Every business should be concerned about payment security. In 2024, 79% of organisations reported that they were targeted by payment fraud. And payment fraud can be incredibly expensive, with the average data breach globally costing $4.4 million. Businesses must prioritise payment security to protect their customers' sensitive information, maintain customer trust and avoid costly financial losses.
This guide contains actionable steps for developing and implementing a robust payment-security strategy. Whether you're an e-commerce retailer, a brick-and-mortar store or a SaaS provider, the success of your business depends in part on a strong payment-security strategy.
What's in this article?
- What is payment security?
- Principles of payment security
- Security features to look for in a payments provider
- Security best practices for businesses
- How Stripe Radar can help
What is payment security?
Payment security refers to the systems, processes and measures that protect financial transactions from unauthorised access, data breaches and fraud. For both online and in-person businesses, ensuring payment security is important for maintaining customer confidence, minimising financial losses and complying with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Principles of payment security
There are several principles of payment security that work together to protect financial transactions and customer data. The main ones to know include:
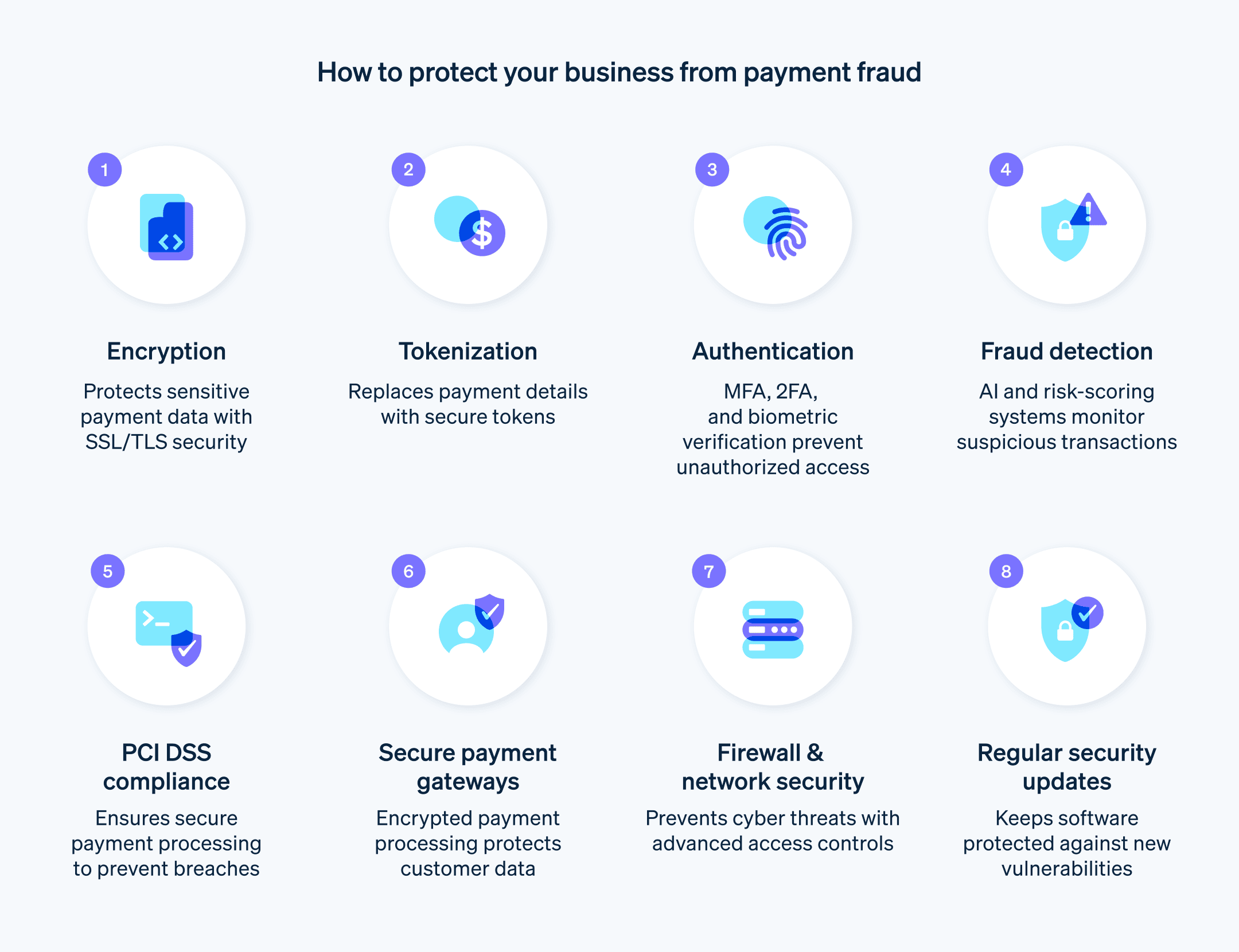
Encryption
Encryption protects sensitive customer data and financial transactions from unauthorised access, tampering and theft. There are two primary types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption involves using the same key for locking and unlocking the data, while asymmetric encryption, also known as "public-key encryption", uses two keys: a public key for locking and a private key for unlocking the data. Generally, asymmetric encryption is considered to be more secure because the private key is not shared.
Businesses use encryption protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure data transmission between customers' browsers and business websites or payment platforms. SSL/TLS encryption uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to establish a secure connection and safeguard data during transmission.
Tokenisation
Tokenisation protects sensitive payment information by replacing it with unique tokens that have no intrinsic value if compromised. This process significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access and data breaches and maintains compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Payment tokenisation replaces sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, with unique tokens generated by a secure system. These tokens are used to reference the original payment information, which is stored in a centralised token vault. The tokens themselves cannot be used to carry out fraudulent transactions or be reverse-engineered to reveal the original payment data.
Authentication
Authentication is a fundamental payment security measure that verifies the identity of users attempting to access or complete a transaction.
There are several types of authentication, including:
- Single-factor authentication (SFA): Requires one form of identification, usually a password or a PIN
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Requires two forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code sent to a registered device
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Requires three or more forms of identification, which may include biometric data, security questions or physical tokens
Fraud detection and prevention
These systems help businesses identify and prevent fraudulent transactions by monitoring transaction patterns, customer behaviours and other risk factors. Techniques such as machine-learning algorithms, behaviour analysis and risk scoring can detect anomalies and prevent fraud. For more details, see our fraud detection guide.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all businesses that process, store or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. PCI DSS compliance protects sensitive customer data and minimises the risk of data breaches.
Achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance is important to protect customers' sensitive payment information and demonstrate a commitment to security.
Payment gateways
Payment gateways facilitate the processing of card transactions while protecting customer payment data from unauthorised access and fraud. By providing a secure channel for transmitting payment information between the customer, business and payment processor or acquiring bank, payment gateways are an important component of a highly secure payment environment.
Firewall and network security
Firewall and network security help protect payment infrastructure and confidential customer data from external threats, such as hackers, malware and other malicious actors.
A firewall is a type of security system that acts like a security guard for a computer network, controlling the information coming in and going out based on specific rules. Firewalls create a protective barrier between a trusted network inside a business, such as the payment system and the untrusted outside world, such as the internet, helping prevent unauthorised access to the network. Firewalls can be hardware based, software based or a combination of both.
Some key aspects of firewall and network security include:
Network segmentation
Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments helps limit the potential damage of a security breach. By keeping sensitive payment data and systems in separate network segments, businesses can better protect these assets from unauthorised access and minimise the workload of PCI DSS compliance.Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS)
IDPS solutions monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, detect potential threats and take action to prevent or mitigate those threats. By using a combination of methods, such as checking for known threats and analysing communication rules, IDPS solutions can identify and block many types of attacks, even those that are brand new.Strong access controls
Access controls, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC) and the "principle of least privilege" (the practice of granting individuals or entities the minimum level of access necessary to perform their specific tasks or functions related to payment processing), help ensure that only authorised users can access network resources and sensitive payment systems.Security monitoring and incident response
Continuous monitoring of network activity, coupled with a well-defined incident response plan, helps businesses quickly identify and respond to security threats, minimising potential damage and downtime.
Security updates and patches
Software vendors, hardware manufacturers and operating-system providers release security updates and patches to address known vulnerabilities, bugs or other security issues in their products. Regular security updates and patches help protect payment infrastructure, customer data and other key systems from vulnerabilities, cyberattacks and unauthorised access.
Applying these updates and patches on a regular basis helps to:
Fix vulnerabilities
Updates and patches resolve security flaws or weaknesses that hackers could exploit to gain unauthorised access to your systems or steal sensitive data. By staying up to date with security patches, you can reduce the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.Improve performance
Updates often include performance enhancements, bug fixes or new features that can improve the overall stability, efficiency and functionality of your systems and software.Maintain compliance
Regulatory requirements often dictate that businesses apply security updates and patches in a timely manner to maintain compliance. Updating your systems regularly can help you avoid fines or penalties associated with non-compliance.Protect against emerging threats
Cyber threats continue to evolve as hackers discover new vulnerabilities and develop new attack techniques. Applying updates and patches helps you stay ahead of these emerging threats and maintain a secure environment.
Security features to look for in a payments provider
When choosing a payments provider, there's a lot to consider – from security features, to compliance, to uptime and reliability.
Key features to look for in a payments provider include:
Encryption
A secure payments provider should employ encryption protocols to encrypt sensitive payment data. These protocols ensure that the customer's payment details stay safe during transmission, protecting the data from interception or tampering.Tokenisation
Payment data such as card details should be tokenised to protect customer data, reduce the risk of data breaches and stay PCI DSS compliant.Authentication and fraud prevention
Build in authentication methods, such as CVV/CVC checks, 3D Secure and biometric authentication, to verify customer identity and prevent unauthorised transactions. Additionally, make sure they employ systems for advanced fraud detection and prevention that use machine learning, behaviour analysis and risk scoring to identify and block fraudulent transactions in real time.Compliance with industry standards
A provider should adhere to PCI DSS and other relevant industry standards to maintain a secure environment for processing, storing and transmitting cardholder data.Uptime and reliability
Maintaining high uptime and reliability ensures that customers can complete transactions without interruptions. Regular monitoring, redundancy measures and robust infrastructure enable a provider to consistently process transactions securely and efficiently.
Security best practices for businesses
All businesses that process, store or transmit payment information, including credit card data, need to be concerned with payment security. Maintaining secure payment processes is important for protecting sensitive customer data, ensuring customer trust and complying with industry standards and regulations – for businesses of all sizes and in all industries.
To ensure a thoughtful playbook for managing payment security, businesses should take the following steps:
1. Conduct a risk assessment
Begin by looking at your current payment infrastructure, processes and systems to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Determine the types of sensitive data that your business handles and where it is stored, processed and transmitted.
2. Understand compliance requirements
Familiarise yourself with the standards and regulations that govern your industry, including PCI DSS and determine your business' specific compliance requirements based on the markets where you operate. Make sure that you understand the security controls and practices mandated by these standards. Train your employees on PCI DSS requirements and best practices for handling cardholder data securely.
3. Develop security policies and procedures
Establish clear policies and procedures that address payment security, including guidelines for handling sensitive data, access controls, incident response, patch management and employee training. Ensure that these policies and procedures align with industry standards and regulations.
4. Put security measures in place
Based on your risk assessment and compliance requirements, implement appropriate security measures, such as encryption, tokenisation, strong authentication and firewall configurations. Choose a secure payments provider and work with PCI DSS–compliant vendors to streamline compliance efforts.
5. Monitor systems and perform stress tests
Regularly monitor your payment systems, networks and applications for potential threats or vulnerabilities. Tactics such as vulnerability scans, penetration tests and system audits can assess the effectiveness of your security measures and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, consider using automated tools that can help identify missing patches or outdated software.
6. Adjust your approach as indicated
Even the best-laid security strategies will need to be adjusted and adapted over time. Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your payment security strategy and make necessary adjustments to address changes in your business, industry regulations or the threat landscape. Regular reviews help ensure that your strategy remains relevant and effective in protecting your customers' data.
7. Create an incident-response plan
Develop a well-defined incident response plan to guide your organisation in the event of a security breach or other incident. This plan should outline roles and responsibilities, communication protocols and procedures for containing and mitigating the incident.
How Stripe Radar can help
Stripe Radar trains AI models to detect and prevent fraud, using data from the global Stripe network. It continuously updates these models based on the latest fraud trends, protecting your business as fraud evolves.
Stripe also offers Radar for Fraud Teams, which allows users to add custom rules addressing fraud scenarios specific to their businesses and access advanced fraud insights.
Radar can help your business:
- Prevent fraud losses: Stripe processes over $1 trillion in payments annually. This scale uniquely enables Radar to accurately detect and prevent fraud, saving you money.
- Increase revenue: Radar's AI models are trained on actual dispute data, customer information, browsing data and more. This enables Radar to identify risky transactions and reduce false positives, boosting your revenue.
- Save time: Radar is built into Stripe and requires zero lines of code to set up. You can also monitor your fraud performance, write rules and more in a single platform, increasing efficiency.
Learn more about Stripe Radar or get started today.
The content in this article is for general information and education purposes only and should not be construed as legal or tax advice. Stripe does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or currency of the information in the article. You should seek the advice of a competent lawyer or accountant licensed to practise in your jurisdiction for advice on your particular situation.