Electronic payment methods have gained significant traction, with the value of digital payments projected to reach nearly US$9.5 trillion in 2023. And according to PwC, the volume of cashless payments is expected to increase by more than 80% from 2020 to 2025. As more businesses expand their e-commerce footprint and accept higher volumes of digital payments, understanding the tax implications of payment processing fees is important for maximising deductions and reducing overall tax liability.
Below, we’ll discuss how payment processing fees impact business taxes, giving you the necessary knowledge to receive every tax benefit that your business qualifies for. By understanding best practices for deducting these fees, you can refine your business’s tax strategy and maximise your financial outcomes.
What's in this article?
- What are payment processing fees?
- Are payment processing fees tax-deductible?
- Are transaction fees tax-deductible?
- Are merchant fees tax-deductible?
- Best practices for writing off payment processing fees
What are payment processing fees?
Payment processing fees are charges that businesses must pay in exchange for using payment processing services, which facilitate the transactions between the business and its customers. These services allow businesses to accept credit and debit cards, digital wallets, mobile payments and other electronic payments.
These fees often involve several components:
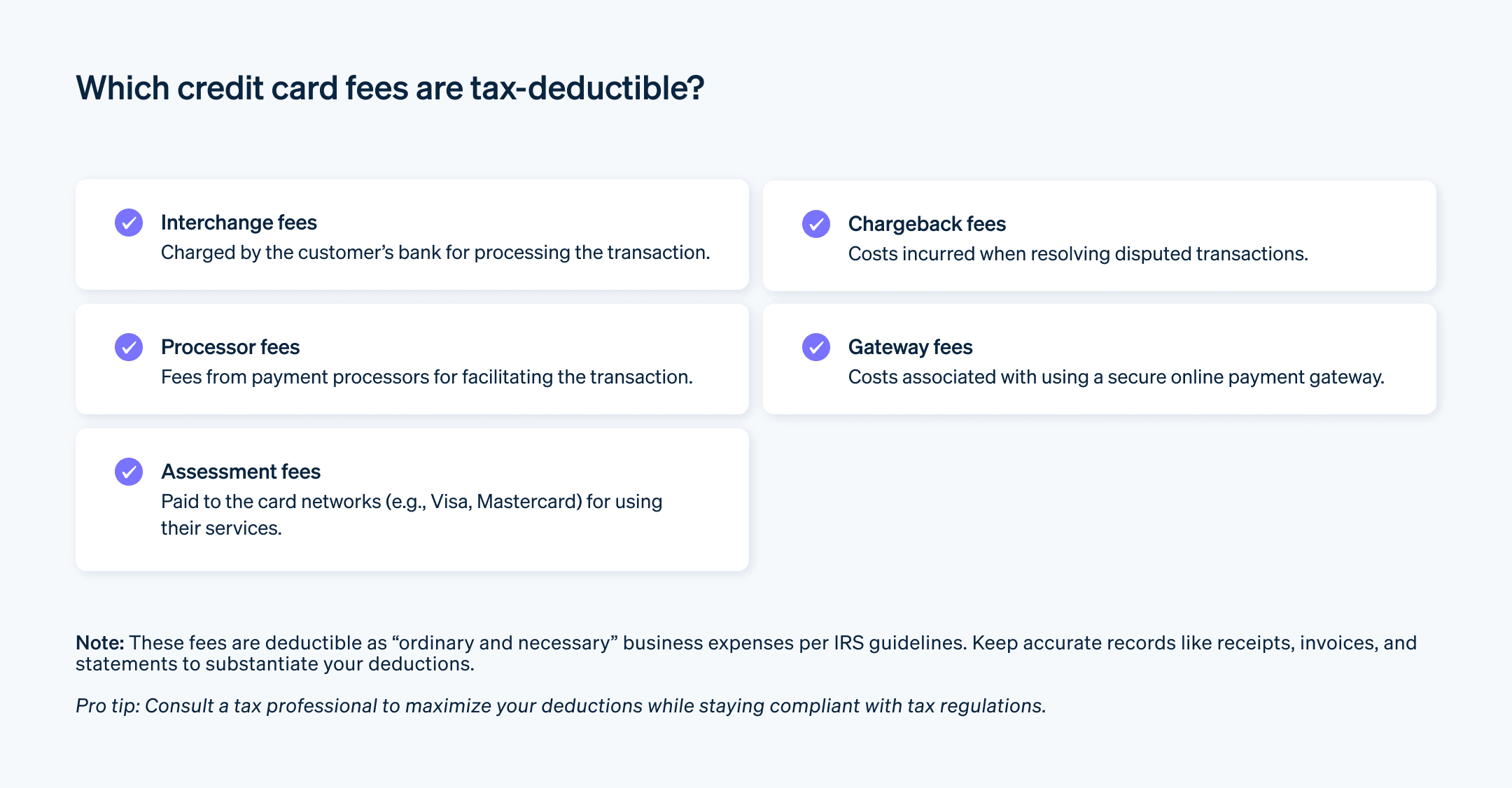
Interchange fees
Issuing banks charge interchange fees, and this type of fee typically constitutes the largest portion of the payment processing fees. They are set by the card networks and are generally non-negotiable.Assessment fees
The card networks charge assessment fees. They’re smaller than interchange fees but also tend to be non-negotiable.Processor markup
This is the fee charged by the payment processor, which is the company providing the service of processing card transactions for the business. This fee is often negotiable and can vary greatly from one processor to another.
Some payment processors also charge additional fees for services such as chargeback handling, payment gateway access or PCI compliance, among others. The exact amount of these fees can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of transaction (in person vs online), the type of card used (debit vs credit, rewards card vs non-rewards card) and the nature of the business.
Are payment processing fees tax-deductible?
Payment processing fees are generally considered to be a necessary business expense and are tax-deductible in many jurisdictions, including the United Kingdom and the United States. This includes fees for credit card transactions, online payment platforms and even bank fees related to business transactions.
In the United States, the IRS Publication 535 provides general guidance on what can be considered as a deductible business expense. Here are some key points from this document:
Ordinary and necessary expenses
To be deductible, a business expense must be both ordinary and necessary. An ordinary expense is defined as one that is common and accepted in your trade or business. A necessary expense is defined as one that is helpful and appropriate for your trade or business.Current expenses vs capital expenses
Business expenses are usually deductible in the year that they are incurred. However, if the expense results in a benefit that will last longer than one year (such as the purchase of equipment), it may have to be capitalised and depreciated over time, rather than deducted all at once.Personal vs business expenses
Only the business portion of an expense is deductible. If an expense is partly personal and partly business, it needs to be divided appropriately.
Payment processing fees are deductible because they are considered to be a necessary cost of doing business. These fees would typically fall under the category of "bank fees" or similar in Schedule C (Form 1040), Profit or Loss from Business for sole proprietors or the corresponding part of the tax return for corporations, partnerships or other business entities.
Are transaction fees tax-deductible?
Transaction fees incurred through a payment processor are generally tax-deductible, since they are also considered to be ordinary and necessary expenses directly related to the operation of your business. By deducting transaction fees, you can reduce your taxable income, resulting in tax savings.
Keep accurate records of transaction fees if you plan to deduct them on your business’s taxes. This means retaining invoices, receipts and statements provided by the payment processor as evidence of the fees paid. These records will help substantiate your deductions and support your tax filings.
Are merchant fees tax-deductible?
Merchant fees incurred by businesses are generally tax-deductible. These fees are considered to be ordinary and necessary expenses directly associated with the operation of your business. When you accept credit card payments from customers, you can deduct the fees charged by the payment processor or merchant services provider, reducing your taxable income and increasing tax savings.
Again, to ensure accurate deductions, it’s important to maintain records of the merchant fees that you incur. Keep invoices, receipts or statements provided by your payment processor or merchant services provider as documentation of the fees paid, to support your deduction in case of a tax audit.
It’s worth noting that tax laws can differ depending on your jurisdiction. While UK tax laws typically allow for the deduction of payment processing fees, it’s still a good idea to consult with a tax professional or accountant who is familiar with the specific tax rules and regulations in the places where you do business. It’s valuable to obtain personalised guidance based on your business’s circumstances, ensuring that you maximise your eligible deductions while remaining compliant with all applicable tax laws.
Best practices for writing off payment processing fees
When deducting payment processing fees from your taxes – or preparing for the next tax season – here are some best practices that you can follow to make tax time smoother:
Accurate record-keeping
It’s important to keep invoices, receipts and any other supporting documentation to substantiate your deductions. A good rule: If you’re going to deduct any expense on your taxes, you need to have documentation to back it up. Set up processes that make accumulating and organising this documentation a standard part of your business operations, so that you don’t have to search for it at tax time.Separate business and personal expenses
Clearly distinguish between business and personal expenses related to payment processing. Deduct only the fees that are directly associated with your business operations. Keeping separate bank accounts or using accounting software can assist in tracking and categorising expenses correctly.Classify expenses correctly
Use the appropriate tax forms and categories when reporting payment processing fees. For example, in the US, sole proprietors report these fees under "bank fees" in Schedule C (Form 1040).Consult with a tax professional
Articles like this one provide basic information, not personalised guidance, and aren’t a substitution for the advice of a tax expert. Work with a qualified tax professional or accountant who specialises in business taxes to help you work through the complexities of tax laws, identify eligible deductions and refine your tax strategy. A professional can provide personalised advice tailored to your business and ensure compliance with tax regulations.Stay informed
Tax policies are not static parts of doing business – they tend to evolve from year to year. Stay updated on relevant tax regulations and guidelines, subscribe to official tax resources, attend seminars/webinars and consult reputable sources to stay informed about changes that could affect the deductibility of payment processing fees.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.