Equity allocation among co-founders is a high-priority, deeply complex issue with significant implications for a startup's future. Constructing equity arrangements that are arbitrary or inadequate can lead to serious challenges, such as internal conflict, demotivation and legal disputes. A Carta survey found that just 26% of startups have a single founder, meaning that the remaining 74% must work out how to divide equity among co-founders. Founders must approach equity allocation with a clear understanding of the factors at play and how different choices will affect future outcomes.
With stakes this high, the topic of equity division demands rigorous scrutiny and a well-thought-out strategy. A carefully designed equity split serves as a strong foundation for the startup, providing stability through various stages, including early financing rounds and potential exits. Here's what co-founders should consider in the pursuit of an equity structure that fits their needs and preferences, both now and in the future.
What's in this article?
- What is equity in a startup?
- Types of equity in startups
- Why does equity matter in a startup?
- How to split equity among co-founders
- Different ways to split equity among co-founders
What is equity in a startup?
Equity represents ownership in a startup, which is often granted through stock options or shares. For co-founders and team members who join the venture at an early stage, this ownership stake serves as both a financial incentive and a form of compensation for the risks and efforts associated with launching a new business. Equity stakes entitle their holders to a proportion of the company's future profits and give them voting rights in company decisions, usually in correlation with the size of their ownership.
Types of equity in startups
Different forms of equity are tailored to different needs and constraints. Types of equity include:
Common stock: this is the most straightforward form of equity, which is generally reserved for founders and employees. It grants the holder voting rights and entitles them to a share of any dividends or exit proceeds.
Preferred stock: preferred shares are often issued to investors and come with additional rights, such as priority in receiving dividends and assets in case of a liquidation event. This type of stock can also include anti-dilution protections.
Stock options: options grant the right to purchase shares at a pre-determined price (the strike price) within a specific time frame. These are usually allocated to employees and may come with various conditions.
Restricted stock units (RSUs): these are commitments to grant a set number of shares at a future date, contingent on certain conditions, such as time-based vesting or achievement of performance metrics.
Warrants: similar to options, warrants confer the right to purchase shares, but are generally issued to investors rather than employees.
Convertible notes and SAFEs: these financial instruments can be converted into equity during a future funding round, typically at more favourable terms for the holder. A Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE) grants the investor the right to receive shares at a later date, while convertible notes are company loans in which the debt is converted to shares instead of being repaid.

Why does equity matter in a startup?
Within startups, equity is the backbone of incentive structures, driving both short-term actions and long-term strategic planning. Its importance extends far beyond the concept of ownership or potential monetary gains. Equity holds implications that affect every aspect of how the startup operates. Here are some key reasons why equity matters in the startup environment:
Motivation and retention
Equity aligns the interests of team members with the overall health and growth of the startup. This approach motivates individuals to invest maximum effort, as their financial rewards are tied directly to the startup's performance.Talent acquisition
Often, startups are unable to offer salaries that are comparable to those at established firms, so equity becomes an alternative and compelling form of compensation to attract top-tier talent. For individuals attuned to the risk-reward dynamics of startups, an attractive equity package can offset lower salaries.Strategic decision-making
Those who hold equity possess voting rights (depending on the type of shares), influencing strategic decisions from fundraising to exit strategies. These rights enable stakeholders to shape the course of the startup in a profound way.Investor relations
Equity structures communicate information to potential investors about how the company values different contributions and risks. Well-structured equity arrangements can instil confidence by demonstrating that the startup has a coherent vision and a fair, deliberate approach to rewarding contributions.Exit opportunities
With liquidity events, such as initial public offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions, equity holders stand to gain significantly. The allocation of equity can become an important part of these negotiations, not only affecting financial gains, but also the governance and strategic direction of the company following an exit.Capital allocation and financial strategy
Equity is integral to the company's financial architecture. The type of equity and associated rights can affect the startup's ability to raise capital, allocate resources and even service debt.Risk mitigation
For co-founders and team members who join in the early stages, the dilution of equity can be an inevitable part of scaling the business. Intelligent equity structuring that takes into account future funding rounds can mitigate excessive dilution, thereby balancing the introduction of new capital with the preservation of the original stakeholders' influence and financial gains.Operational flexibility
Different equity instruments come with varying degrees of operational obligations and financial benefits, offering tactical leeway in governance and decision-making. For example, certain instruments, such as convertible notes or SAFEs, can defer valuation discussions until a more opportune time, providing the startup with valuable operational flexibility.Tax planning
Knowledgeable stakeholders use equity as a means for efficient tax planning. From the timing of exercising stock options to structuring the sale of shares, astute planning can reduce tax burdens and enhance financial gains (although this varies by jurisdiction).
The elements of equity can be an important tool in conducting negotiations, setting growth strategies and deciding on exit pathways. For instance, negotiating for more voting rights or anti-dilution provisions can give a co-founder or employee a stronger position in future fundraising rounds or acquisition talks. Beyond just representing the percentage of ownership, the specific type and terms of equity are tactical levers for power and profit within the startup environment.
How to split equity among co-founders
Deciding how to allocate equity among co-founders is a complex process with long-lasting implications. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Skill sets and contributions
Different founders bring different strengths and capabilities to the table. One founder might have the technical skills to build the product, while another might excel at market strategy and customer acquisition. Quantify the value of these contributions, both at present and in future, in relation to the company's objectives.
2. Time commitment
Not all founders work full time. Some may hold another job and work on the startup during their free time and at weekends, while others may be able to commit themselves fully from day one. Consider the amount of time that each founder can give to the venture, both today and in the foreseeable future.
3. Financial investment
Some founders may provide essential starting capital for the company, which could justify a different equity stake.
4. Business connections and credibility
Access to valuable networks can be a significant asset. A co-founder's ability to provide introductions to key players in the industry or potential clients can accelerate growth significantly.
5. Past and future roles
Consider what each founder has contributed up to this point and which roles they will fulfil in future. Someone who brought an invaluable asset to the table early on may not be as involved later, and the equity split should reflect this continuum of involvement.
6. Tolerance for risk
Each founder may have a different appetite for risk, which will often affect their willingness to make key, high-stakes decisions for the business. This factor can influence how much control each co-founder should have and is something that can be reflected in their equity stake.
7. Vesting schedules
While the idea of a vesting schedule is not tied directly to the initial equity split, it can be helpful to consider this when making big decisions. Understanding that stakes may be subject to change based on certain conditions allows for a more flexible yet controlled approach to equity allocation.
8. Exit strategy preferences
Different founders may have diverging views on the business's endgame. Whether the ultimate goal is a quick acquisition or long-term growth will affect the value that each founder brings and their respective fair equity share.
9. Legal implications
Consider the legal responsibilities that each founder will take on. Regulatory compliance, fiduciary responsibilities and other legal matters may fall heavier on some than others, which could warrant a different share of equity.
10. Emotional and psychological factors
Emotional intelligence, strong personal relationships and the ability to maintain a positive work environment are important but often overlooked skills that a founder can bring to a startup. A founder's contributions to team morale can also be a factor in equity allocation.
11. Opportunity costs
Consider what each founder is giving up to join the startup. The loss of a high-paying job or another significant opportunity can be factored into the equity equation.
There's no fixed, one-size-fits-all solution to equity distribution because the "right" equity strategy is one that reflects a startup's unique needs and circumstances. No two founding teams operate in the same way and every founder has their own set of priorities surrounding what they're hoping to get out of the experience – financially or otherwise. The bottom line is that there's no way to arrive at the right outcome without undergoing a careful and thoughtful exercise that takes into account the nuances of your venture and team.
Different ways to split equity among co-founders
Just as there's no fixed way to decide how much equity a co-founder is entitled to, there's no single structure by which equity can be arranged and distributed among founders. Here are some of the most common ways in which co-founders organise and manage their equity breakdown:
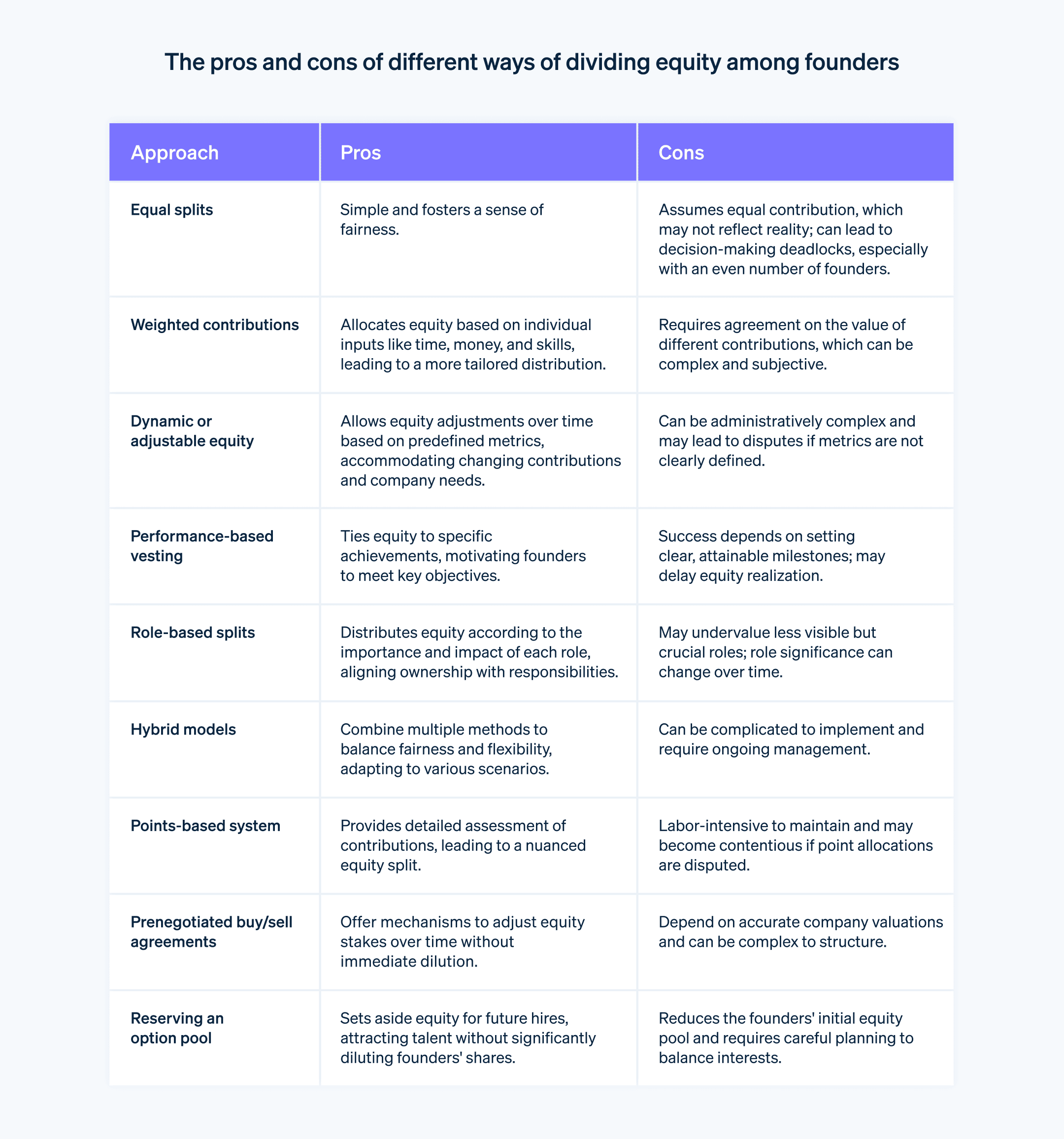
Equal splits
Although equal splits may seem like the fairest method, splitting equity evenly among all founders brings its own set of challenges. It assumes that each founder will contribute equally to the company's growth, which might not hold true over time. Moreover, this method can create governance issues, especially when there is an even number of co-founders, leading to deadlocks in decision-making.Weighted contributions
This method attempts to quantify each founder's input, such as time commitment, financial investment and their skill set. It then splits equity proportionally based on these weighted contributions. This method allows for a more nuanced allocation, but it requires a comprehensive assessment and agreement on the value of the different types of contributions.Dynamic or adjustable equity
With this method, the founders agree on a set of metrics or key performance indicators that will influence the equity distribution over time. These metrics can include revenue milestones, customer acquisition rates or product development goals. The equity split is adjusted automatically based on these pre-determined metrics. This model provides the flexibility to account for changes in contribution levels, market conditions or strategic direction.Performance-based vesting
Under this structure, equity vests when specific objectives are accomplished. Unlike a traditional time-based vesting schedule, performance-based vesting ties equity to measurable outcomes. For example, a founder who is responsible for technology may decide on a setup in which equity vests when they reach certain product development milestones.Role-based splits
Here, equity is divided according to the roles that each founder assumes. This structure often categorises roles into different tiers, each with its own equity range. For instance, a CEO may receive a larger equity stake compared with a CTO or COO, based on the perceived value of that role in achieving the company's goals.Hybrid models
In some cases, a combination of methods can be effective. For example, an initial equity split can be determined through weighted contributions, but with a clause that enables dynamic adjustments based on specific performance metrics.Points-based system
Some startups opt for a points-based system, in which each founder earns points for their contributions, responsibilities and risks. These points are then used to calculate each founder's percentage of equity. This system adds valuable granularity, but it can be labour-intensive to maintain.Pre-negotiated buy/sell agreements
Another option is to have pre-negotiated buy/sell agreements that specify the conditions under which a founder can increase their equity stake by purchasing shares from the company or other founders. This provides a mechanism to adjust equity based on ongoing valuations and contributions, without diluting ownership unnecessarily.Reserving an option pool
While this method doesn't affect the founder-equity split directly, an option pool can provide the flexibility to bring in key recruits without overly diluting the founders' stakes. The size of this pool and the terms under which options are granted are matters of strategic importance.
Each method for allocating equity has its own advantages and disadvantages. The most effective approach is one that is tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the startup. Document all agreements carefully, taking into account future scenarios, such as new funding rounds, exits or changes in founder involvement. Consider seeking legal and financial advice to help craft an equity agreement that serves the long-term interests of all stakeholders.
How Stripe Atlas can help
Stripe Atlas sets up your company's legal foundations so you can fundraise, open a bank account and accept payments within two business days from anywhere in the world.
Join 75K+ companies incorporated using Atlas, including startups backed by top investors like Y Combinator, a16z and General Catalyst.
Applying to Atlas
Applying to form a company with Atlas takes less than 10 minutes. You'll choose your company structure, instantly confirm whether your company name is available and add up to four co-founders. You'll also decide how to split equity, reserve a pool of equity for future investors and employees, appoint officers and then e-sign all your documents. Any co-founders will receive emails inviting them to e-sign their documents, too.
Accepting payments and banking before your EIN arrives
After forming your company, Atlas files for your EIN. Founders with a US Social Security number, address and mobile phone number are eligible for IRS expedited processing, while others will receive standard processing, which can take a little longer. Additionally, Atlas enables pre-EIN payments and banking, so you can start accepting payments and making transactions before your EIN arrives.
Cashless founder stock purchase
Founders can purchase initial shares using their intellectual property (e.g. copyrights or patents) instead of cash, with proof of purchase stored in your Atlas Dashboard. Your IP must be valued at US$100 or less to use this feature; if you own IP above that value, consult a lawyer before proceeding.
Automatic 83(b) tax election filing
Founders can file an 83(b) tax election to reduce personal Income taxes. Atlas will file it for you – whether you are a US or non-US founder – with USPS Certified Mail and tracking. You'll receive a signed 83(b) election and proof of filing directly in your Stripe Dashboard.
World-class company legal documents
Atlas provides all the legal documents you need to start running your company. Atlas C corp documents are built in collaboration with Cooley, one of the world's leading venture capital law firms. These documents are designed to help you fundraise immediately and ensure your company is legally protected, covering aspects like ownership structure, equity distribution and tax compliance.
A free year of Stripe Payments, plus $50K in partner credits and discounts
Atlas collaborates with top-tier partners to give founders exclusive discounts and credits. These include discounts on essential tools for engineering, tax, finance, compliance and operations from industry leaders like AWS, Carta and Perplexity. We also provide you with your required Delaware registered agent for free in your first year. Plus, as an Atlas user, you'll access additional Stripe benefits, including up to a year of free payment processing for up to $100K in payments volume.
Learn more about how Atlas can help you set up your new business quickly and easily and get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.