM)
- Civil construction and sales companies (SCCV)
- Civil Society for Agricultural Exploitation (SCEA)
- Copyright collection and distribution companies (SPRD)
Civil real estate companies (SCI) are the most widespread in France and allow for the management and structured transfer of joint real estate assets. There are also many professional civil companies (SCP) made up of notaries, lawyers, doctors, architects, etc.
What are the differences between a civil company and a commercial company?
The main differences between a civil and a commercial company are summarized in the table below.
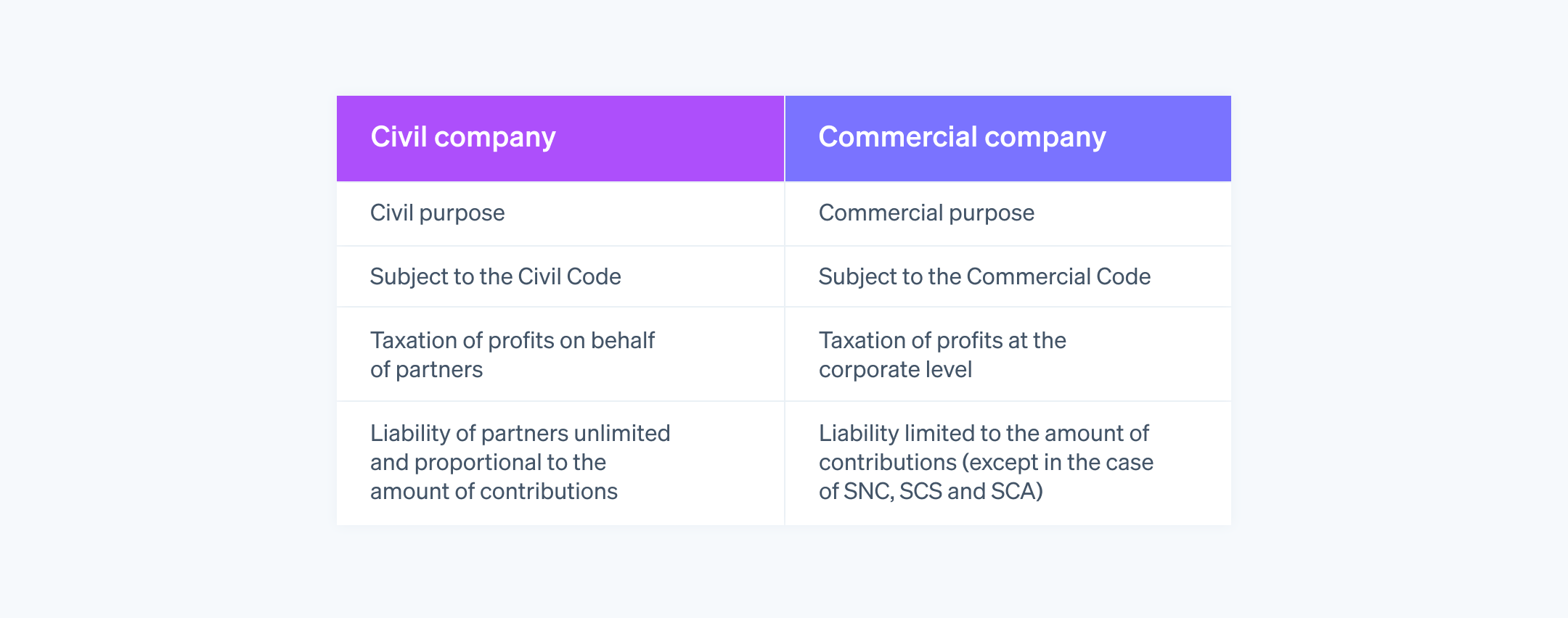
How does a civil company function?
According to articles 1845 to 1870-1 of the French Civil Code, a civil company is managed by one or more managers acting on behalf of the company. The manager can be a partner or a third party as well as a natural or legal person. They represent the company to third parties and are responsible for management reports.
Decisions in the civil company are made collectively in a meeting. The company’s articles of association, drawn up at the time of incorporation, determine the operating procedures (quorum, majority, unanimity, etc.).
Note that the manager’s powers can be limited by the partners in the articles of association.
Share capital of a civil company
The partners of a civil company are free to determine the amount and constitution of the share capital. The law does not prescribe a minimum or maximum amount. Furthermore, the partners’ contributions can be in cash or in kind.
Note that the liability of the partners is unlimited and proportional to their contributions to the share capital. This means that in the event of financial difficulties, the partners’ personal assets might be at risk—but only up to the percentage of their participation in the share capital.
What is the fiscal regime of a civil company?
By default, the partners of a civil company are subject to the income tax (IR) regime. There is no taxation at the level of the company: profits are taxed in the partners’ personal names; conversely, commercial companies are taxed at the level of the company. If they want, the partners of a civil company can opt for the corporate tax regime (IS).
Social security of the manager
Typically, as soon as they receive remuneration, the manager is considered a self-employed worker, or TNS (travailleur non salarié). This is covered by the social security system for the self-employed, or SSI. Learn more about the self-employed professional in our article.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a civil company?
Civil companies have several advantages:
- Free operation and flexible drafting of articles of association
- The absence of a minimum amount of required capital for registration
- A lower cost in terms of social security coverage for the manager because of their status as a self-employed professional.
However, it has some downsides:
- An indefinite and joint liability of the partners
- Collective decision-making
- Potential reclassification as a commercial company (a civil company might find itself reclassified as a commercial company when it undertakes to carry out an activity of a commercial nature)
How do you create a civil company?
The steps for creating a civil company are the same as those for a commercial company:
- Draft the articles of association, notification of the manager, and the registered office of the civil company.
- Deposit the share capital in cash into the bank account of the civil company (if applicable).
- Publish a notice of establishment in a legal notices journal.
- Register online via the business formalities portal.
Certain costs are associated with establishing a civil company, such as registration fees (€66.88), declaration of beneficial owners (€21.41), publication of the legal notice (€216 or €185 for an SCI), and drafting of the articles of association (between €1,500 and €2,000 to consult a legal professional).
Accelerate your business startup with Stripe Payments, a payment system designed for civil and commercial companies. Stripe gives you access to over 100 payment methods and lets you accept payments in over 195 countries.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.