Discover what key performance indicators (KPIs) are, which KPIs are most important for the success of your online shop and why you should monitor them regularly.
What's in this article?
- What is e-commerce?
- What are e-commerce KPIs and why are they important?
- What are the most important KPIs in e-commerce?
- Why must KPIs always be measured in relation to each other?
What is e-commerce?
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. E-commerce provides countless benefits for businesses, such as expanding their customer base, providing greater flexibility in the product range and the ability to sell at any time.
In order to be successful in e-commerce, it is important to understand current trends and developments, and to react accordingly. This includes optimising mobile devices or integrating social media channels into the sales process, for example.
What are e-commerce KPIs and why are they important?
It is essential for e-commerce businesses to measure and analyse the success of their online shops accurately, in order to continue being successful in the long term and to scale their business. To do this, they need to measure the right metrics to provide a complete picture of their business's performance. These metrics are known as "key performance indicators", or "KPIs" for short. KPIs are measurements that reveal how successful certain processes or activities are within an e-commerce business. They include the conversion rate, average order value and the number of orders per month.
When businesses monitor and optimise their KPIs on a regular basis, this not only helps make their business more successful, but also highlights areas that require improvement. Without KPIs, it is hard to know which business areas or processes are functioning, and which are not. KPIs represent a valuable instrument for measuring the success of an e-commerce business accurately and increasing sales. For businesses, it's important to be familiar with this topic and to select KPIs carefully.
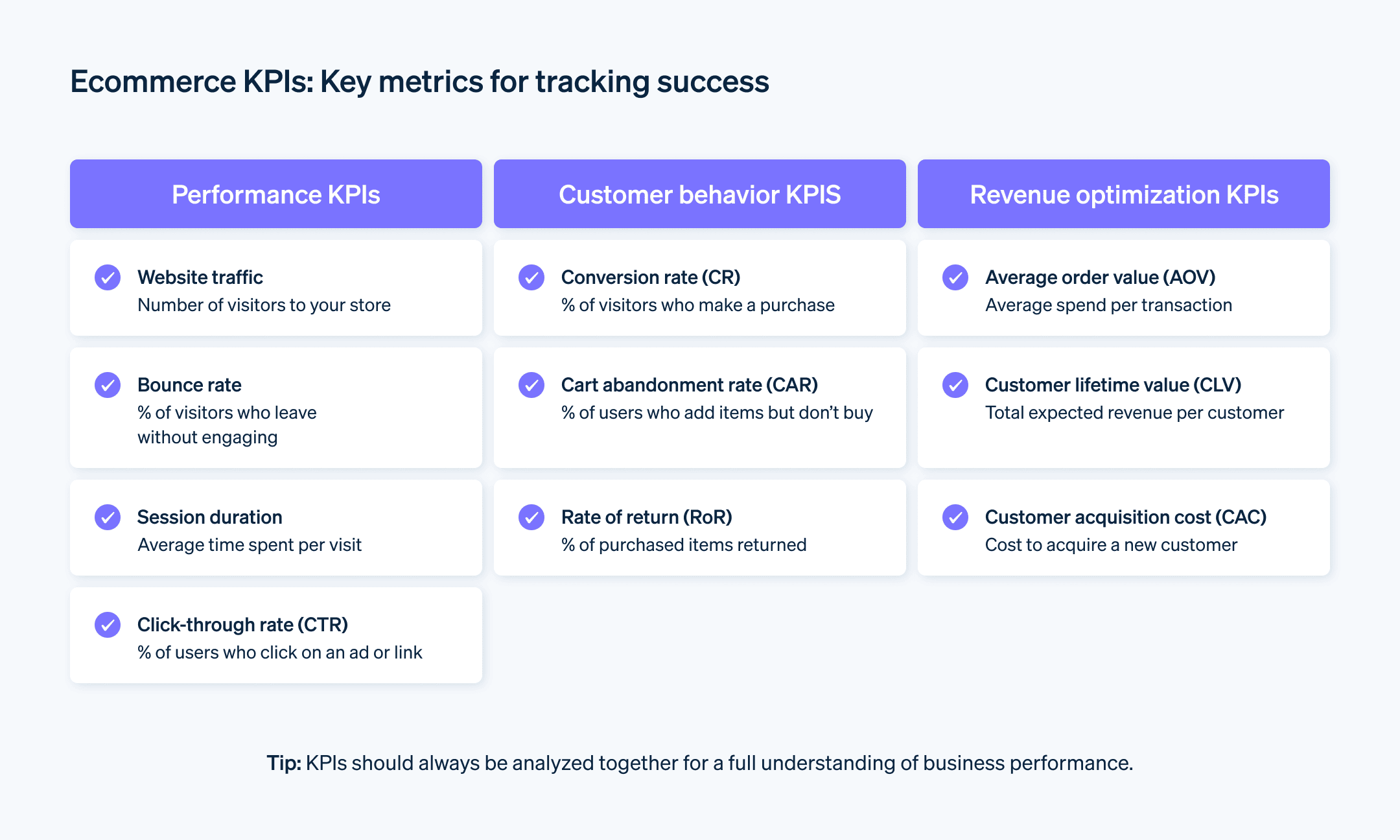
What are the most important KPIs in e-commerce?
Some of the most important KPIs for online businesses include the conversion rate – in other words, the ratio between visitors and actual purchasers – and the average order value (AOV), which reveals the value of an average purchase from the shop. Customer lifetime value (CLTV) is also an important KPI, as it provides information on how much an individual customer spends in the shop over their "life cycle".
Other relevant KPIs include the abandonment rate or rate of return. By analysing and optimising these indicators on a regular basis, you can improve your shop's performance and ultimately increase your sales.
Familiarise yourself with the following KPIs:
Website traffic
The success of an e-commerce business is highly dependent on the number of visitors that a website receives. Website traffic (i.e. the number of visitors or the number of times a page is visited per day) is key for understanding how much traffic your website is receiving. Bounce rate and session duration (see below for definitions) are also relevant as they provide information on how much time users spend browsing a site or whether they move straight on to another page.
Traffic source
Traffic source is a key indicator for measuring the success of your marketing activities. It provides answers to the question of how visitors arrive on your site. There are many types of traffic sources, such as organic hits, paid hits or social media. Every source has its pros and cons and should be analysed appropriately.
A further factor in measuring the traffic source is identifying trends. By recognising patterns in data traffic, you can act quickly and optimise your strategies.
Conversion rate
The conversion rate (CR) measures the ratio of targets achieved to the number of visitors to a website. These targets may be a purchase, newsletter sign-up or contact query. To achieve their targets, businesses should ensure that their online shop is user-friendly and that it is easy to find products.
Bounce rate
The bounce rate (BR) tells you how many visitors leave your website without looking around the online shop or making a purchase. A high bounce rate indicates that something with your website is not quite right. As a result, you may need to make changes to reach more customers and achieve higher conversion rates.
Click-through rate
The click-through rate (CTR) represents the ratio between the number of clicks on an advert and the number of times the ad has been shown (known as impressions). Impressions show how often a user has viewed the website or ad. Every time an ad appears on the user's screen constitutes an impression.
A high click-through rate means that the target group is responding well to the business's message and is interested in its offer. It is also important to bear the conversion rate in mind as this shows how many users then actually carry out a desired action on your website.
Customer acquisition cost
The customer acquisition cost (CAC) indicates how much it costs to gain a new customer. This means calculating all of the marketing and customer care expenditure directed towards gaining and retaining new customers. By measuring the customer acquisition cost, businesses can optimise their marketing strategy and monitor the effectiveness of their measures.
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
The customer lifetime value reveals how much a customer is expected to spend on products and services over the course of their relationship with the business. A high customer lifetime value means that a customer will be profitable for the business in the long-term, making investing in their loyalty worthwhile.
Different factors need to be considered when calculating customer lifetime value, such as the customer's average order volume and frequency, as well as their loyalty to the business.
Average order value (AOV)
Average order value (AOV) measures the average amount spent by a customer at an online merchant for each order they make. This KPI helps businesses to understand how much is spent and how much profit is made per order. The average order value can help businesses recognise trends in customers' buying behaviours. As a result, it represents a source of valuable information with regard to a business's market research and competitiveness.
Basket abandonment rate
The basket abandonment rate (BAR) indicates how often customers terminate the payment process without concluding a purchase. A high basket abandonment rate may be attributable to a range of factors, such as poor website navigation, limited payment methods or high delivery costs.
Rate of return
The rate of return (RoR) indicates how many products customers return after purchase. Businesses can use this information to develop better, customised strategies to achieve a lower return rate.
Time on site
The time on site (TOS), or length of a visit per page, provides information about how long a visitor spends on a website (or its sub-pages), as well as which pages they visit. A long time on site can mean that the customer is interested and is more likely to purchase. However, a short time on site could indicate that the website is not relevant, is hard to navigate or is visually unappealing.
Session duration
The session duration describes the period of time during which active interactions regularly take place on a website. The session will be declared over if no further action is taken within 30 minutes. Unlike time on site, the session duration takes into account the entire length of time that a customer spends on a website. Based on this data, optimisations can be made to the website.
Why should KPIs always be measured in relation to other KPIs?
To measure the success of an e-commerce business as effectively as possible, it is essential that KPIs are never considered individually. Instead, they should always be measured in relation to other KPIs. This enables a comprehensive understanding of the business and of the customer experience. In addition, when taken in isolation, individual KPIs may not be informative enough to make informed decisions about a business's strategy.
More information on how you can calculate individual KPIs can be found in our article on SaaS metrics. Take advantage of the possibilities offered by KPIs to raise your e-commerce business to the next level.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.