What is the recurring business model? “Recurring” refers to a service where a customer pays a fee at regular intervals. This helps a business generate ongoing revenue.
Traditional business models seek to generate one-time or one-off revenue through the sale of products (“one-off sales”). Modern businesses have diversified, and newer models seek to generate continuous and recurring income, rather than completing the transaction with a one-off product sale. The recurring business model is one example of this new approach.
This article describes the advantages, disadvantages, and points to remember about recurring business models.
What’s in this article?
- What is a recurring business model?
- Advantages of a recurring business model
- Disadvantages of a recurring business model
- Considerations for recurring business models
- Services that are compatible with a recurring business model
- Examples of recurring business models
- How to increase profitability in a recurring business model
What is a recurring business model?
Recurring means “to repeat”. Recurring revenue is the revenue that a business repeatedly generates from the goods and services it provides under a recurring contract with a customer. A recurring business model is not a one-off sale but a business model that earns recurring revenue through ongoing billing for a product or service.
Typical recurring business models include products such as multi-functional printers with replacement toner and game consoles with software. With multi-functional printers, users need to replace toner periodically, and many games consoles require users to purchase software for use on their devices to enjoy a large number of games.
Recurring billing is a way to generate revenue from services and products that customers use repeatedly.
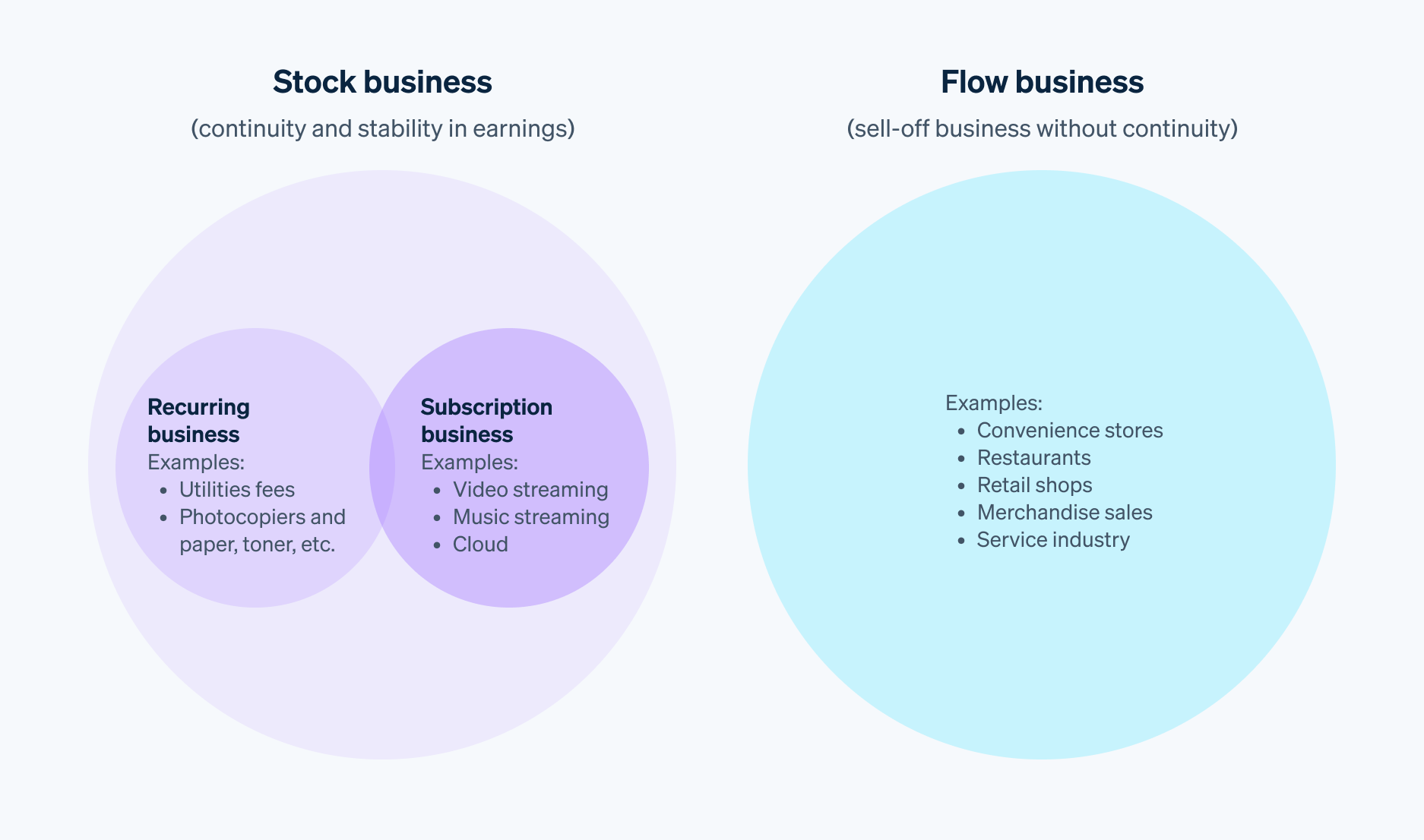
Are there differences between subscription and recurring business models?
The subscription business model requires customers to pay a regular, fixed fee to receive ongoing services. Typical subscriptions include streaming (i.e. content delivery) of movies, music, e-books, etc.
Subscriptions are another business model based on recurring revenue, as a way to generate recurring and ongoing revenue by getting customers to use a service. Subscription-based business models and recurring business models are similar because the goal is to earn recurring revenue and collect fees on an ongoing basis. However, the two systems differ in how they charge, as subscription is a “fixed price” business model, while recurring is primarily a “pay-as-you-go” business model.
For example, a subscription fee for a streaming service is a fixed amount. A recurring business model bills based on usage, so the amount paid varies. For example, electricity, water, gas, and other utility bills all fall under the recurring business model. The total amount paid is the basic monthly fee plus a usage fee for the amount used. The monthly bill varies depending on the amount used.
Are there differences between stock-based and recurring business models?
Stock-based business models ensure continuous, stable revenue by providing services through long-term contracts with customers. Subscription-based and pay-as-you-go businesses are types of recurring business models, but they are also types of stock-based business models.
Therefore, recurring businesses and stock-based businesses are essentially the same; both subscription services and pay-as-you-go services fall under the category of stock business, since a recurring business is a type of stock business.
Advantages of a recurring business model
Stable earnings
Once it gets off the ground, a recurring business can expect to generate revenue over the long term. For example, if you buy food at the supermarket only once, the transaction ends there. However, if a customer uses a regular delivery service to their home or office, sales for each purchase made on each delivery become a recurring revenue stream.
The greatest advantage of the recurring business model is that it generates continuous revenue as long as there are users.
Convenient and inexpensive service
Customer convenience is important in the recurring business model. For one-off purchases, it takes time and effort to go through the purchase process and visit the store over and over. Prices might also be higher for one-off purchases of goods and services.
A recurring business can save customers the hassle of making multiple purchases and could also provide them with goods and services at lower prices. This can help increase customer satisfaction and retention.
Data-based strategies
Recurring businesses can collect sales and customer data to create and improve future sales strategies.
This marketing data enables businesses to reach a more specific target audience. For example, if you know which products sell best by age, gender, region, time of year (or season), etc., you can conduct campaigns that target specific customer segments at specific times of year.
Disadvantages of a recurring business model
Expenditure surpassing recurring income
Expenses might exceed recurring revenues, resulting in unstable or unpredictable profits. Therefore, while it’s important to consider customer satisfaction, businesses should take care not to set prices so low that they can’t break even.
For example, if a business emphasises customer satisfaction too much by offering free shipping, that free shipping service might result in unexpectedly high shipping costs that the company then has to cover. Additionally, the labour costs for preparing the shipping and controlling the quality of product could also result in higher-than-expected expenses that the business has to cover.
Not recovering initial investment
In the early stages of starting a recurring business, there is a risk that you might not recoup initial outlay for advertising and promotion.
For example, if a business takes a while to get going, the service churn rate is high, and the customer lifetime value (LTV) doesn’t increase, the business might not recoup its up-front cost.
Price competition
If the products and services a business handles have little to differentiate them from other companies, they might face price competition. For products and services prone to new entrants (i.e. businesses offering similar products or services), there is a risk that the business’s profit margins might decline if the market becomes saturated.
Considerations for recurring business models
To avoid the disadvantages described above, it can be helpful to consider the following details:
Set aside some funds
It takes time before recurring businesses actually generate revenue. Businesses should set aside some funds to ensure they can continue to operate even while not generating revenue. It’s also important for new businesses to plan well in advance so they don’t have to worry about cash flow until they begin to gain recognition and attract a customer base.
Respond quickly to problems
Business owners should prepare and implement risk management measures to ensure profits are not lost.
For example, if a customer is unhappy with the service they received due to a problem (e.g. a technical issue on the business’s online store), and the business owner fails to take appropriate action, the customer might leave the site. To avoid this, business owners should identify the cause of the problem as soon as possible and take appropriate measures to address it and improve their service.
Understand the market
It’s also important to stay up to date with the latest information and trends in the market to keep up with what customers want and to analyse and understand target clientele.
For example, if customers who use a regular cosmetics delivery service are primarily in their 20s and 30s, one strategy would be to closely analyse the categories that are steadily increasing in sales in this age group and incorporate more relevant and on-trend products.
Services that are compatible with a recurring business model
Industries with specific audiences
Hobby or interest services tend to attract a specific audience, such as anime or video game enthusiasts. This type of service can expect to attract a reliable number of customers, making it suitable for a recurring business model.
Businesses with established distribution networks
When providing a regular delivery service for perishable goods – such as fruits and vegetables or daily necessities – an established proprietary distribution network will enable quick and smooth shipment preparation and delivery, ensuring reliability for your customers.
Examples of recurring business models
Co-op
Co-op and Co-op home delivery services, which offer a variety of products including perishable food and daily necessities, have no minimum order amount and can deliver even a single item. There is no minimum order amount, and you can order as little as one item for delivery. Since Co-op is available throughout Japan, you can receive home delivery service from your new location even if you move to a new one.
Once you register, you will receive a variety of different items once a week on a predetermined day and time. However, as mentioned above, ordering is not mandatory every week, and you can skip it when you don't need it, such as when you are away on holiday, and use it only on the weeks you need it. In addition to online orders, you can also make recurring orders by order form or phone, and some stores also support smartphone apps.
Sony’s PlayStation Plus
PlayStation Plus is a paid subscription service for PlayStation users that offers a wide range of game content, features, and member-only services.
Canon
Replacement services for inkjets used in printers are also typical of recurring services. Canon generates stable revenues through consumables tied to printers (such as inkjet and other consumables), product quality control, and maintenance services.
Amazon Prime
Amazon Prime offers a variety of member-only benefits – such as free shipping and express delivery when ordering products – if you pay a fixed annual membership fee.
How to increase profitability in a recurring business model
This article provides an overview of the recurring business model, including advantages, disadvantages, and things to consider. As the one-off, sell-out business model of the past becomes less popular, the recurring business – with its increased convenience – is likely to continue expanding into many more industries in the future.
To provide quality service, it’s important to keep improving customer satisfaction in all areas and not just product quality. Providing a convenient, satisfying service for customers will lead to increased revenues. One way to do this is to implement a system that allows customers to easily make payments and businesses to improve back-office operations, such as accounting operations for sales.
Stripe offers Stripe Billing, which supports ongoing payment processing – including subscriptions and recurring payments – and provides a variety of features such as recurring billing and payment instruments for customers and payment management systems. In addition, Stripe designs services to meet the needs of each business line and to optimise all administrative tasks related to regular and ongoing payments.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.