Bank transfers in US dollars (USD) are the basis for countless transactions across the globe—and an important part of modern finance. The ability to transfer money swiftly and securely in a widely accepted and stable currency such as USD helps support international commerce by connecting far-flung economies and regions.
USD bank transfers support both domestic transactions within the United States and international remittances, where USD often serves as the preferred currency for cross-border transactions between family members. The reliability of USD bank transfers has made them a fixture of global financial exchanges, facilitating trade, investment, and personal financial management.
For businesses, the stakes around USD bank transfers are high. This guide will discuss what businesses need to know about USD bank transfers: how they work, who uses them and why, and what the requirements are to accept USD bank transfers as a payment method.
What’s in this article?
- How do USD bank transfers work?
- Where are USD bank transfers used?
- Who uses USD bank transfers?
- How are USD bank transfers used?
- Benefits of accepting USD bank transfers
- USD bank transfer security measures
- Business requirements for accepting USD bank transfers
- How Stripe Payments can help
How do USD bank transfers work?
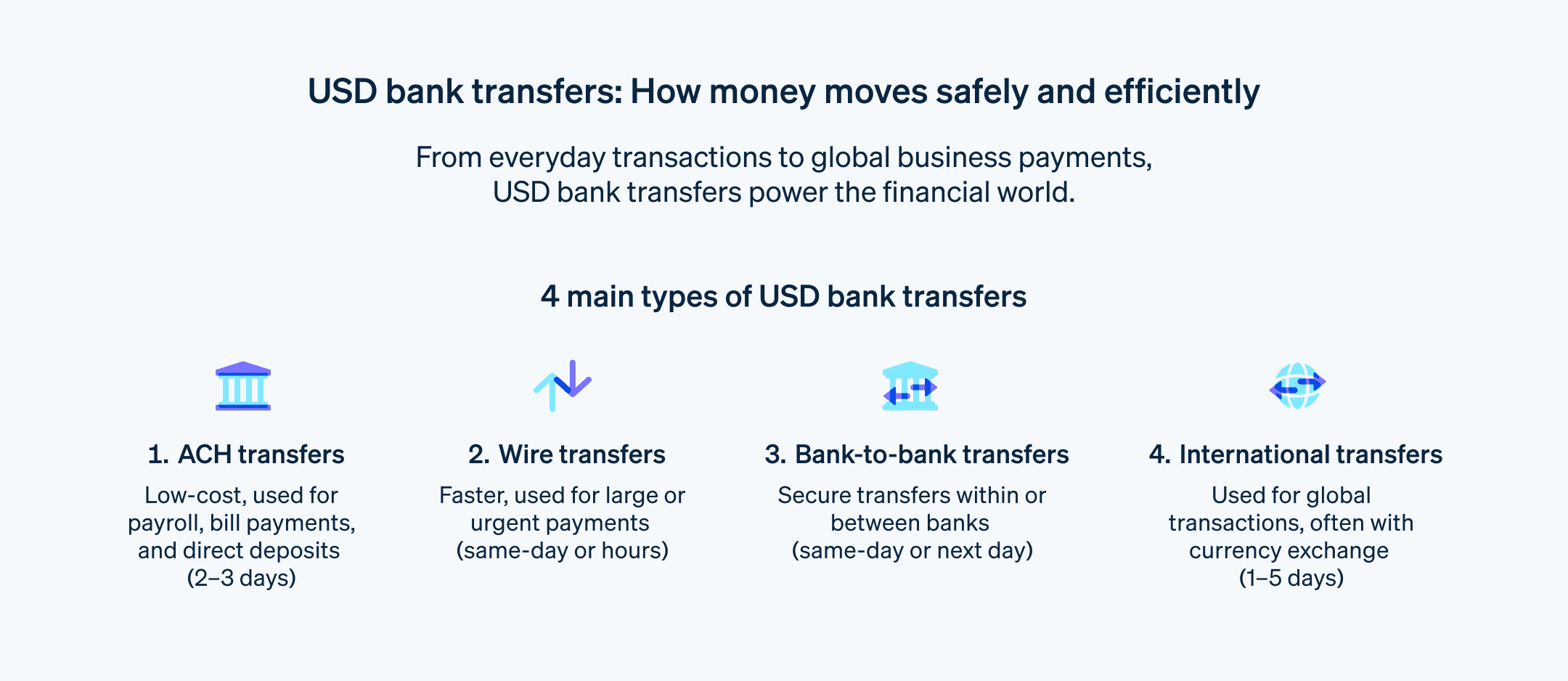
There are four main types of USD bank transfers. They all involve moving USD between bank accounts, but each one suits a specific need. Here’s a closer look.
Automated Clearing House (ACH) transfers
ACH transfers move funds electronically between bank accounts in the US through the ACH network, which is operated by Nacha. These transfers are a popular method for domestic money transfers and are typically used for regular, recurring payments such as payroll, direct deposits, and bill payments. ACH transfers usually take two to three business days and have the lowest fees, making them the most cost-effective method for businesses.
Wire transfers
Wire transfers are a faster method of transferring funds and are often used for larger or more urgent transactions such as real estate purchases, car loans, and immediate financial needs. Funds generally arrive in the recipient’s account the same day—sometimes within hours. This type of electronic funds transfer usually comes with higher fees compared to ACH transfers, and charges can vary based on the transfer amount and level of urgency.
Bank-to-bank transfers
Bank-to-bank transfers are transfers between accounts within the same banking institution or at different banks. They’re a convenient way to move money between personal accounts or accounts held with different institutions, and they can be conducted online or in person. These transfers are usually processed within the same day or by the next business day. Fees can vary depending on the banks involved and the transfer amount, although they’re typically more affordable than wire transfers.
International transfers
An international transfer is when USD is sent from a US bank account to an account in another country. These transfers—which often involve currency exchange—are a common way for individuals to send money to family or friends abroad, make overseas investments, or settle international business transactions. International transfers are usually more expensive than domestic transfers due to currency exchange fees and intermediary bank charges.
Where are USD bank transfers used?
USD bank transfers are a popular payment method globally. The emergence of digital technologies such as digital wallets and online banking platforms has reduced USD transfer fees and made these transfers more accessible. Here’s how prevalent USD transfers are in developed and emerging markets.
Developed markets
As of July 2025, USD accounts for about 50% of cross-border SWIFT flows. This dominance comes from the currency’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency and its integral role in global finance. In the UK and EU, international transactions are often carried out in USD: a 2022 Bank of England report found that USD was the most traded currency in the UK market that year, with over 90% of all trades using USD on at least one side of the trade.
Emerging markets
The need for a stable, reliable currency drives the use of USD bank transfers in emerging markets. Remittances sent in USD play a major role, too. Global remittance flows were estimated to total $905 billion in 2024, reflecting the enduring appeal of USD in low- and middle-income markets.
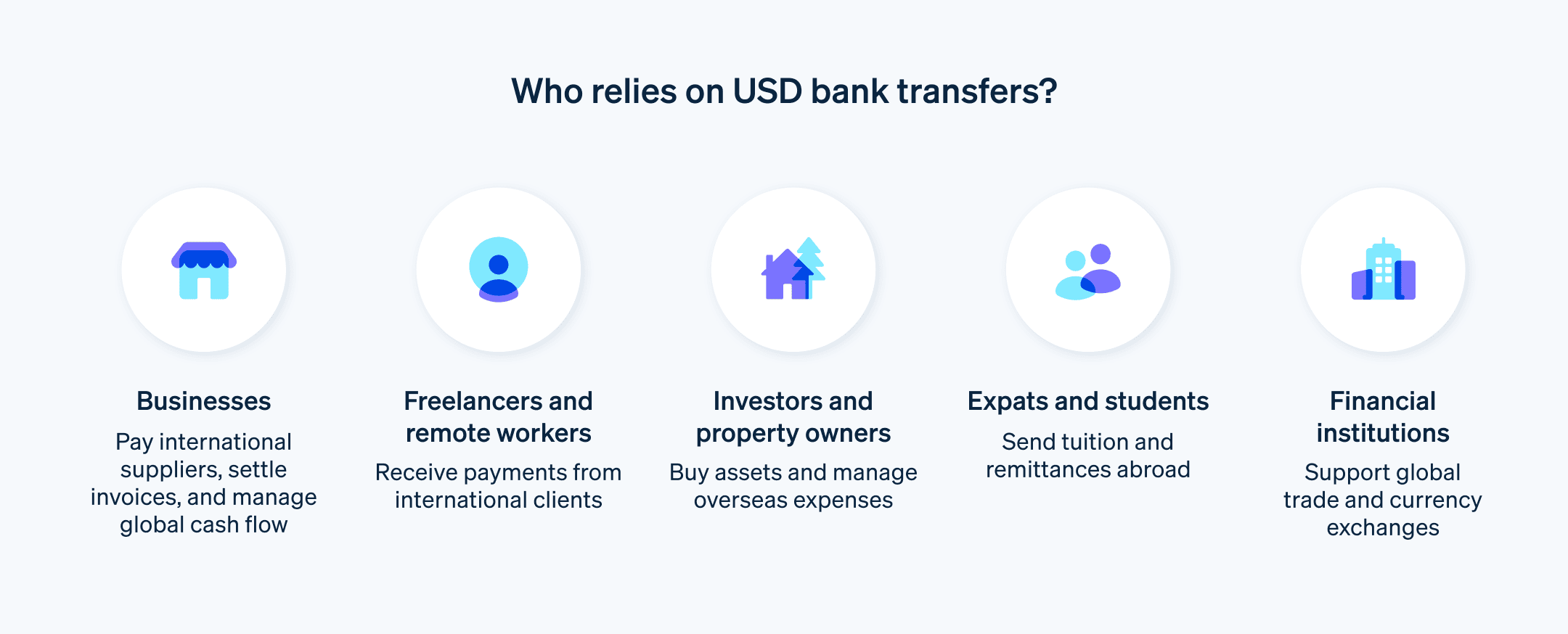
Who uses USD bank transfers?
USD bank transfers are a major pillar of international finance, facilitating trade, investment, and personal transactions across the globe. These are the primary users of this payment method:
Multinational corporations: These entities rely on USD transfers to move funds between subsidiaries in different countries, to pay suppliers and receive payments from customers for international trade, and to invest in foreign assets and manage global portfolios.
Financial institutions: These institutions use USD transfers to initiate and receive USD transfers on behalf of their clients and to buy and sell currencies, both to meet client demand and for speculative purposes.
Import and export businesses: These businesses use USD transfers to pay international suppliers and receive payments from overseas customers.
Ecommerce platforms: These platforms use USD transfers to facilitate transactions between sellers and buyers in different countries and to settle payments with suppliers and vendors located abroad.
Travel and tourism companies: These companies use USD transfers to pay hotels, airlines, and other travel-related vendors located abroad. They also provide prepaid travel cards and other financial services to international travelers.
High-net-worth individuals: These individuals use USD transfers to invest in international assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, and they buy luxury goods and real estate in other countries.
Expats and migrant workers: These individuals use USD transfers to support families and dependents in their home countries, and they invest their earnings in USD-denominated accounts.
International students and families: These groups use USD transfers to cover the cost of tuition and other educational expenses at international universities.
Freelancers and remote workers: These individuals use USD transfers to receive payments from international clients and contribute to USD-denominated accounts for savings and investments.
How are USD bank transfers used?
USD bank transfers are the go-to payment method for many different use cases. Here are several of them:
Cross-border payments: USD transfers are the dominant method for transferring funds internationally. Total global payments are expected to grow from $190 trillion in 2023 to $290 trillion by 2030.
International trade settlements: USD is the preferred currency for settling global trade transactions. About half of global trade was invoiced in USD in 2022.
Foreign exchange transactions: USD is the most traded currency in the daily foreign exchange market. It was involved in nearly 90% of global foreign exchange transactions in 2022.
Investment and asset management: USD is a key currency for foreign direct investment. The US recorded $5.25 trillion in foreign direct investment in 2022.
Financial aid and remittances: USD transfers are an important tool for supporting individuals and families across borders. The World Bank forecasts that global remittance flows will reach $690 billion in 2025.
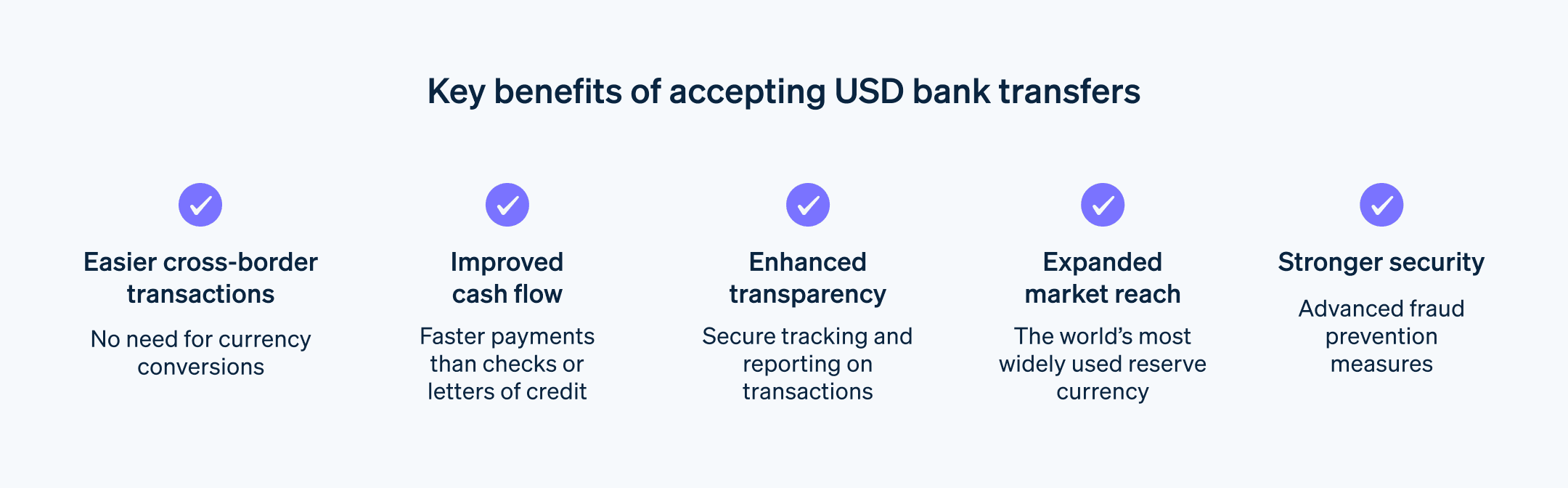
Benefits of accepting USD bank transfers
USD bank transfers are a catalyst for growth, expansion, and international relationship building. Here’s a closer look at the benefits businesses might see from working with USD bank transfers:
Easier cross-border transactions: USD transfers are a standardized, efficient method for exchanging funds across borders because they eliminate the need to manage different currencies and regulations. Businesses can rely on a single, familiar system for sending and receiving payments, simplifying their international operations.
Improved cash flow: USD bank transfers have faster transfer speeds than traditional methods such as checks and letters of credit, allowing businesses to manage their cash flow more effectively. This improved liquidity enables businesses to capitalize on opportunities and react quickly to market changes.
Enhanced transparency: Secure tracking features and detailed transaction reports provide businesses with greater transparency and control over their international finances. This enables informed decision-making and reduces the risk of ecommerce fraud or errors.
Expanded market reach: As the world’s most widely used reserve currency, USD is readily accepted by businesses and individuals in virtually every country. Businesses that accept USD bank transfers can expand their market reach and attract customers globally by offering a familiar payment option that’s capable of cross-border transactions.
Reduced transaction costs: USD bank transfers have competitive fees compared to other international payment methods, particularly for large transactions. This translates to cost savings and improved profitability for businesses.
Enhanced security and reliability: USD transfers employ strong payment security features and fraud prevention measures, which help ensure the safe, reliable movement of funds.
International investment capability: USD transfers allow businesses to invest in opportunities around the world, diversifying their portfolios and mitigating risks associated with overexposure to a single market.
Global asset management: Businesses can use USD transfers to efficiently manage their global assets—including real estate holdings, intellectual property, and other investments—which enables centralized control and coordinated investment strategies.
Access to international capital markets: USD bank transfers provide businesses with access to international capital markets, where they can raise funds for expansion, acquisitions, or other initiatives. This access to capital fuels growth and can facilitate ambitious business goals.
International partnership opportunities: The secure, standardized nature of USD transfers builds trust and transparency between businesses located in different countries, encouraging collaboration and allowing businesses to use global expertise and resources to achieve their objectives.
Supply chain support: USD transfers let goods and services flow smoothly across international borders, minimizing disruptions and delays in supply chains and contributing to business continuity and profitability.
USD bank transfer security measures
USD bank transfers come with a suite of security measures designed to protect both sender and recipient. These measures are important for preserving the integrity and safety of financial transactions. USD bank transfers include the following technical security features.
Secure key management
Hardware security modules: These tamper-resistant devices store encryption keys, preventing unauthorized access.
Regular key rotation: Encryption keys are updated regularly to maintain security and prevent breaches.
Multisignature key management: For added control, multiple authorized individuals must approve key usage.
Data encryption
Tokenization: Sensitive information (e.g., account numbers) is replaced with tokens, minimizing exposure risk in the event of data breaches.
Homomorphic encryption: Computations can be performed on encrypted data without decryption, ensuring data privacy during transactions.
Quantum-resistant algorithms: Encryption algorithms are developing to be resistant to future quantum computing threats.
Network security
Secure communication protocols: Data is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3. The encrypted envelopes are then used for data transmission, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
Zero trust network access: Access to sensitive data is granted based on need, minimizing the attack surface and restricting unauthorized access.
Segmentation and firewalls: Bank networks are segmented and assigned varying security levels and firewalls that filter traffic for enhanced protection.
Vulnerability management
Penetration testing: Regular scans address vulnerabilities in systems before attackers can exploit them.
Security information and event management: Security logs are analyzed to help businesses detect suspicious activity and identify potential threats.
Threat intelligence: Threat intelligence feeds are used to anticipate and adapt to developing cyberthreats.
Blockchain technology
Distributed ledger technology: Shared ledgers provide a transparent, secure way to record financial transactions, improving auditability and traceability.
Smart contracts: Automated contracts execute specific actions based on predefined conditions, eliminating the need for manual intervention and minimizing human error.
Business requirements for accepting USD bank transfers
Businesses that want to use USD bank transfers must meet certain requirements. As a baseline requirement, they must comply with all relevant financial regulations specific to their jurisdictions and industries, including Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations that govern customer identification and transaction recordkeeping.
Another starting requirement for businesses that conduct USD bank transfers is establishing a business bank account specifically designated for USD transfers. This creates a clear separation between personal and professional finances and facilitates smoother tracking and management of business transactions. Different banks will have different requirements for opening an account and might request business registration documents, tax identification numbers—such as an Employer Identification Number (EIN)—and other paperwork.
Once a business establishes a business bank account, it should choose its transfer provider by analyzing the transfer fees, processing times, supported currencies, and international capabilities that different banks and payments service providers (PSPs) offer. Businesses should also consider any niche functionalities they might need, such as multicurrency accounts, advanced fraud protection, and application programming interface (API) integrations.
At this point, businesses should alert their chosen banks or PSPs about their intent to conduct USD bank transfers. Different banks might have specific documentation requirements or onboarding procedures for USD transfers, and businesses should consult a bank’s website or contact customer support for setup instructions. Companies that want to conduct international transactions with USD bank transfers should also familiarize themselves with the SWIFT network’s requirements and fees.
Some businesses might find it helpful to integrate their bank accounts with accounting software to automate transaction reconciliation, facilitate real-time cash flow tracking, and maintain accurate financial records. Before it commits to a product, a business should confirm that its chosen accounting software can integrate with its bank’s system.
Companies will also need to establish the following rules and procedures for how they will handle USD bank transfers:
Authorization procedure: Establish clear procedures for authorizing USD transfers, including who has the authority to initiate transactions and any required approval processes.
Transaction limits: Set limits on transfer amounts to control risk and monitor potentially suspicious activity.
Reconciliation process: Develop efficient reconciliation procedures for accurate tracking and accounting of all USD transfers.
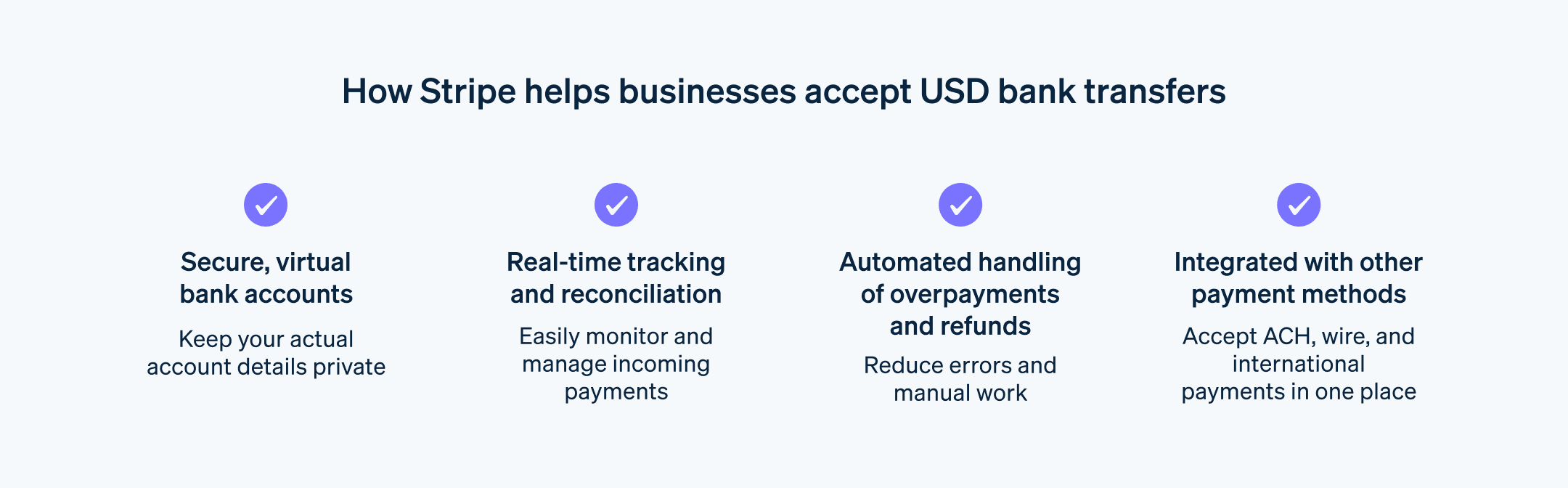
How Stripe Payments can help
Stripe Payments enables businesses to set up and accept 100+ payment methods, including USD bank transfers, and makes reconciliation automatic. It provides a unified, global payment solution that helps any business—from scaling startups to global enterprises—accept payments online, in person, and around the world.
Stripe Payments can help you:
- Reconcile payments automatically: Easily reconcile USD bank transfers to a specific payment or invoice with an automatic reconciliation engine that uses virtual bank accounts for each customer and tools for troubleshooting.
- Simplify refunds: Make refunds or return excess funds to the customer.
- Optimize your checkout experience: Create a frictionless customer experience and save thousands of engineering hours with prebuilt payment UIs and Link, Stripe’s digital wallet.
- Unify payments in person and online: Build a unified commerce experience across online and in-person channels to personalize interactions, reward loyalty, and grow revenue.
- Improve payment performance: Increase revenue with a range of customizable, easy-to-configure payment tools, including no-code fraud protection and advanced capabilities to improve authorization rates.
- Move faster with a flexible, reliable platform for growth: Build on a platform designed to scale with you, with 99.999% uptime and industry-leading reliability.
Learn more about how Stripe Payments can power your online and in-person payments, or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accurateness, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent attorney or accountant licensed to practice in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.