Seed money – often referred to as seed funding or seed capital – is an initial investment that entrepreneurs or founders use to cover initial operating expenses when starting a business or a new project. This type of funding is usually a relatively small amount of capital compared with other sources of startup funding.
Seed money can come from a variety of sources. These include the founders themselves, friends and family, angel investors and early-stage venture capital firms. The amount of seed money required can vary significantly depending on the nature of the business and its initial needs. Seed money allows entrepreneurs to move from the idea stage to a tangible business or product. From there, they can demonstrate the feasibility and potential of their business to attract further investment.
After the seed stage, a startup may seek additional funding rounds – such as Series A, B and C – which usually involve larger amounts of capital and may come from venture capital firms, private equity or other investors.
Below, we'll describe what early-stage founders need to know about how to raise seed money, including where to seek it, how to choose the right funding source for specific business goals, how to close the deal and how to spend seed money wisely.
What's in this article?
- How seed funding differs from other types of funding
- Why seed funding is important for startups
- Preparing to raise seed money
- Sources of seed money
- How to raise seed money for a startup
- How to negotiate seed funding with investors
- Best practices for managing seed money
How seed funding differs from other types of funding
Startups go through different stages during their lifecycle. While each stage of development (and the funding round that accompanies it) can vary depending on the individual startup, there are general traits that define each stage.
The seed stage is arguably the most volatile – and exciting – time for startups. Here's how seed funding differs from other types of funding that may come later:
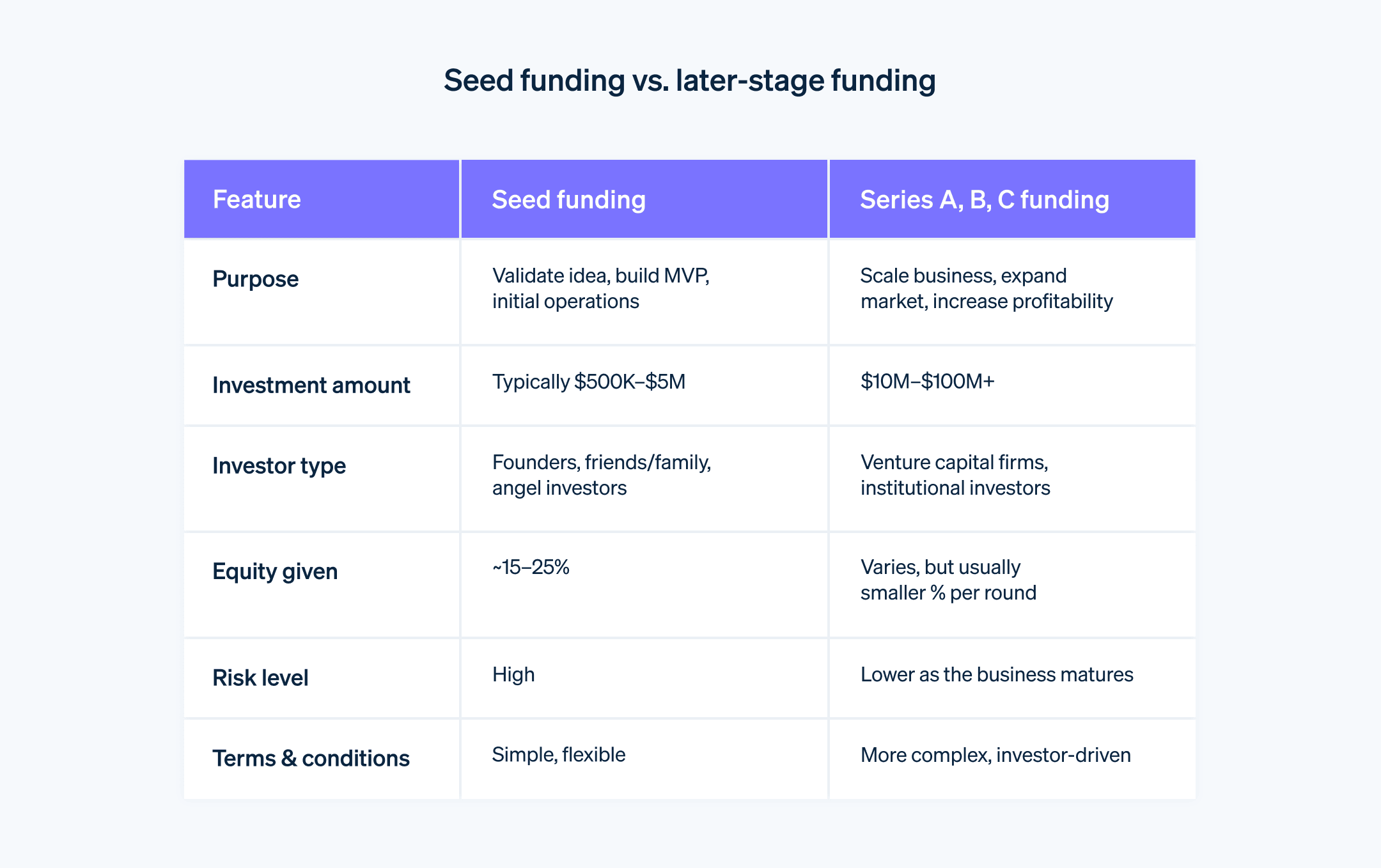
Purpose and use
Seed funding is primarily aimed at turning an idea into a viable business concept. This often includes conducting market research, developing the product and building a team. In contrast, later rounds of funding – such as Series A, B or C – focus more on scaling the business, expanding market reach, enhancing the product or entering new markets.Amount
Generally, the amount raised during the seed stage is much smaller compared with that of later funding rounds. The average seed round in the first quarter of 2023 was just US$3.6 million, compared with an average Series A round of US$18.7 million. It's usually enough to prove a concept or reach a significant milestone. As the startup grows and shows its potential, it can attract larger investments in subsequent rounds.Type of investors
Seed funding often comes from the founders themselves, friends, family and angel investors. These are individuals or groups who are willing to take a risk on a very early-stage idea. In contrast, later stages attract institutional investors, such as venture capital firms, which invest larger amounts of money into more established companies with a proven track record. Venture capital firms invested US$671 billion across 38,644 deals worldwide in 2021, representing larger deals than the average seed round.Equity and valuation
During the seed stage, the valuation of the startup may not be well established yet. As a result, investors can receive significant amounts of equity for a relatively small amount of money. In later stages, as the company's valuation increases, it will give away smaller portions of equity for larger amounts of capital. Every deal is different, but as a general rule, founders should plan to sell approximately 20% of their equity in the seed round.Risk and reward
Seed funding is typically considered to be higher risk because the business model and market fit may not be fully tested. But there is potential for high levels of reward, as early investors often get a more significant stake in the business's equity. As the startup matures and moves into later funding rounds, the risk decreases, as does the potential reward in terms of equity share.Terms and conditions
Seed funding agreements usually include fewer terms and conditions compared with later funding rounds. As startups grow and attract more sophisticated investors, the complexity of funding agreements typically increases, with more stringent terms and conditions.
Why seed funding is important for startups
While every funding round is important, seed funding may make more of an impact for startups than future investment rounds – even though the investment is often smaller. Seed funding can influence a startup's trajectory by:
Validating the business idea
Seed funding provides the necessary capital to validate a startup's concept. This stage is about proving that there's a market need for the product or service, which is important for attracting future investors. Without seed funding, many ideas would never progress any further.Building the foundation
This initial capital allows startups to set up important operations, recruit key team members and begin initial product development.Facilitating early growth and development
With seed funding, startups can focus on early growth, refine their product or service, and establish a customer base. This early growth demonstrates the potential for scalability and long-term success.Attracting future funding opportunities
A successful seed round brings in capital and validates the startup with future investors. It often leads to more substantial funding rounds, such as Series A, as it demonstrates that the startup has moved beyond the concept stage and has a viable, growing business.Gaining partners and mentors
Investors in the seed stage often bring more than just capital – they can be invaluable sources of advice, industry connections and mentorship. This guidance can be useful for navigating the early challenges of running a startup.Allowing flexibility and autonomy
Seed funding usually comes with fewer conditions compared with later rounds. Startups have more freedom to experiment and pivot if necessary in this stage, without the pressure of large-scale investor expectations and intricate agreements.Establishing credibility
Seed funding is often seen as a stamp of approval, enhancing the credibility of the startup in the eyes of customers, partners and future investors. It's a sign that knowledgeable individuals or entities believe in the startup's potential.
Preparing to raise seed money
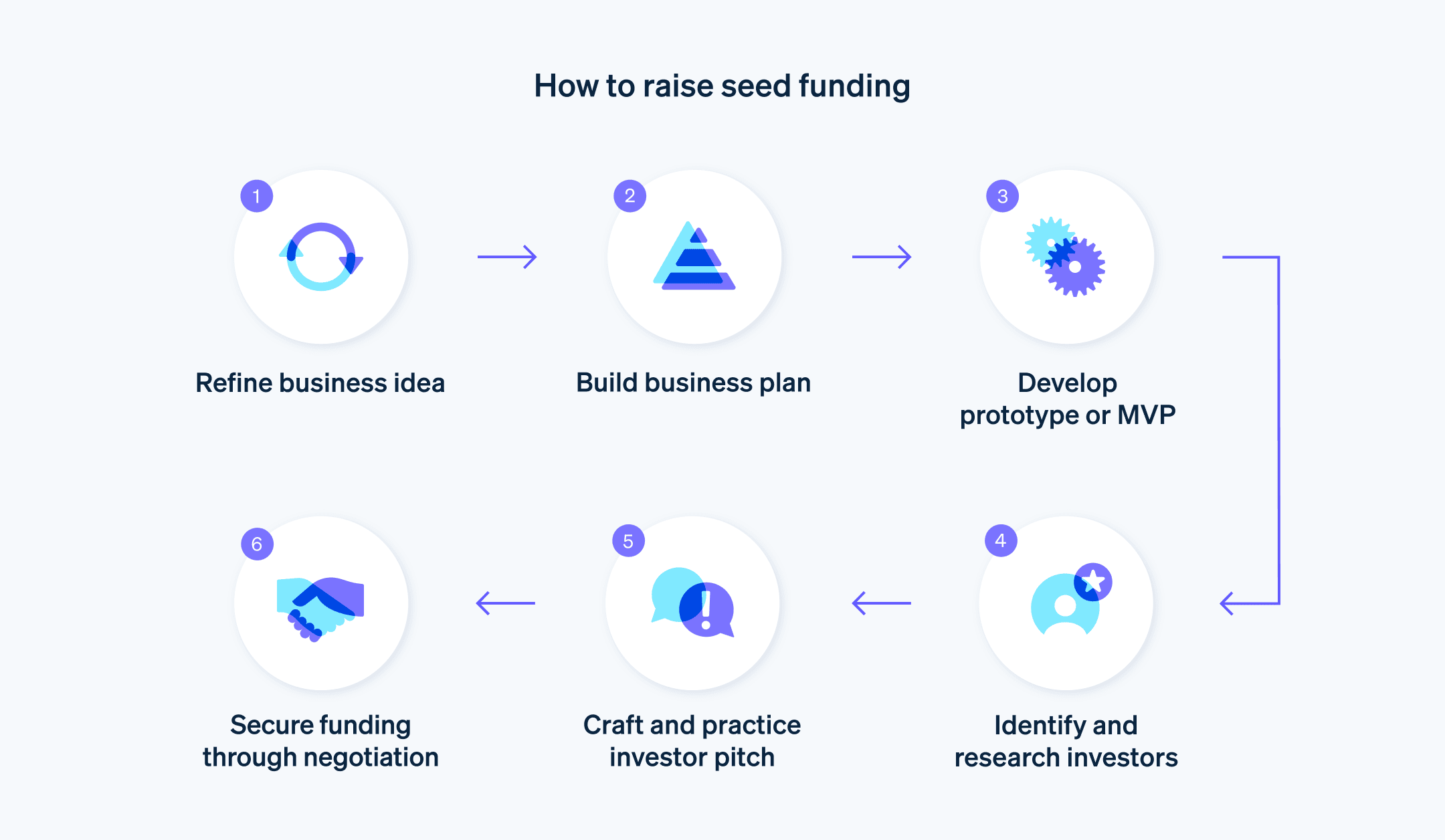
Startups must do a lot of preparatory work before they get in touch with their first potential investors for seed funding. Here's what you need to do at the beginning of the fundraising process:
Refine your business idea
Before approaching investors, ensure that your business idea is clear and innovative, and addresses a genuine market need. This involves conducting thorough market research, understanding your target audience and developing a unique value proposition.Formulate a solid business plan
A well-structured business plan should outline your business model, market analysis, operational strategy, financial projections and long-term goals. This document will be a roadmap for your business and a persuasive tool for potential investors.Develop a prototype or an MVP
If applicable, develop a prototype or a minimum viable product (MVP). This tangible representation of your idea shows investors that you've moved beyond the conceptual stage and have something that works and can be tested in the market.Build a strong team
Investors don't just invest in ideas – they invest in people. Assemble a team with diverse skills and experiences. Demonstrating that you have a capable team in place can significantly boost investor confidence in your startup.Incorporate financial planning
Have a clear understanding of how much funding you need and how you plan to use it. Be prepared to explain your financial model and projections, showing a clear path to profitability or growth.Create an investor pitch
Develop a compelling pitch that explains your business idea, market opportunity, team and financials succinctly. To attract the attention of potential investors, your pitch should be engaging, clear and concise.Identify potential investors
Research and identify potential investors who are a good fit for your startup. These could include angel investors, venture capitalists, incubators or accelerators. Make sure that you understand their investment thesis and portfolio to customise your approach.Network and build relationships
Start building relationships within the startup environment. Attend industry events, join startup communities and engage on platforms where you can meet potential investors and mentors.Ensure legal and regulatory compliance
Ensure that your startup complies with all legal and regulatory requirements. This may include incorporating your business, trademarking your brand or addressing any other industry-specific regulations.Prepare for due diligence
Investors will conduct thorough due diligence before investing. Organise all of your legal, financial and business documents so that they are ready for review.
Sources of seed money
Where early funding comes from will influence the first phase of the startup's life – and potentially affect its future. This is mostly due to significant differences in the terms of various funding agreements and what kind of relationship founders will have with the investors.
Before you start actively seeking seed money from any source, weigh up your options carefully. Make sure that you're choosing a funding source that maximises the benefits that you value the most, while minimising the drawbacks and risks that you're most averse to. Here's an overview of potential seed funding sources:
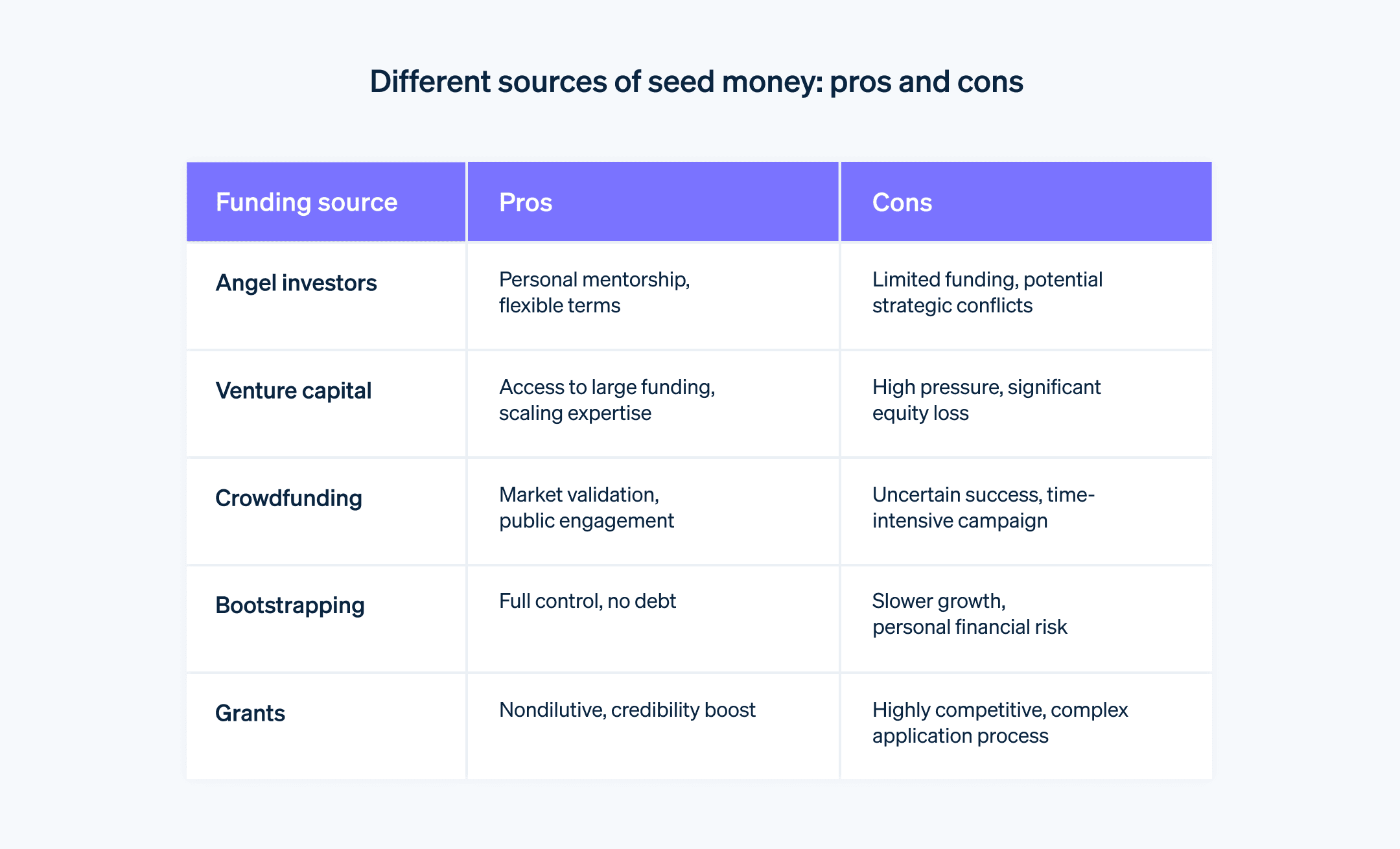
Angel investors
What they are: Angel investors are affluent individuals who provide capital for a business startup, usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. They often are entrepreneurs themselves or retired business executives.
Suitability: Ideal for early-stage startups that need guidance and networking opportunities.
Pros
Personalised attention and mentorship
Flexible terms and less formal processes
Valuable networking opportunities
Cons
Limited funding capacity
May have less business acumen compared with professional investors
Possible conflicts in business direction or strategy
Venture capitalists (VCs)
What they are: Venture capitalists are professional groups that manage pooled investments in high-growth startups in exchange for equity.
Suitability: Best for startups with high growth potential and a clear path to substantial revenue and profitability.
Pros
Access to significant amounts of capital
Expertise in scaling businesses
Strong networking opportunities
Cons
Rigorous vetting process and competitive
Loss of some control and equity
Pressure to deliver high growth and returns
Crowdfunding
What it is: Crowdfunding involves raising small amounts of money from a large number of people, typically online.
Suitability: Suitable for consumer-focused startups, innovative products, or companies with a compelling story or social angle.
Pros
Access to a broad audience
Validation of the business concept
Non-dilutive financing (in most cases)
Cons
Time-consuming and uncertain
Requires compelling marketing
May face intellectual property exposure
Bootstrapping
What it is: Bootstrapping is when entrepreneurs start a business with little capital, relying on personal finances and the company's revenue.
Suitability: Best for businesses that can be started with minimal capital and founders who want full control.
Pros
Full control over the business
No dilution of equity
Encourages lean operations and resourcefulness
Cons
Limited resources can hinder growth
Personal financial risk
Can be slow to scale
Grants
What they are: Grants are non-repayable funds or products that grant-makers – often a government department, corporation, foundation or trust – disburse to a recipient.
Suitability: Suitable for research-oriented, social, educational or eco-friendly startups, or those in specific industries that are favoured by grant programmes.
Pros
Non-dilutive funding
Adds credibility
Can fund specific projects
Cons
Highly competitive and stringent criteria
Often limited in scope and scale
Time-consuming application process
How to raise seed money for a startup
Once you feel confident about which funding sources you're going to pursue, here's how to approach them strategically:
If you're seeking funds from angel investors
Identify suitable angel investors
Research and identify investors whose interests align with your startup, using your network, angel investor directories and industry events. Find angels who understand and are passionate about your industry and vision.Craft a compelling pitch
Your pitch should weave a compelling narrative about your startup, emphasising the problem that you're solving and your vision. Support this story with market analysis, financial projections and a detailed business plan.Build relationships
Approach each interaction as an opportunity to build a long-term relationship. Engage in genuine conversations, value their advice and be receptive to feedback. Note that you're seeking a partner, not just a financier.Be prepared for in-depth discussions
Be prepared to articulate your long-term vision and how the investor's expertise and network can contribute to your growth.Negotiate terms fairly
Negotiations with angel investors often allow for more flexibility. Communicate your needs clearly and be prepared to understand and accommodate the investor's expectations and perspectives.Leverage the relationship
Once an angel has invested, use their experience and network to your startup's advantage. Keep them updated and involved in key decisions, turning the investment into a collaborative journey.
If you're seeking funds from venture capitalists
Identify the right VCs
Research and target venture capitalists with a history of investing in your industry and at your stage of business. Use your network, online databases and industry events to find VCs with an investment thesis that aligns with your startup's goals and needs.Prepare a detailed pitch deck
Your pitch deck should be comprehensive and data-driven, showcasing your business model, market size, competitive landscape, product, team and financial projections. VCs are looking for scalable businesses with high growth potential, so highlight these aspects convincingly.Demonstrate traction and market fit
VCs typically invest in startups that already have some market traction or validation. Present any evidence of customer interest, revenue, growth metrics or partnerships that demonstrate your startup's market fit and potential for growth.Understand and prepare for rigorous due diligence
Be ready for a thorough due diligence process. This will include a deep analysis of your financials, legal matters, business model, market research and team background. Organise all of your documents and information to streamline this process.Negotiate terms and valuation
Be prepared for tough negotiations on valuation and terms. Understand your startup's valuation and be prepared to discuss and justify it. Familiarise yourself with common VC terms and conditions, and consider the long-term implications of these on your business.Build a relationship and communicate your vision
While VCs are primarily focused on returns, building a relationship with them is also important. Communicate your long-term vision and how their funding, network and expertise can help you to achieve your goals.
If you're crowdfunding your seed money
Choose the right platform
Select a crowdfunding platform that aligns with your startup's product or service. Different platforms cater to different types of projects and audiences, so choose one that resonates with your target market and type of offering – whether that is equity, reward or donation-based crowdfunding.Create a compelling campaign
Your campaign should tell a compelling story about your startup, why it matters and what makes it unique. Use engaging visuals and clear, persuasive language. Videos can be particularly effective in conveying your message and connecting emotionally with potential backers.Set realistic goals and rewards
Set a funding goal that reflects what you need to move your project forwards, in a manner that is achievable based on your audience size. For reward-based crowdfunding, design attractive, feasible rewards which incentivise contributions without overextending your resources.Promote your campaign
Use social media, your personal network and community forums to announce your campaign. Update your backers and audience regularly about your progress to drive continuous engagement.Engage with your backers
Treat your backers as more than just funders – they're your early supporters and potential future customers. Engage with them throughout the campaign with updates, responding to comments and showing appreciation for their support.Plan for post-campaign
Have a clear plan for what happens after the campaign. This includes fulfilling rewards and continuing communication with backers, as well as building on the success of your campaign to gain further traction and visibility.
If you're bootstrapping your seed money
Manage finances wisely
Prioritise financial prudence and budget management. Minimise expenses and reinvest profits back into the business. Keep personal and business finances separate to maintain clear records and avoid unnecessary financial complications.Focus on cash flow
Cash flow is key in bootstrapping. Develop a business model that generates consistent revenue and keep a close eye on cash flow management to sustain and grow your business operations.Use existing resources
Use available resources to their fullest potential. This includes your skills, network and existing assets. Find low-cost or free tools and services that can support your business operations.Grow gradually
Bootstrapping often means slower growth. Focus on gradual, sustainable growth rather than rapid expansion. This cautious approach allows you to build a solid foundation for your business without overextending your resources.Implement a customer-centric approach
Given that external funding isn't influencing the direction of your startup, you can align your business closely to your customer needs and feedback. Use this to your advantage by building strong customer relationships and customising your offerings to market demands.Plan for scaling
Have a clear strategy for scaling your business. As profits grow, reinvest in areas that will offer the most significant benefits, such as product development, marketing or the recruitment of key personnel.
If you're seeking grants
Research relevant grants
Identify grants that align with your startup's industry, mission or technology. Use online databases, government websites and industry publications to find grants that are a good fit for your business model and goals.Understand grant requirements
Read the eligibility criteria, application requirements and deadlines carefully for each grant. Grants often have very specific requirements and objectives, so ensure that your startup and proposal align with these.Create a detailed proposal
Include a thorough, compelling proposal in your application. Outline your business idea clearly, as well as its impact, how the grant money will be used and the expected outcomes. Use clear, concise language and adhere to any specific guidelines that were provided in the grant.Demonstrate impact and innovation
Many grants focus on funding projects that drive innovation, social impact or technological advancement. Highlight how your startup meets these criteria, providing evidence of potential impact and innovation.Incorporate budget and financial planning
Include a detailed budget which shows how the grant funds will be allocated. Demonstrate financial responsibility and a clear understanding of how the funding will move your project forwards.Prepare for follow-up and reporting
Be prepared for follow-up if your application is successful. This may include providing progress reports, financial statements or evidence of milestone achievements, as stipulated by the grant terms.
How to negotiate seed funding with investors
Potential investors will negotiate either on their own behalf or on behalf of the investors in their fund. Here's how to advocate for yourself successfully during the negotiations:
Understand the investor's perspective
Investors are looking for a return on their investment. They may love your idea, but ultimately, they're assessing risk versus reward. Recognising this will help you to frame your arguments and understand their counterpoints.Know your worth
Before entering any negotiation, have a clear understanding of your startup's valuation. Beyond the numbers, this includes your business's potential, the market and how much you've already achieved. Be prepared to defend your valuation with data and confidence.Listen to the investor
Good negotiation is rooted in effective communication. This means listening actively to what the investor is saying and responding thoughtfully. It's not about pushing your agenda – it's about finding common ground and a deal that benefits both parties.Be prepared to walk away
One of your biggest strengths in any negotiation is being willing to walk away. This doesn't mean being confrontational, but rather being firm about what you need for your startup to succeed. If an investor's terms undervalue your company or don't align with your vision, be prepared to say no.Be flexible, within reason
While it's important to know what you want, being too rigid can be a deal-breaker. Have clear boundaries, but be flexible within your boundaries. This may mean negotiating on equity, the structure of the investment or other terms.Value long-term relationships
Remember, you're potentially entering into a long-term relationship with your investor. Approach negotiations with respect and the desire for a partnership. The goal is not just to secure funding, but also to build a relationship that will support your startup's growth.Pay attention to the details
Pay close attention to the terms of the deal, not just the headline figures. This includes understanding specific clauses, such as liquidation preferences, anti-dilution provisions and board rights. It's often worth obtaining legal advice to ensure that you understand the implications of these terms in full.Communicate post-negotiation
Following a successful negotiation, maintain open lines of communication with your investors. Keeping them informed and involved (to an appropriate degree) can build a strong, ongoing relationship.
Best practices for managing seed money
Once you've secured your seed funding, you'll need to decide how to use it. Here are some best practices:
Prioritise spending based on your business plan
Start by revisiting your business plan. You should allocate funds primarily to the areas that drive business growth and development, as outlined in your business plan. This may include product development, market research or key areas of recruitment. Following your business plan ensures that you're using your funds to achieve specific, strategic goals.Avoid unnecessary expenses
Exercise frugality without compromising on quality. This means considering each expense carefully and avoiding unnecessary spending. For instance, opt for functional, cost-effective office space rather than luxurious premises. Every penny saved is a penny that can be invested in areas that contribute directly to growth.Invest in talent wisely
Your team is your most valuable asset. Recruit skilled individuals who share your vision and are committed to the startup's success. However, be judicious in how you expand your team. Over-recruiting too early on can deplete your resources quickly.Focus on product development and market fit
Use a significant portion of your seed money to refine your product or service. This includes investing in development, testing and feedback mechanisms to ensure that your offering meets market needs and is competitive.Be strategic about marketing and customer acquisition
Invest in cost-effective, targeted marketing strategies. Focus on channels that offer the highest return on investment and track the performance of your marketing campaigns closely.Maintain a cash reserve
Keep a portion of your seed money as a cash reserve. This can be useful for unforeseen expenses or if the business hits a rough patch. A reserve can give you the flexibility and security to address challenges with less financial stress.Monitor cash flow closely
Monitor your cash flow regularly to ensure that your startup stays financially healthy and adjust your spending, if needed.Reinvest profits back into the business
If your startup begins generating profit, consider reinvesting a significant portion back into the business. This reinvestment can fuel further growth and reduce the need for additional external funding.Seek advice from mentors or financial advisors
Don't hesitate to seek advice from mentors or financial advisors. Their experience and perspective can be invaluable in helping you to make sound financial decisions.Be prepared to pivot
Be flexible and ready to pivot your strategy if necessary. The startup environment is dynamic and the ability to adapt your spending in response to market feedback or new opportunities can affect your success.
How Stripe Atlas can help
Stripe Atlas sets up your company's legal foundations so you can fundraise, open a bank account and accept payments within two business days from anywhere in the world.
Join 75K+ companies incorporated using Atlas, including startups backed by top investors like Y Combinator, a16z and General Catalyst.
Applying to Atlas
Applying to form a company with Atlas takes less than 10 minutes. You'll choose your company structure, instantly confirm whether your company name is available and add up to four co-founders. You'll also decide how to split equity, reserve a pool of equity for future investors and employees, appoint officers and then e-sign all your documents. Any co-founders will receive emails inviting them to e-sign their documents, too.
Accepting payments and banking before your EIN arrives
After forming your company, Atlas files for your EIN. Founders with a US Social Security number, address and mobile phone number are eligible for IRS expedited processing, while others will receive standard processing, which can take a little longer. Additionally, Atlas enables pre-EIN payments and banking, so you can start accepting payments and making transactions before your EIN arrives.
Cashless founder stock purchase
Founders can purchase initial shares using their intellectual property (e.g. copyrights or patents) instead of cash, with proof of purchase stored in your Atlas Dashboard. Your IP must be valued at US$100 or less to use this feature; if you own IP above that value, consult a lawyer before proceeding.
Automatic 83(b) tax election filing
Founders can file an 83(b) tax election to reduce personal Income taxes. Atlas will file it for you – whether you are a US or non-US founder – with USPS Certified Mail and tracking. You'll receive a signed 83(b) election and proof of filing directly in your Stripe Dashboard.
World-class company legal documents
Atlas provides all the legal documents you need to start running your company. Atlas C corp documents are built in collaboration with Cooley, one of the world's leading venture capital law firms. These documents are designed to help you fundraise immediately and ensure your company is legally protected, covering aspects like ownership structure, equity distribution and tax compliance.
A free year of Stripe Payments, plus $50K in partner credits and discounts
Atlas collaborates with top-tier partners to give founders exclusive discounts and credits. These include discounts on essential tools for engineering, tax, finance, compliance and operations from industry leaders like AWS, Carta and Perplexity. We also provide you with your required Delaware registered agent for free in your first year. Plus, as an Atlas user, you'll access additional Stripe benefits, including up to a year of free payment processing for up to $100K in payments volume.
Learn more about how Atlas can help you set up your new business quickly and easily and get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.