Marketplaces are digital platforms that connect businesses and customers and handle transactions between them. They offer businesses a new way to meet customer needs. With a global revenue projected to reach over $83 trillion USD by 2030, ecommerce—including marketplaces—can be important to growing your business, creating new revenue streams, and boosting your online presence.
Marketplace platforms—such as Amazon, Airbnb, and Uber—have transformed their industries, but creating a marketplace can be challenging. In this article, we cover the key factors to consider when developing and launching a marketplace in France.
What’s in this article?
- What is a marketplace?
- What’s the difference between a marketplace and an ecommerce site?
- What are the different types of marketplaces?
- Why create a marketplace?
- How much does it cost to create a marketplace?
- How to create a marketplace
- How Stripe Connect can integrate payments into your marketplace
What is a marketplace?
A marketplace is an ecommerce platform where multiple third-party businesses offer products or services, and the platform operator processes the transactions. Marketplaces are digital versions of markets or shopping malls. They serve as intermediaries, enabling exchanges between customers and businesses and guaranteeing secure transactions.
Marketplaces can be B2B, B2C, or consumer-to-consumer (C2C). Etsy, Amazon, and eBay are well-established international marketplaces, while Vinted, Leboncoin, and Cdiscount are among the most widely used in France.
What’s the difference between a marketplace and an ecommerce site?
The key difference between a marketplace and an ecommerce site is ecommerce sites sell their own products or services, while marketplaces offer third-party products or services. Ecommerce sites are typically single-business sites, while marketplaces are multibusiness platforms.
Although both are online sales platforms, ecommerce sites and marketplaces have several other important differences:
- Range of businesses
- Marketplaces feature products or services from several third-party businesses, offering a very broad selection to a wide range of customers. Traditional ecommerce sites sell a single business’s products or services.
- Inventory management
- Every marketplace business manages their own inventory, and the platform doesn’t hold any stock. By contrast, traditional online stores usually manage their own inventory and supply chain, unless they operate on a dropshipping model.
- Price competition
- With marketplaces, multiple businesses offer similar products on a single platform, creating direct price competition. On a traditional ecommerce site, the business sets its own prices, and there is no competition within a single platform.
- Business model
- Marketplaces typically generate revenue by charging a commission or fee on each transaction processed on the platform. An ecommerce site’s revenue comes directly from the sale of products or services.
- Order fulfillment
- In the case of marketplaces, businesses are typically in charge of shipping their products to customers, though some marketplaces do offer centralized fulfillment services. In the case of traditional ecommerce sites, the business running the site fulfills the orders.
What are the different types of marketplaces?
Marketplaces can be B2B, B2C, or C2C. Marketplaces that provide goods are usually different from those that offer services. There are also hybrid marketplaces, where the platform operator sells products or services alongside third-party businesses.
Here is a closer look at the different types of marketplaces:
- B2B marketplaces
A B2B marketplace facilitates transactions between businesses. Manufacturers and wholesalers sell their products in bulk to businesses around the world. Revenue is generated through membership or transaction fees. Alibaba is an example of a prominent B2B marketplace. - B2C marketplaces
With B2C marketplaces, businesses sell directly to individuals. The operator charges a commission—typically, a percentage of every sale. Amazon is widely considered the world’s most popular B2C marketplace. - C2C marketplaces
C2C platforms allow individuals to trade with each other. On these platforms, revenue comes from listing fees or commissions on transactions. For instance, eBay allows customers to auction items to other customers. - Service marketplaces
Service marketplaces connect service providers with customers. They typically charge a commission on every transaction. For example, Uber and BlaBlaCar connect drivers with passengers, and Malt and Upwork connect freelancers with clients. - Vertical marketplaces
These platforms focus on a specific category of products or services. Their business models vary, but their revenue is typically generated through registration fees or commissions. Etsy, for example, specializes in handmade and vintage goods, while Zillow focuses on real estate. - Horizontal marketplaces
These platforms offer a wide range of products and services across multiple categories. Their income is typically generated through sales commissions. Amazon and eBay are leading examples because they offer a broad selection of product categories. - Hybrid marketplaces
These platforms combine different types of marketplaces. For example, Amazon started as a B2C marketplace before expanding into B2B activities with Amazon Business. In addition, the company has also expanded into C2C activities with Amazon Marketplace, which is dedicated to secondhand items. - Decentralized marketplaces
This new type of marketplace uses blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer transactions without a central authority. These platforms typically don’t charge transaction fees. Instead, they earn revenue through other means, such as the sale of proprietary tokens. Examples include Origami Network and Origin Protocol.
Why create a marketplace?
Marketplaces offer benefits to operators, businesses, and customers. They allow operators to meet a market need and secure recurring revenue streams. For businesses, marketplaces offer a cost-effective way to sell products. Businesses can use the platform’s infrastructure, traffic, and visibility.
Creating a marketplace allows operators to:
- Facilitate the sales of products or services without having to manage logistics
- Meet market needs by focusing on products or services in a growing or underserved field
- Earn recurring income through different revenue models (e.g., membership fees, transaction fees, sales commissions, sale of proprietary tokens, etc.)
- Take advantage of potential rapid growth by attracting businesses and customers with a minimal financial investment
- Reach international markets, especially since the marketplace model can be customized for different local markets
- Promote customer loyalty by offering customers a time-saving, centralized purchase experience and more competitive prices
Marketplaces allow third-party businesses to:
- Achieve economies of scale by relying on the marketplace to manage payments, customer service, and platform maintenance
- Take advantage of the marketplace’s visibility and traffic to boost their presence and sales potential
- Offer various payment methods to grow their revenue
Marketplaces allow customers to:
- Easily access a broad range of products or services from multiple businesses
- Enjoy a convenient shopping experience, as products from various businesses can be included in a single purchase
- Take advantage of convenient delivery options
- Read customer reviews of businesses’ products or services
How much does it cost to create a marketplace?
Creating a marketplace can cost anywhere from €50,000 to millions of euros. This cost depends on the project’s scope and complexity and whether it’s a ready-to-use or customized solution. Costs include design, programming, feature integration (e.g., product listings and online payments), hosting, customer support, and marketing.
To lower the cost of creating a marketplace, you can opt for a ready-to-use software-as-a-service (SaaS) solution that includes the platform’s design, development, hosting, and maintenance.
How to create a marketplace
From the original idea to launching and promotion, building an online marketplace involves several steps. Here’s a quick overview of the process:
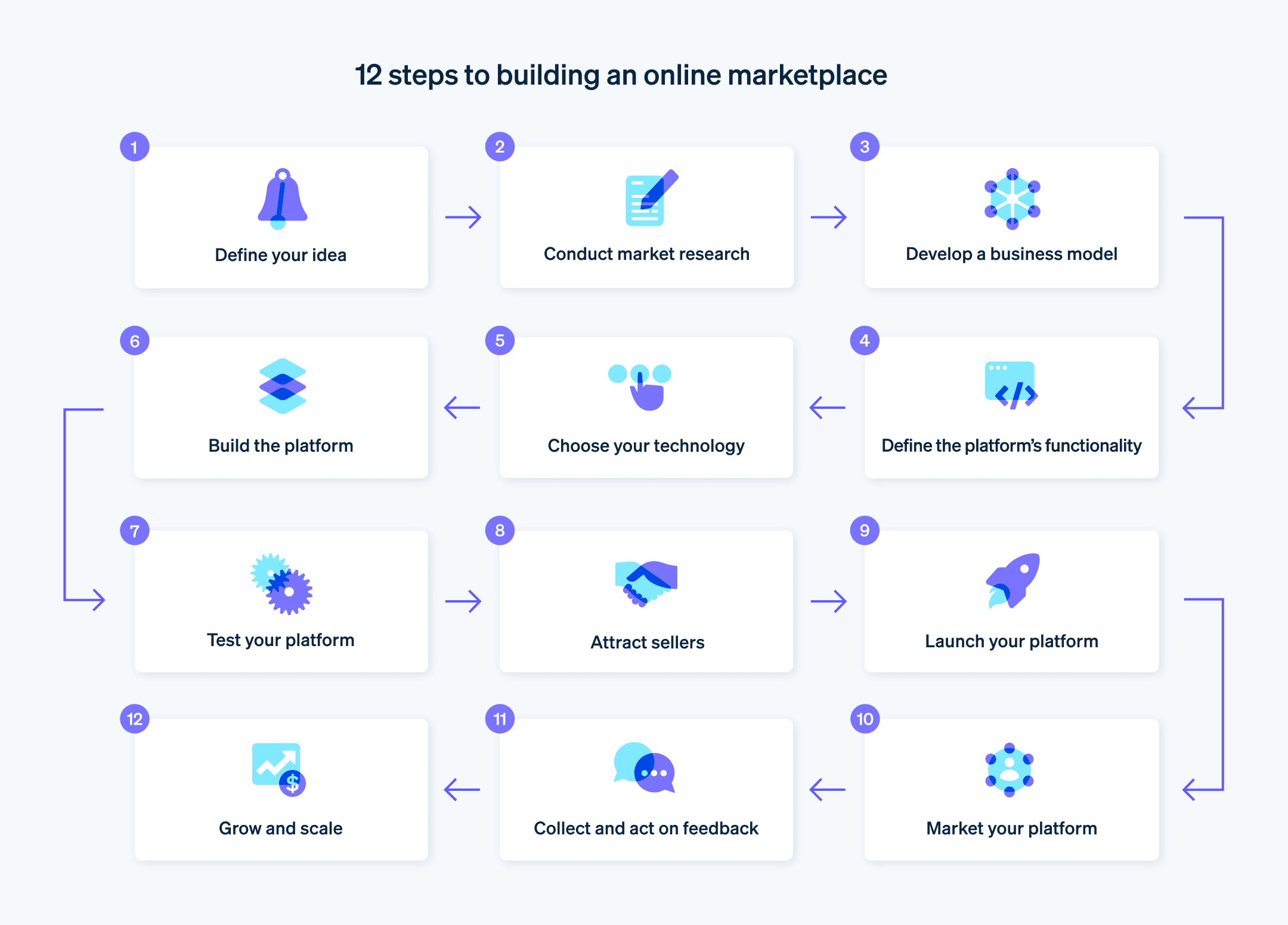
- Define the concept
Define your marketplace concept clearly and precisely. This includes the types of products or services you will offer and your target businesses and customers. You should also consider how you will stand out from existing platforms. - Conduct a market analysis
Study the market, identify competitors, and gain insights into customer needs. Examine successful marketplaces to pinpoint their strengths, and discover opportunities for improvement. - Select a business model
Determine how you intend to generate revenue. This could include fees for transactions, listings, subscriptions, or a combination. Define your pricing strategy, and assess how it compares to competitors. - Specify platform functionalities
List the key features and functionalities your platform will need. These typically include search and discovery tools, customer profiles, product listings, a secure payment system, rating and review features, and messaging tools for customers and businesses. - Select a development solution
- You can create your marketplace, use a ready-made platform, or opt for specialized software. Take your budget, timeline, and technical skills into account when choosing the best option. You can also integrate payment processing solutions, such as Stripe.
- Develop the platform
Whether you’re building your marketplace or not, you’ll need to implement the functionalities you wish to integrate. You can use your own developing skills or rely on a development team. - Test your platform
Before going live, perform tests to make sure everything runs smoothly. Test the purchasing and selling flows, payment experience, and platform’s features. - Bring businesses on board
Before you can attract customers, you need businesses. Contact businesses who might be a good fit for your marketplace. Consider incentivizing them. - Launch your marketplace
Once you’ve tested your platform thoroughly and secured your initial businesses, you’re ready to launch your marketplace. Begin with a soft launch by inviting a small group of customers to try the platform, complete actual transactions, and provide feedback. - Promote your marketplace
Combine various marketing strategies to attract customers. This could involve search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, social media campaigns, paid ads, and partnerships. - Gather feedback and act upon it
As customers start using your platform, gather feedback to determine what’s working well and what needs improvement. Use this feedback to continuously improve your platform. - Grow and scale
As your marketplace becomes established, implement a growth strategy. It could include expanding into new markets or product categories, adding community features, or using data to customize the customer experience and product recommendations.
To create a successful marketplace, you need to foster trust and manage the interactions between customers and businesses. This requires constant improvement based on customer feedback. Investing the time from the beginning could allow you to build a strong foundation and deliver exponential results as your marketplace expands.
To find out how Stripe has enhanced payments for leading marketplaces, check out these case studies.
How Stripe Connect can integrate payments into your marketplace
Payment processing and infrastructure are key to online marketplace operations. Frictionless transactions between customers and businesses are a cornerstone of the marketplace business model.
A fast, secure, and reliable payment system—such as Stripe Connect—can foster trust, enhance the customer experience, boost sales, and support business growth. Learn how Connect makes it easy to integrate payments into your marketplace:
Costs
Stripe charges a percentage plus a fixed fee for every transaction. There are no installation fees, chargeback management fees, or monthly commissions.Global coverage and multicurrency support
If your marketplace caters to international customers, you’ll need a payment service provider (PSP) that is available in several countries and supports multiple currencies. Stripe supports over 135 currencies and is available in about 50 countries around the world.User-friendly integration
Stripe’s application programming interfaces (APIs)—widely recognized as flexible and easy to integrate—provide you with a payment system that embeds smoothly into your marketplace platform.Payout options and planning
You’ll want to offer businesses flexible payout options. Stripe allows you to customize your payout schedules and supports payout methods customized for different types of marketplaces.Security
Stripe uses machine learning to detect fraud and is certified as a Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) Level 1 service provider—the highest security certification in the payment industry. This ensures the security of sensitive financial data.Regulatory compliance
Stripe ensures compliance with current regulations, including with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) that protects European customers.Customer support
High-quality customer support is key to solving any issues that arise. Stripe offers 24/7 support via email, chat, or phone.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.