Digitisation is changing the corporate landscape worldwide, including in Germany. Businesses have almost unlimited opportunities to improve and advance by using a well-thought-out digitisation strategy. In this article, you will learn what a digitisation strategy is, what its benefits are, and how businesses can develop one. We will also give you examples of measures to digitise your business.
What’s in this article?
- What is a digitisation strategy?
- What are the advantages of a digitisation strategy?
- How can businesses develop a digitisation strategy?
- Measures for the digitisation of businesses
What is a digitisation strategy?
A digitisation strategy is a business’s systematic plan to transform its business processes as well as its products and services using digital technologies. Digitisation is fundamentally changing businesses and influencing the structures and processes of all areas of business – including research and development, production, logistics, sales, administration, human resources, information technology (IT), marketing, and communication. Businesses that want to take advantage of the opportunities digitisation offers need to implement measures to do so.
However, it is best to implement a comprehensive change process and not rely on individual measures. This is where a digitisation strategy can help. It ensures individual measures align with corporate objectives and can be implemented successively. A comprehensive plan enables the integration and coordination of all the business’s digital initiatives. A digitisation strategy thus serves as a road map and constant point of reference for a sustainable transformation.
Why is digital transformation important for businesses?
Digitisation is not a temporary trend; rather, it’s a profound change that affects all areas of life and work. Businesses that adapt to new conditions and use digital opportunities gain an advantage over those that do not. On the one hand, digitisation promises positive effects such as higher sales and stronger market positions. On the other hand, businesses in at least some industries seem to have little choice but to keep up with digital progress. There are several reasons for this:
- The market environment is changing, including new digital competitors.
- As digitisation increases, new business models are emerging.
- The needs and expectations of customers and employees are changing in the digital age.
What are the advantages of a digitisation strategy?
A digitisation strategy offers businesses numerous advantages over the implementation of individual measures without an overall plan.
Holistic approach
A digitisation strategy ensures you do not implement your digital measures in isolation but in a coordinated manner. This prevents inefficient, isolated solutions and enables business-wide integration, in which all departments benefit from the digital changes. In addition, a digitisation strategy ensures all measures align with overarching corporate objectives.
Long-term planning
Digitisation strategies help businesses set long-term goals and plan digital developments. This lets businesses react early to technological trends and shape their digital transformation gradually and sustainably.
Cultural change in the business
A well-thought-out strategy facilitates cultural change within businesses by making employees aware of the importance and benefits of digitisation and by using targeted training measures. This can promote employee acceptance and commitment.
Better resource allocation
Instead of implementing digital projects spontaneously or ad hoc, a strategy sets clear priorities. This allows resources – such as time, money, and personnel – to be invested specifically in the most promising measures. This reduces the risk of bad investments.
Improved customer experience
Digitisation strategies help create personalised and smooth customer experiences by connecting different digital channels such as apps, websites, or social media. You can then identify and address customers’ needs faster.
Risk control
A well-thought-out strategy lets you identify digitisation risks early and provides you time to take preventive measures. Possible risks include threats from cybercrime or data protection issues. Digitisation strategies thus increase business security and stability.
Faster decision-making
Ideally, as part of the digitisation strategy, you would integrate real-time data and analysis tools that measure the success of digitisation measures. With extensive data, management can make decisions faster.
Continual optimisation
A measured approach ensures the regular review and adaptation of digital initiatives. You should ensure all measures contribute to the business’s objectives and keep pace with technological developments.
Competitive advantages
Businesses that pursue a comprehensive digitisation strategy can stand out from the competition by providing faster response times, innovative products, and optimised processes.
Safeguarding the future
Digitisation strategies help businesses prepare for technological developments and market requirements. Businesses can position themselves early and continually develop. This ensures businesses are competitive now and can respond to future challenges and opportunities.
How can businesses develop a digitization strategy?
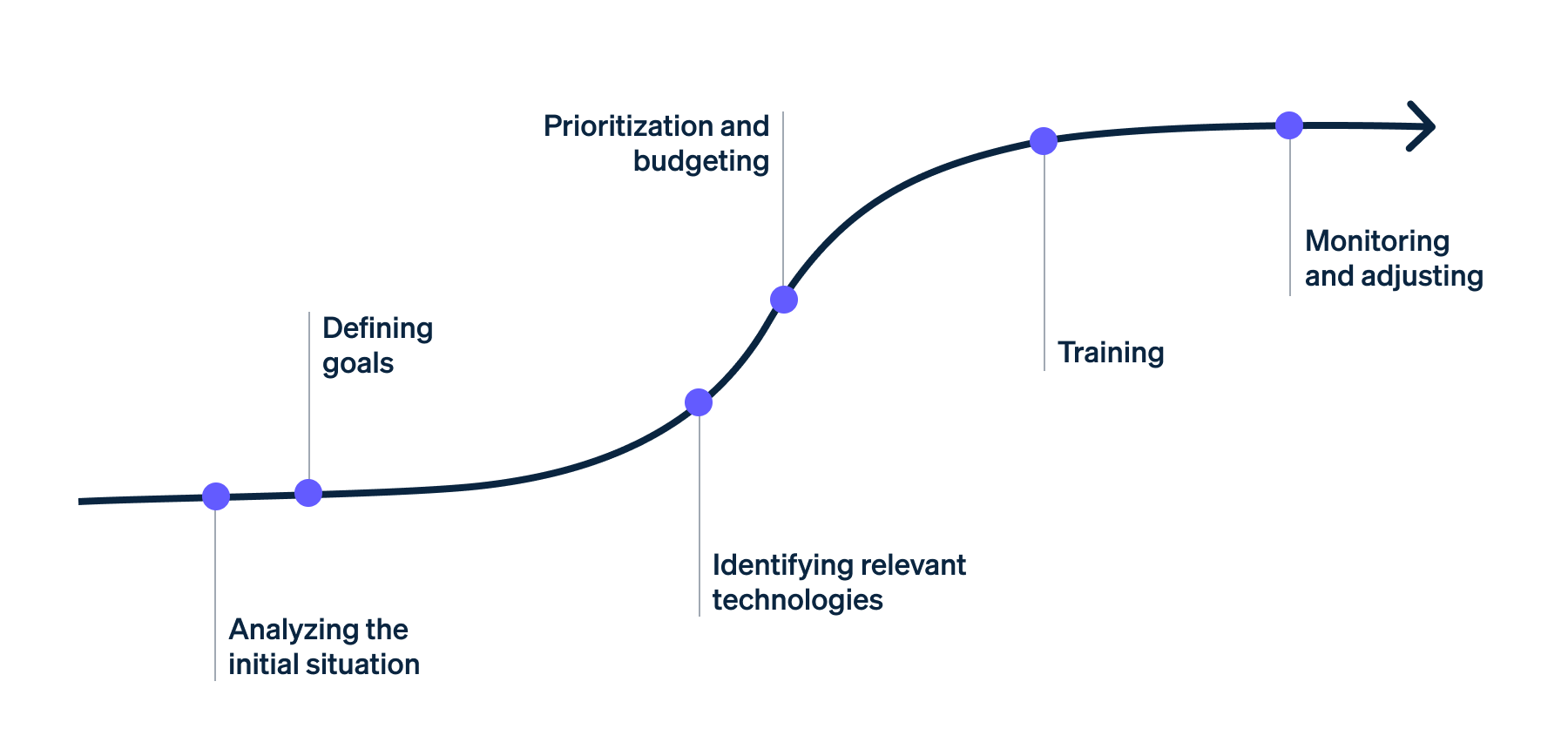
Here are the six most important steps to developing a digitisation strategy:
Step 1: Analysing the initial situation
The first step in developing a digitisation strategy is a comprehensive analysis and assessment of the status quo. Businesses should check which processes are still analogue and which are already digital, among other factors. In addition, businesses should identify all areas and processes they can fine-tune using digital technologies. Furthermore, a more detailed analysis can provide information on whether a business can develop new business areas through digitisation measures.
Step 2: Defining the goals
Once you have answered all questions regarding the state of the business, the second step is to define goals for the digitisation strategy. This should include the processes and areas the business plans to digitise, among other things. Businesses also need to define the expected effects. Should the business’s digitisation strategy increase sales, acquire customers, or improve their satisfaction with products, services, or processes? There are numerous potential effects, which is why it’s important to spend sufficient time formulating objectives.
Step 3: Identification of relevant technology
The third step is to create the conditions for the practical implementation of the digitisation strategy. To this end, businesses should obtain comprehensive information about suitable technologies and tools. There are numerous providers of digital solutions and new trends a business can incorporate into the research. Finally, businesses must make decisions as to which providers, technology, and tools they want to implement for individual digitisation projects.
Step 4: Prioritisation and budgeting
In the fourth step, the business can prioritise planned measures based on management preferences and urgency. At the same time, businesses should consider their available budget. For practical and financial reasons, businesses are unable to implement all measures simultaneously. Therefore, prioritise all projects in a sensible order so the business can implement them one after the other.
Step 5: Training
New technologies usually require new know-how. This is why businesses should provide internal and external training to all employees to familiarise them with the processes.
Step 6: Monitoring and adaptation
In the sixth step, businesses should implement monitoring and evaluation systems. The aim is to comprehensively analyse the implemented measures and their impact. Are the individual initiatives meeting the targets defined in the digitisation strategy? Which measures does the business need to adapt? Which ones might need rethinking? In addition to the findings from ongoing monitoring, businesses should incorporate new trends and market requirements into the adaptation of the digitisation strategy.
Graphic: Digitisation development strategy road map
Measures for the digitisation of businesses
There are many examples of measures that businesses can implement as part of a digitisation strategy. The switch from physical to digital documents offers many advantages. Digitised documents are easy to search through, speeding up processes and increasing productivity. Digital documents also save on paper, printer, and storage costs. Another advantage: businesses improve their ecological footprint by saving resources.
You can also store digital documents and information centrally in a second step. Using a digital platform or cloud system, all employees have access to the content anywhere, at any time. This improves collaboration within the team and ensures information is always up to date. The centralised availability of information is important, especially with home office and hybrid working models.
Another approach is the automation of accounting processes. Modern software solutions make it possible to automate time-consuming and error-prone processes such as invoice approval or accounts-receivable management. Businesses can approve invoices, send automated reminders, and enhance payment processes with one click. This reduces the burden on accounting and ensures faster and more efficient processes, which in turn improves the business’s liquidity.
If you need help with digital invoicing, learn more about Stripe Invoicing. Invoicing lets you automate the creation and sending of legal invoices. In addition, Stripe Billing enables recurring invoicing. Stripe Revenue Recognition provides a quick and comprehensive overview of your sales. With just a few clicks, you can automate and configure sales reports or book transactions periodically.
The digitisation of customer service can be a good alternative to analogue formats for businesses. Instead of a telephone hotline, they can use chatbots or self-service portals. In this way, they can process customer inquiries faster and around the clock. Digital tools can improve service quality, reduce employee workload, and increase customer satisfaction.
Customer convenience should also be a priority in payment processes. A key factor is being able to choose among payment methods. With Stripe Payments, you can offer customers more than 100 payment options and quickly and easily accept and manage all payments. This benefits you as a business and your customers, who can pay their invoice in the way they want at any time.
Businesses that sell products in a store or offer services on site, for instance, can use digital solutions to let customers pay by card. With Stripe Terminal, you can use pre-certified card readers such as Stripe Reader S700 or a mobile device such as the BBPOS WisePad 3. Cashless payments are also possible without an additional device: Tap to Pay enables this with an iPhone or Android device. All transactions are automatically transferred to the business’s accounting systems.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.