The XML invoice is becoming increasingly common in Germany, not least because of the legal requirements that companies in the B2G (business-to-government) and B2B sectors must comply with. But what exactly is behind this format, and why is it important for organisations to deal with it?
In this article, you will learn what an XML invoice is, how it works, and how it differs from the XRechnung and the ZUGFeRD invoice. We will also give you a concrete example of an XML invoice and explain the many benefits of this digital billing format.
What’s in this article?
- What is an XML invoice?
- How do XML, XRechnung, and ZUGFeRD invoices differ?
- How does the XML invoice format work?
- XML invoice: An example
- What are the advantages of an XML invoice?
What is an XML invoice?
An XML invoice is an electronic invoice created and transmitted in XML format. XML is “Extensible Markup Language”, a uniform, internationally recognised language for data structuring. The term is usually used without translation in German-speaking countries, as it has been established as a global standard.
XML is a systematic format developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an internet standardisation committee. The first version of the text data structure was released in 1998 as an evolution of Standard Generalised Markup Language (SGML). The goal was to create a format that was easier to use, more platform-independent, and better suited for exchanging information on the internet than its more complex predecessor. Since version 1.0, XML has been updated several times. It now plays a central role in standardising data structures and is used in numerous applications such as web services, document formats, and electronic invoices.
One of the characteristics of XML-based invoice formats is that they are optimised for computerised processing. They consist of a record in the form of lines of code in which all invoice data has a pre-determined place. Unlike PDF statements or paper documents, software can read and process them automatically.
The XML invoice became relevant for German companies in 2014 with EU Directive 2014/55/EU. The directive made e-invoicing mandatory for public procurement in the European Union, aiming to simplify administration and facilitate cross-border co-operation within. Since November 2020, all contracting authorities in Germany have been required to be able to receive and process them in electronic format. Since then, German companies issuing invoices to public administrations and federal authorities have preferred to do so in XML.
As of 1 January 2025, e-invoicing and XML invoices will be mandatory for B2G and B2B organizations. In March 2024, the German parliament passed the Growth Opportunities Act, which stipulates that companies can exclusively use electronic formats when billing other organisations as of 2025. There is an exception for small-scale entrepreneurs: they can still send invoices on paper or as PDFs. However, it will be mandatory to accept and process electronic invoices they receive. This regulation for small entrepreneurs was included in the Annual Tax Act 2024. Detailed information can be found in the small-scale entrepreneur rule in 2025 article.
Businesses can choose which framework they want to use for their e-invoices. The XRechnung and ZUGFeRD formats are among Germany’s most commonly used options.
How do XML, XRechnung, and ZUGFeRD invoices differ?
The terms XML, XRechnung, and ZUGFeRD invoices are often used interchangeably, although there are differences. An XML invoice consists of an XML record and refers to the general technical layout of an electronic invoice.
An XRechnung is an electronic invoice that also contains only an XML file. That said, it is a strictly regulated framework explicitly developed for the public sector in Germany by the Co-ordination Office for IT Standards (KoSIT). As of 2020, it will be used in Germany to exchange them with contracting authorities electronically.
A ZUGFeRD invoice is a hybrid format that contains an XML and a PDF file, which allows it to be read automatically or manually. It looks like a conventional invoice in PDF so that recipients can process it without additional software, making the ZUGFeRD suitable for B2G, B2B, and B2C sectors. This framework was developed by the Forum for Electronic Invoicing Germany (FeRD) in 2014.
XML, XRechnung, and ZUGFeRD invoices comply with EU Directive 2014/55/EU and the EU standard EN 16931 for electronic invoices, making them legally compliant.
How does the XML invoice format work?
XML invoices function like traditional ones: they need to be made and delivered. There are, however, some technical requirements for both their creation and recipient processing.
Technical requirements
They can be made using specialised accounting software or online generators. Many accounting programs have a built-in XML format that allows automated creation, delivery, and archiving.
Web-based tools offer similar capabilities, but invoices must be manually downloaded and archived. For companies that issue a large number of them and require long-term cataloguing, using specialised software is usually more advantageous – especially because, unlike online generators, the number that can be made is unlimited.
A third way to create an XML invoice is to convert an existing PDF invoice into XML format. The first step is to use an OCR tool to read the content of the original. Still, the first two options are preferable because errors can occur in this process.
Invoice creation
The key invoice data must be entered into the system, whether it is created with special software or an internet tool. Section 14 of the German VAT Act (UStG) states that these must contain all the following mandatory information to comply with German tax law:
- Full name and address of the recipient and company providing the product or service
- Date of the invoice
- Date of delivery of the product or service
- Tax number issued to the supplying company by the tax office or the value-added tax identification number (VAT ID) issued by the Federal Central Tax Office (BZSt)
- A sequential, unique invoice number
- Quantity and type of products delivered or the scope and type of service provided
- Gross and net amount
- Applicable tax rate and the corresponding amount or, in the case of a tax exemption, a reference to the exemption
In addition to information about the service provider, the service recipient, and the service itself, the bank details of the performing companies are also queried in XML invoice format.
Finally, the software or online generator converts the invoice data into an XML file. The file is created according to a particular definition that specifies the structure of the information it contains. This model can be based on either general XML or specific invoicing guidelines such as XRechnung.
Validation
The resulting XML file must then be validated to ensure that it conforms to the standards and that all necessary data is formatted correctly. This validation is performed using an XML validator. Successful validation confirms that the file meets the technical requirements and can be processed without errors. Once the validation is complete, the XML file is converted to the final format.
Invoicing dispatch
In the final step, companies send the XML invoice to the recipient. There are several ways to do this: as a file upload, email attachment, or via dedicated transmission platforms. Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement OnLine) is one such transmission platform, and is a network established throughout Europe and recommended by the Federal Ministry of the Interior. It enables the secure and unified exchange of business documents, including XML invoices. Companies can use this network to send them directly to government agencies and other organisations, regardless of the software solutions they use.
Another effective way to send electronic invoices is with Stripe Invoicing. Businesses with a Stripe account can use the Billit partner app to create and send electronic invoices easily and compliantly. Once the application is set up, sending is fully automated, significantly reducing administrative overhead. Another advantage of the system is the ability to monitor the status of all invoices in real time, allowing for transparent tracking and control. If there is an error in the system, users are notified to identify and resolve problems quickly.
Invoice processing and archiving
Recipients also need a suitable software solution to read and process the invoice data. In the best case, the software will automatically integrate the XML invoice into the company’s accounting systems. To ensure auditability, it must be stored in an archiving system that assures the file is not modified or deleted during the legally required retention period. The GoBD (principles for the proper keeping and retention of books, records, and documents in electronic form) also applies to XML invoices.
XML invoice: An example
Here is a fictional example of an XML invoice: Company A issues an invoice for $1,000 for the product delivery to Company B on 15 December 2024.
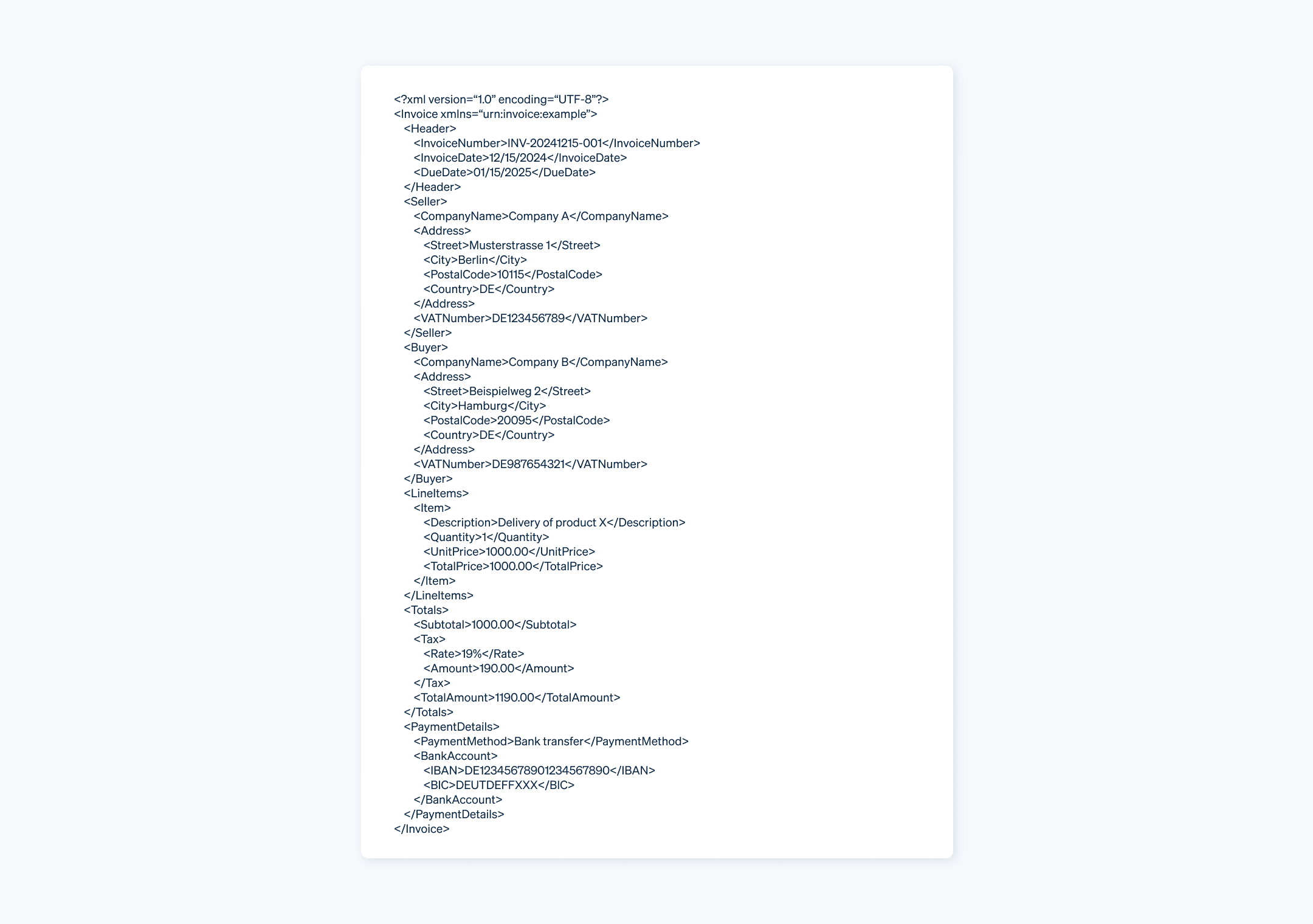
The XML invoice header contains basic information such as its number, date, and due date. The “Seller” and “Buyer” sections list the addresses and tax data of the companies involved. “LineItems” lists the products or services provided, including description, quantity, unit price, and total price. The “Totals” section includes the net amount, the calculated sales tax, and the gross amount. The “PaymentDetails” line contains the payment methods, including the invoicing firm’s bank details.
What are the advantages of an XML invoice?
XML invoicing offers many benefits that help companies make their processes more efficient, secure, and cost-effective. Below are the key points at a glance.
Legal and revision security
The XML format meets all legal needs for e-invoicing, such as EU Directive 2014/55/EU. Additionally, they can be archived in an audit-proof manner, meeting the requirements of the GoBD in Germany.
Compatibility and standardisation
Using internationally recognised standards, XML invoices can be easily exchanged between systems and partners. This enables seamless international collaboration, regardless of the software used.
Automation and efficiency
Because the data is structured and machine-readable, appropriate systems can automatically process XML invoices – there is no need for extra manual processing of incoming ones. This saves time and money and can be especially beneficial for companies with high volumes.
Error reduction
This format reduces errors not only during processing by the recipient but also, thanks to the standardised data structure, minimises the likelihood of input and transmission errors. Validation mechanisms check the completeness and accuracy of the information before it is sent.
Transparency and control
XML invoices make it easier to track and analyse their data. Digital tools such as Stripe Invoicing allows businesses to monitor invoice status in real time and take action when necessary, making receivables management more transparent and efficient.
Cost savings
Using XML invoices saves money in several areas – printing and paper costs are eliminated. Digital delivery is also faster and cheaper than traditional post. Automation also reduces labor costs for manual processes.
Sustainability
Eliminating paper contributes to sustainable business practices. Furthermore, companies improve their environmental footprint by removing the need to physically send invoices, reducing CO₂ emissions.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.