Reach new customers with Cash App Pay
Cash App Pay allows your US customers to seamlessly pay using Cash App, the number one finance app in both app stores.¹
Capture more revenue
Access a unique audience—more than two-thirds of Cash App’s monthly transacting actives are millennial or Gen Z customers.¹ 55% of Cash App customers don’t have a credit card,² allowing you to convert previously untapped customers.
Remove friction at checkout
Enable your customers to check out with a seamless user experience—just scan a QR code on desktop or get automatically redirected to Cash App on mobile.
Gain a loyal customer base
Cash App users are highly engaged, with two-thirds of monthly actives transact every week on average.¹
Simplify operations
Add Cash App Pay to any Stripe integration for unified monitoring, reporting, and payouts with seamless onboarding. There’s no additional application or onboarding process to get started.
How it works
Faster checkout on web and mobile
Wallets provide a fast and secure way for customers to pay with a saved card or a stored balance. With Cash App Pay, customers pay with their Cash App balance or debit card at their favorite brands by scanning a QR code on desktop or redirecting to the app on mobile.
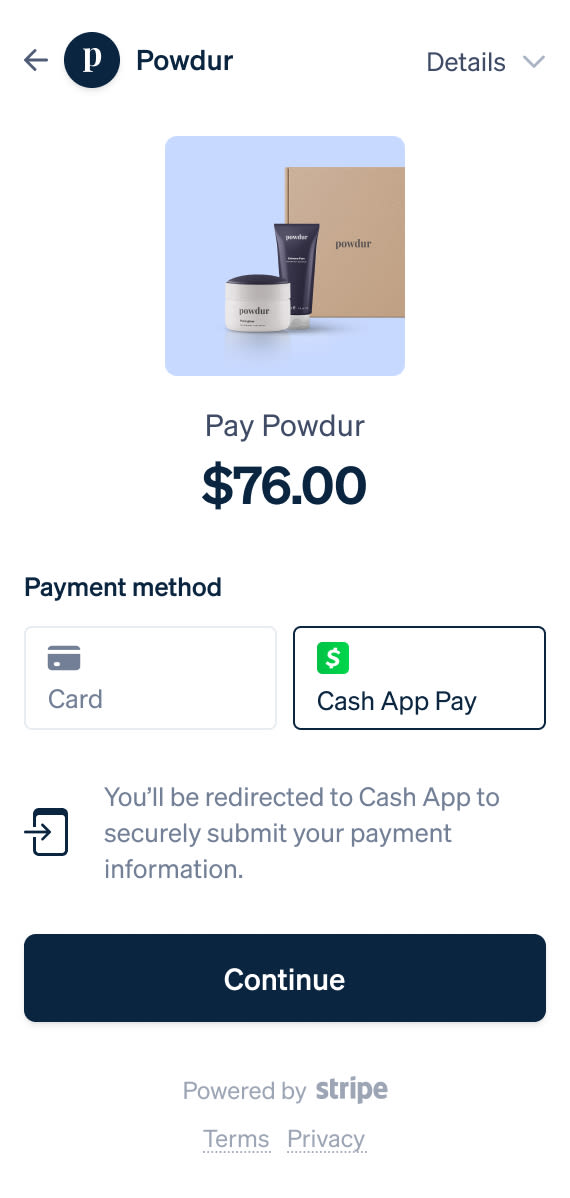
Fully integrated
Get started fast on Stripe
With Stripe, you can get up and running with Cash App Pay in minutes. There’s no additional paperwork for eligible businesses to get started, and everything from maintenance to reconciliation is simpler with a unified payments integration.
Cash App is exploding in our demographic, but it was always a black box for us because we couldn’t implement it with our previous payments provider. It’s huge that we’re able to offer it now with Stripe.
Pricing
Know what you’ll pay
Ready to get started?
There’s no additional paperwork for eligible businesses in the US to start accepting Cash App Pay on Stripe.
Eligibility
Check if your business category is supported in the docs, or visit your Dashboard settings to confirm if you are eligible.
Payment Method Guide
Understand the importance of payment methods and which ones to offer based on your business model and customer preferences.


